Metal material crack quantitative monitoring method based on ultrasonic guided wave
A metal material, ultrasonic guided wave technology, applied in the analysis of solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, can solve the problems of inability to determine the size and direction of cracks, low detection efficiency, shutdown detection, etc., to achieve quantitative real-time monitoring, monitoring range The effect of large and large detection range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
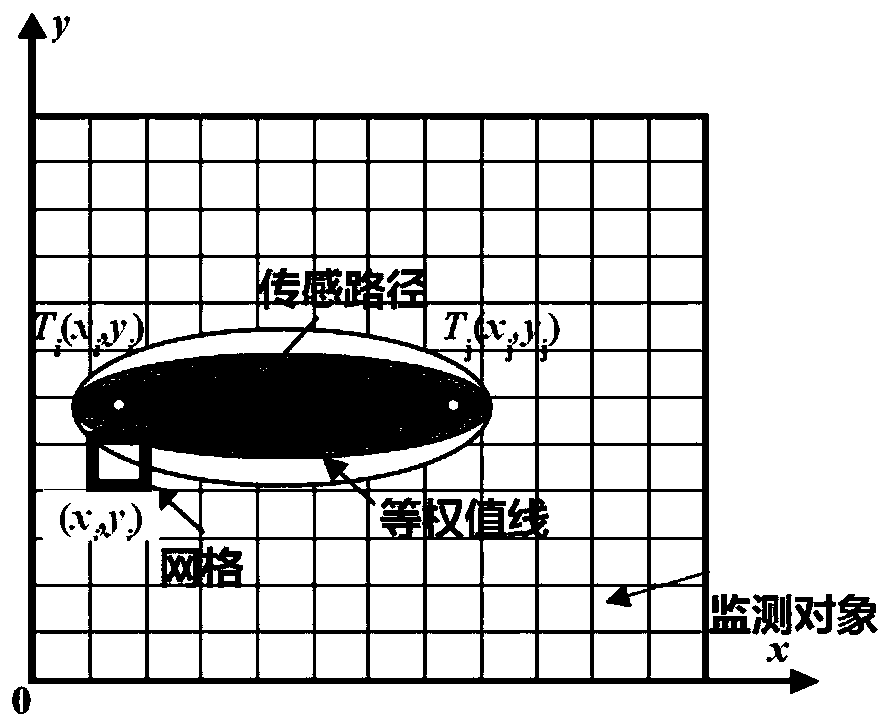
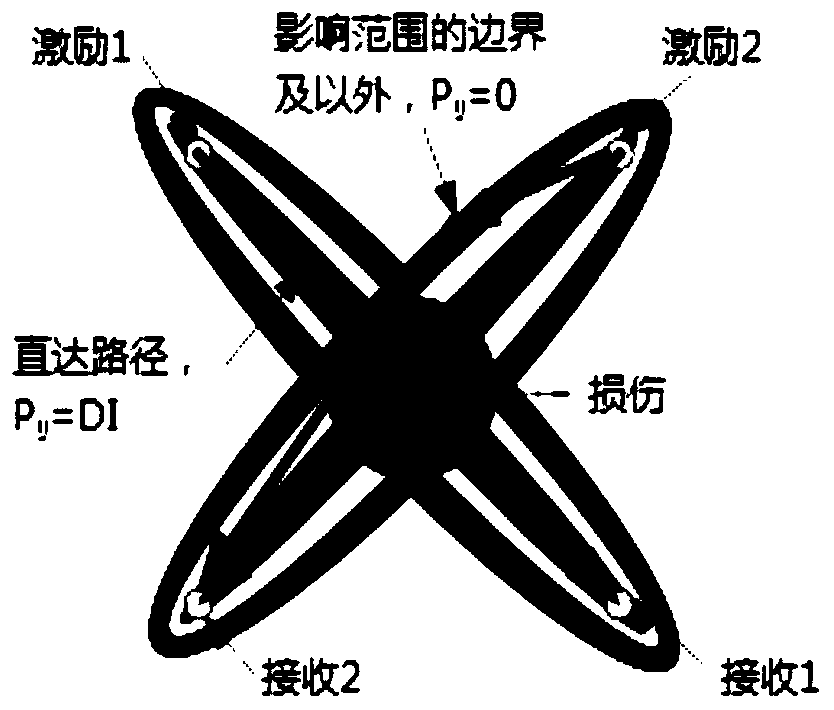
[0055] Based on the correlation analysis method and the damage path probability imaging method, the invention analyzes the ultrasonic guided wave signal of the metal material plate structure, and realizes the quantitative evaluation of cracks.
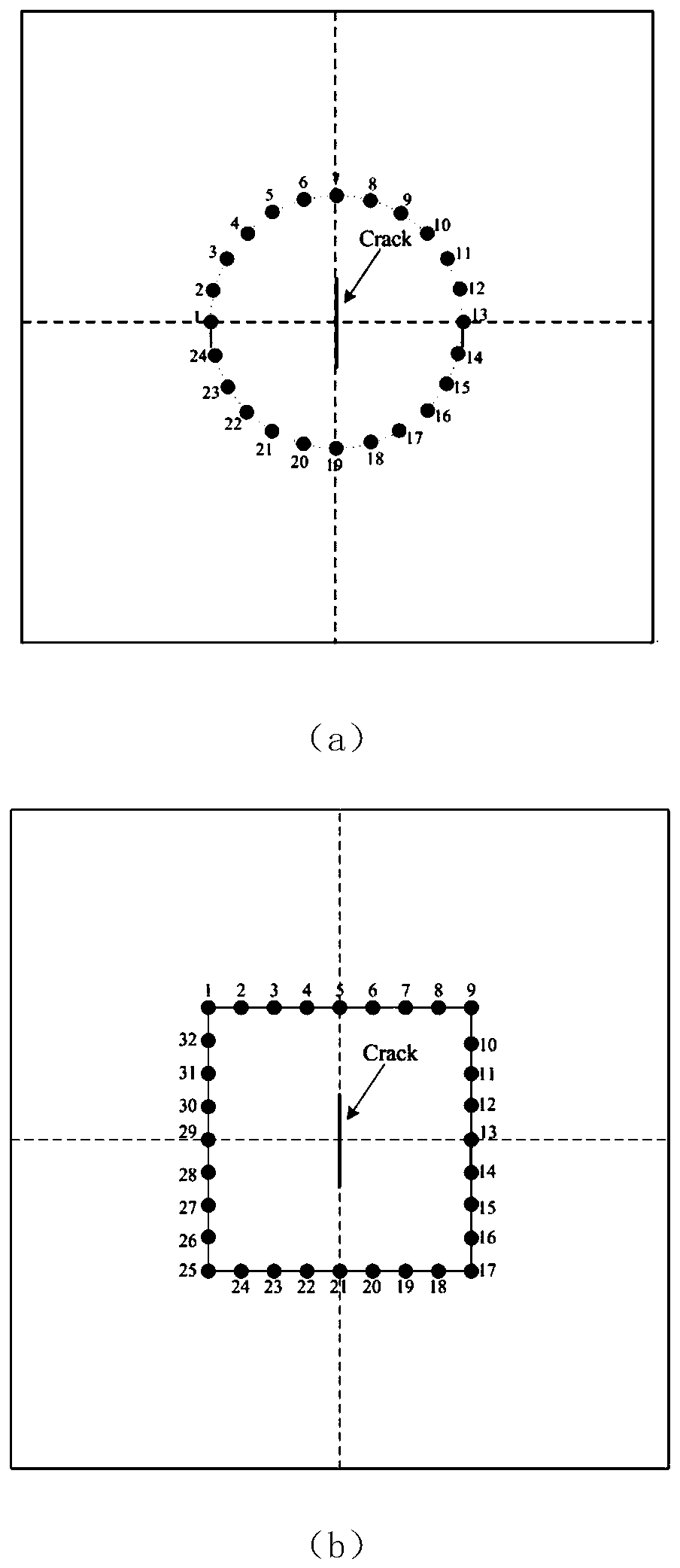
[0056] The sensor uses piezoelectric ceramics (PZT), and multiple sensors form a circular or square sensor network, such as figure 1shown. The sensor is bonded to the tested board structure by epoxy glue. A professional ultrasonic guided wave monitoring system is used to generate excitation signals and collect monitoring signals. Each sensor is used as an excitation, and the rest of the sensors are used as receivers to collect signals. The excitation signal is a modulated 5-peak narrow-band sine wave signal, see formula 1.
[0057]
[0058] Among them, A is the amplitude of the signal, f c is the center frequency of the signal, n is the number of signal peaks, and H is the Heaviside step function.
[0059] If there is an impair...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Using 24 piezoelectric sensors to form a sensing network, the arrangement is as follows figure 1 As shown in (a), 24 sensors are evenly arranged on a circle with the center point of the tested plate structure as the center and a radius of 20 mm. A rectangular groove with a length of 50mm and a width of 0.2mm is processed on the metal plate structure to be tested to simulate cracks. The position is as follows: Figure 7 shown. Each sensor is used as the excitation, and the rest of the sensors are used as the receiver, and the non-destructive signal and the signal with cracks are collected sequentially, and a total of 552 sets of data are collected.
[0075] The damage factor DI was calculated from the reference (non-destructive) signal and the monitoring (cracked) signal in each set of data. The maximum value of DImax among the 552 DI values is 1.3, and the corresponding path is sensor 7-9, so the direction of the crack is perpendicular to the sensing path 7-19, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com