Method for planning route in warehousing system
A warehousing system and path planning technology, applied in the field of warehousing, can solve the problems that path planning does not achieve the shortest driving time, does not consider the cost of robot turning, and the impact of large-scale warehousing system efficiency, achieves high practical application value, and reduces independent decision-making ability. and real-time adaptability requirements, the effect of reducing cornering consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0030] A path planning method in a storage system provided by an embodiment of the present invention is applicable to a storage system.
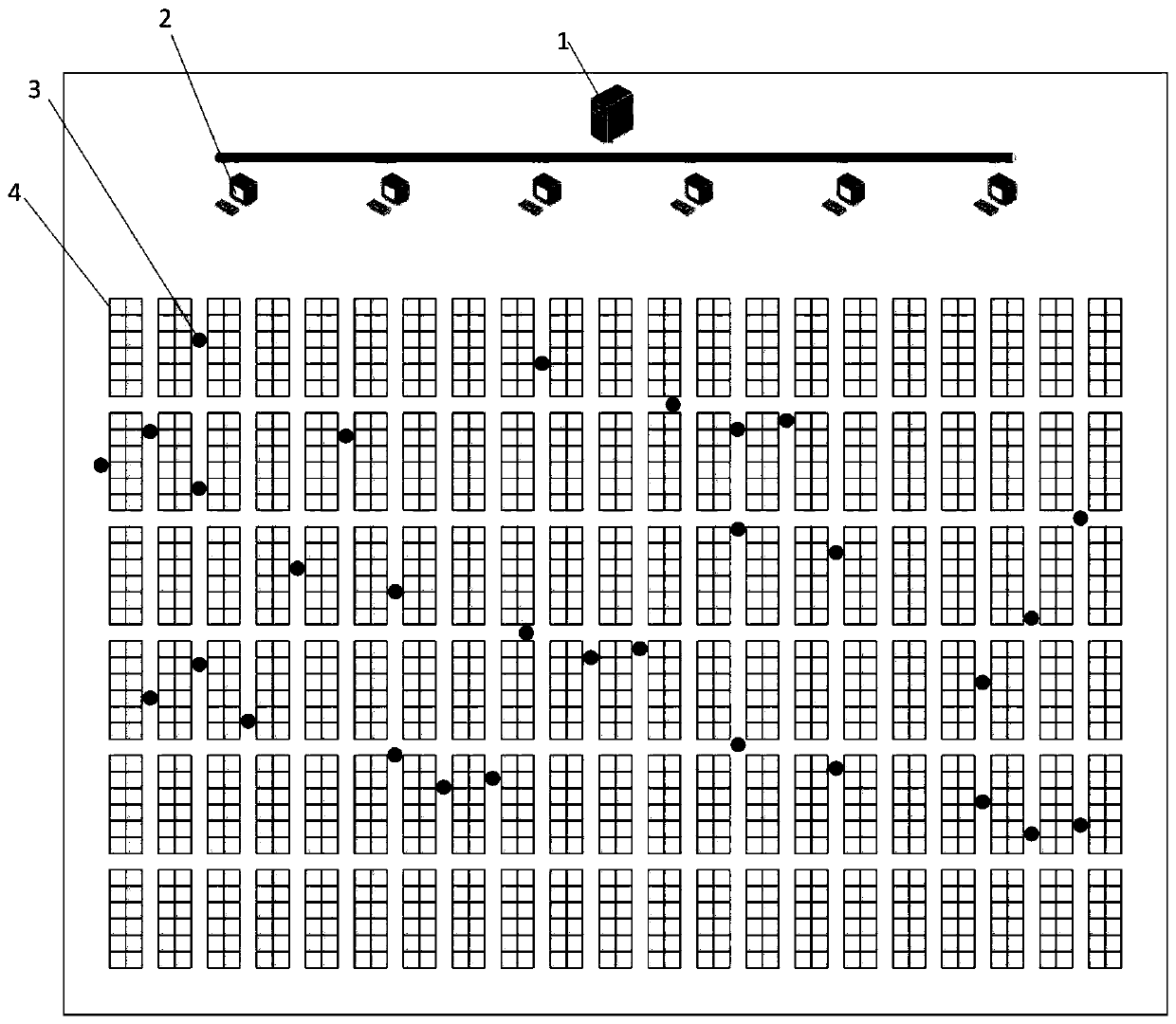
[0031] refer to figure 1 , the system environment to which the present invention is applied includes a central control server 1 , a plurality of sorting stations 2 , a plurality of mobile robots 3 and a plurality of movable shelves 4 . Wherein, each mobile robot 3 is connected wirelessly with a movable shelf 4 and a sorting platform 2 respectively, and each sorting platform 2 is connected with the central control server 1 by wire.
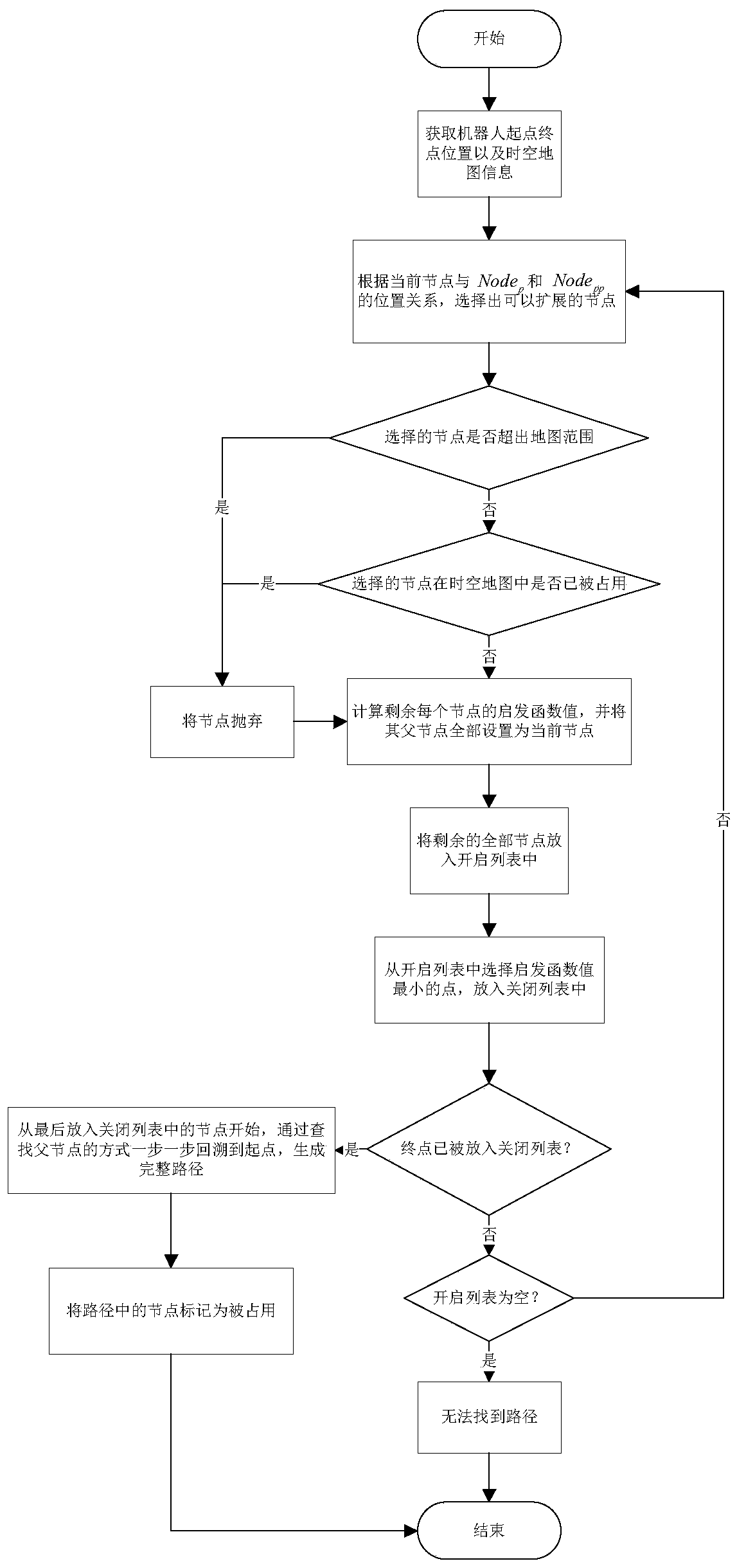
[0032] refer to figure 2 , the implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
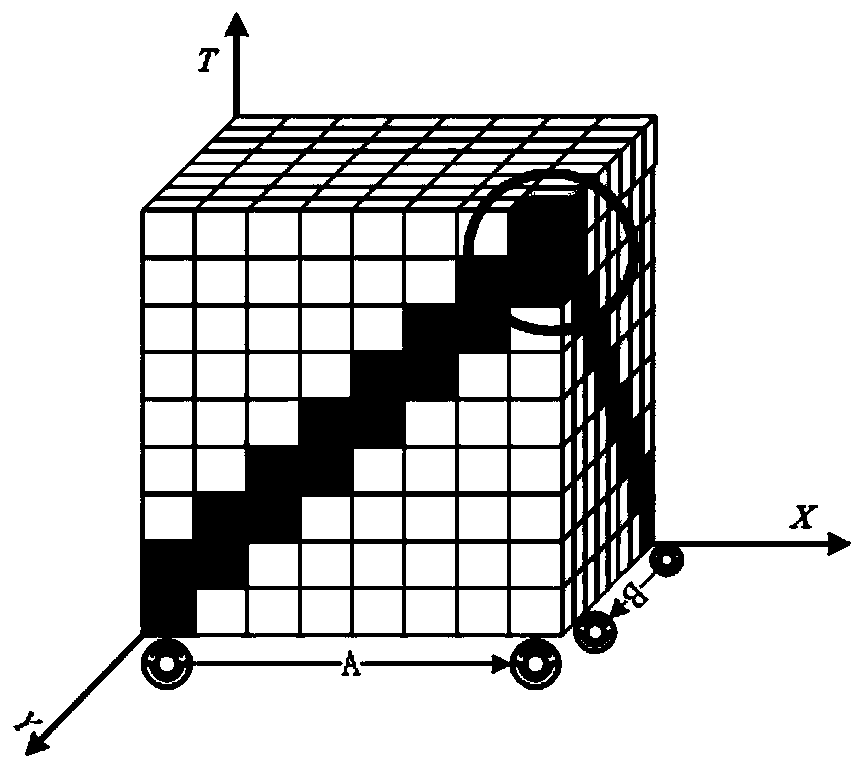
[0033] Step 1, create a 3D space-time map.
[0034] The three-dimensional space-time map is an upgrade to the two-dimensional map, and its realization is as follows:
[0035] 1.1) Use the grid me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com