A three-dimensional bubble recognition method in gas-solid bubbling bed based on distance constraint algorithm
A gas-solid bubbling bed and distance-constrained technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, computing, computer components, etc. Overlap phenomenon and other problems, achieve high precision, overcome randomness and one-sidedness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
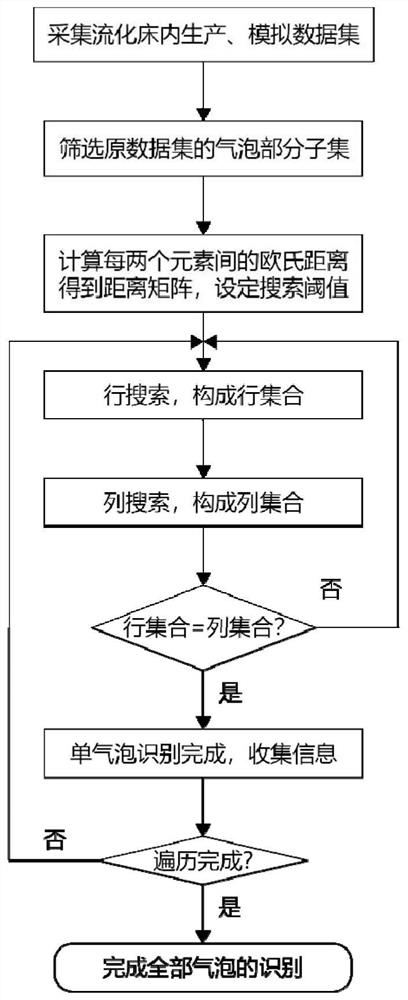
[0040] Such as figure 1As shown, the present invention provides a method for identifying three-dimensional bubbles in a gas-solid bubbling bed based on a distance constraint algorithm, which includes the following steps:
[0041] 1) Obtain the point coordinates (x, y, z) in the gas-solid bubbling bed at a certain moment and the solid holdup corresponding to the point coordinates Constitute a data set D of size n t ;
[0042]
[0043] 2) from step 1), obtain the data collection and screen out the bubble data point set;
[0044] Specifically include the following steps:
[0045] 2.1) Define the bubble boundary, that is, the solid holdup satisfies The coordinate points of belong to the bubble data points, and from the data set D t Screened out the solid content rate to meet the Coordinate points of , constituting the subset D containing bubb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com