Electromagnetic sounding constraint inversion methods based on resistivity equivalence principle
An electromagnetic sounding and constrained inversion technology, applied in the field of geophysical exploration, can solve problems such as poor adaptability, difficulty in obtaining inversion results, and slow calculation speed, so as to simplify the working process, highlight formation information, and reduce work intensity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] An electromagnetic sounding constrained inversion method based on the principle of resistivity equivalence, comprising the following steps:
[0051] a. Assuming that the result of an inversion is m, calculate the derivative of the layer thickness for the forward modeling response, normalize the negative derivative value, and take the positive derivative value as 0 to obtain Δm;
[0052] b. Use Δm as the coefficient corresponding to ε in the S equivalence convergence algorithm of each layer;
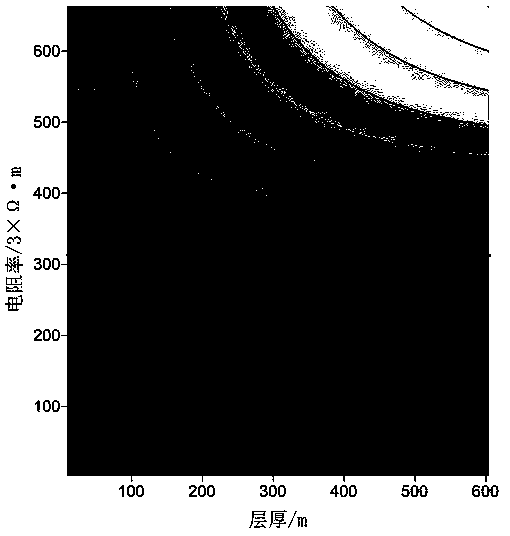
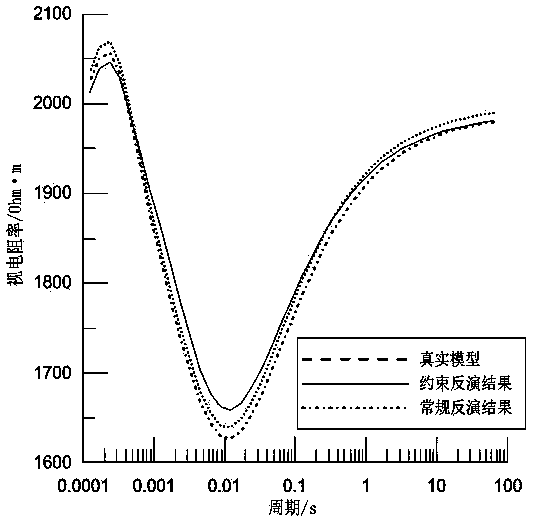
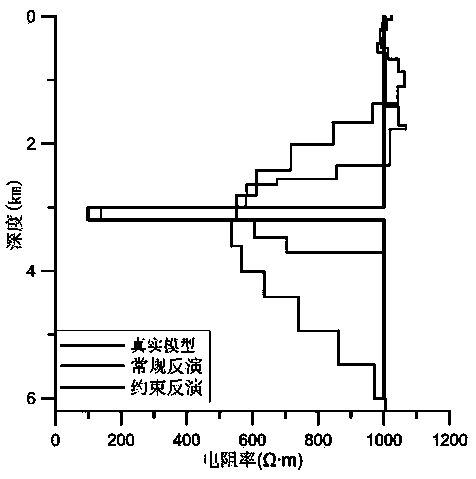
[0053] c. Use S equivalence to converge low-resistance thin layers, and iteratively obtain Equation 2 through Equation 1; solve the m-th layer z through the inversion data m 、h m and ρ m , gradually decrease h at the speed of Δ m The value of h is reduced every time m The value of ρ will iteratively calculate the unique corresponding ρ m , until h m and ρ m The value of satisfies formula 1, the convergence ends, and the sheet resistivity and sheet thickness after convergence...
Embodiment 2
[0061] An electromagnetic sounding constrained inversion method based on the principle of resistivity equivalence, comprising the following steps:
[0062] a. Assuming that the result of an inversion is m, calculate the derivative of the layer thickness for the forward modeling response, normalize the negative derivative value, and take the positive derivative value as 0 to obtain Δm;
[0063] b. Use Δm as the coefficient corresponding to ε in the S equivalence convergence algorithm of each layer;
[0064] c. Use S equivalence to converge low-resistance thin layers, and iteratively obtain Equation 2 through Equation 1; solve the m-th layer z through the inversion data m 、h m and ρ m , gradually decrease h at the speed of Δ m The value of h is reduced every time m The value of ρ will iteratively calculate the unique corresponding ρ m , until h m and ρ m The value of satisfies formula 1, the convergence ends, and the sheet resistivity and sheet thickness after convergence...
Embodiment 3
[0073] An electromagnetic sounding constrained inversion method based on the principle of resistivity equivalence, comprising the following steps:
[0074] a. Assuming that the result of an inversion is m, calculate the derivative of the layer thickness for the forward modeling response, normalize the negative derivative value, and take the positive derivative value as 0 to obtain Δm;
[0075] b. Use Δm as the coefficient corresponding to ε in the S equivalence convergence algorithm of each layer;
[0076] c. Use S equivalence to converge low-resistance thin layers, and iteratively obtain Equation 2 through Equation 1; solve the m-th layer z through the inversion data m 、h m and ρ m , gradually decrease h at the speed of Δ m The value of h is reduced every time m The value of ρ will iteratively calculate the unique corresponding ρ m , until h m and ρ m The value of satisfies formula 1, the convergence ends, and the sheet resistivity and sheet thickness after convergence...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com