Linear deviation degree method-based intelligent path planning method
A path planning and deviation degree technology, applied in the field of artificial intelligence research, can solve problems such as high computational time complexity, poor work efficiency and real-time performance, and achieve low computational time complexity, short planning time, and good real-time performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0040] The intelligent body path planning method based on the straight line deviation method includes the following steps:
[0041] 1. Establish an environmental model, that is, establish a scaled-down model according to the actual environment, and establish a coordinate system correspondingly;
[0042] In order to realize and verify the straight-line deviation strategy, the present invention makes the following assumptions when carrying out environmental modeling in the robot motion space:
[0043] (a) The mobile robot moves in a two-dimensional limited space;
[0044] (b) There are a limited number of known static obstacles distributed in the robot's motion space. The obstacles can be described by polygons and the height information of the obstacles can be ignored, only described by the (x, y) plane;
[0045] (c) In order to ensure that the path is not too close to the obstacle, the boundary of the obstacle is expanded outward, and the expanded size is 1 / 2 of the maximum si...
Embodiment
[0099] One, utilize the present invention to carry out simulation experiment
[0100] 1. Realization of environment topology
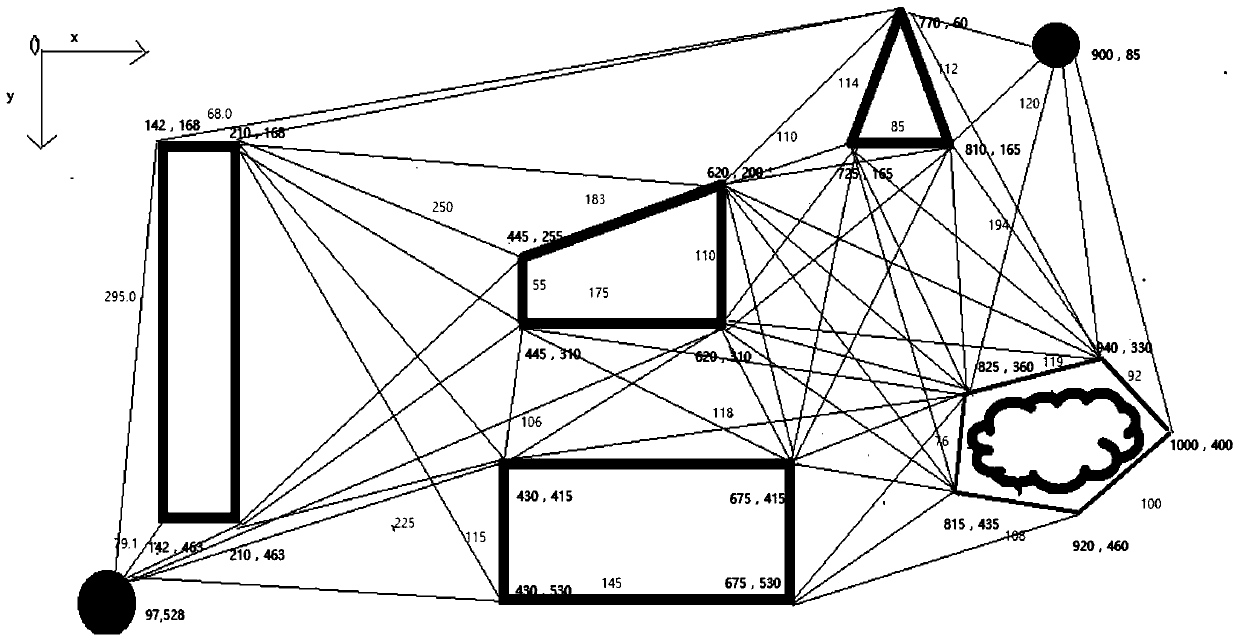
[0101] First of all, this experiment simulates the static global working environment of the intelligent mobile robot, and projects it into the Cartesian coordinate system in equal proportions, and marks the coordinates of each node and the connection lines between each node, as shown in figure 1 shown.
[0102] The experiment hopes that such an optimal route can be achieved in a simpler working environment roadmap, so that it can be extended to a more complex working environment.
[0103] 2. Implementation of node addition based on route adjustment
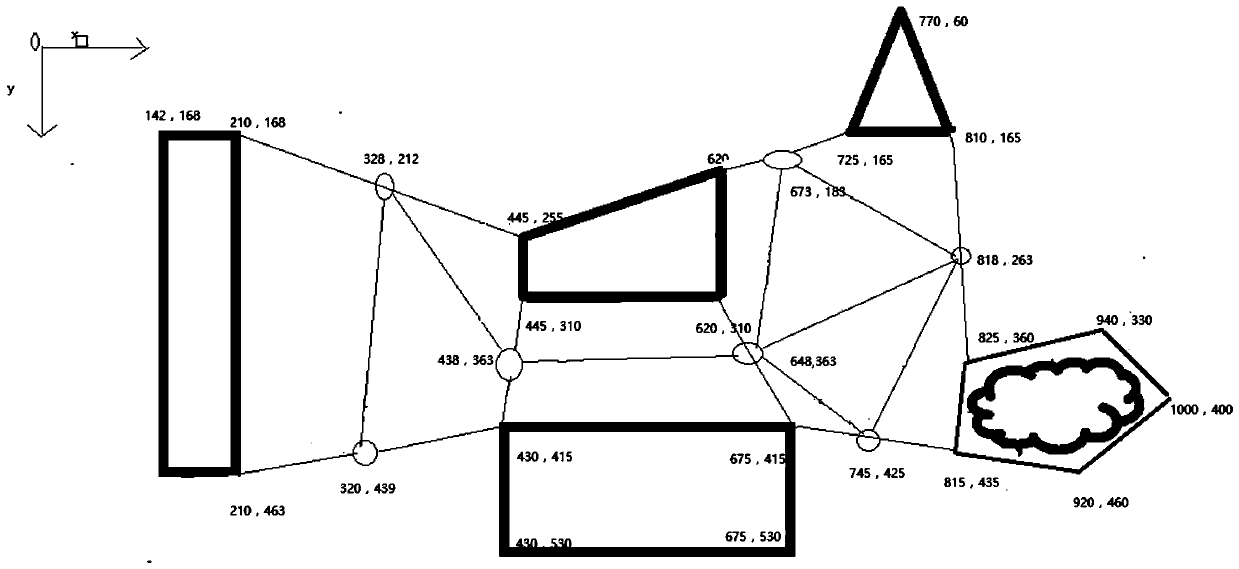
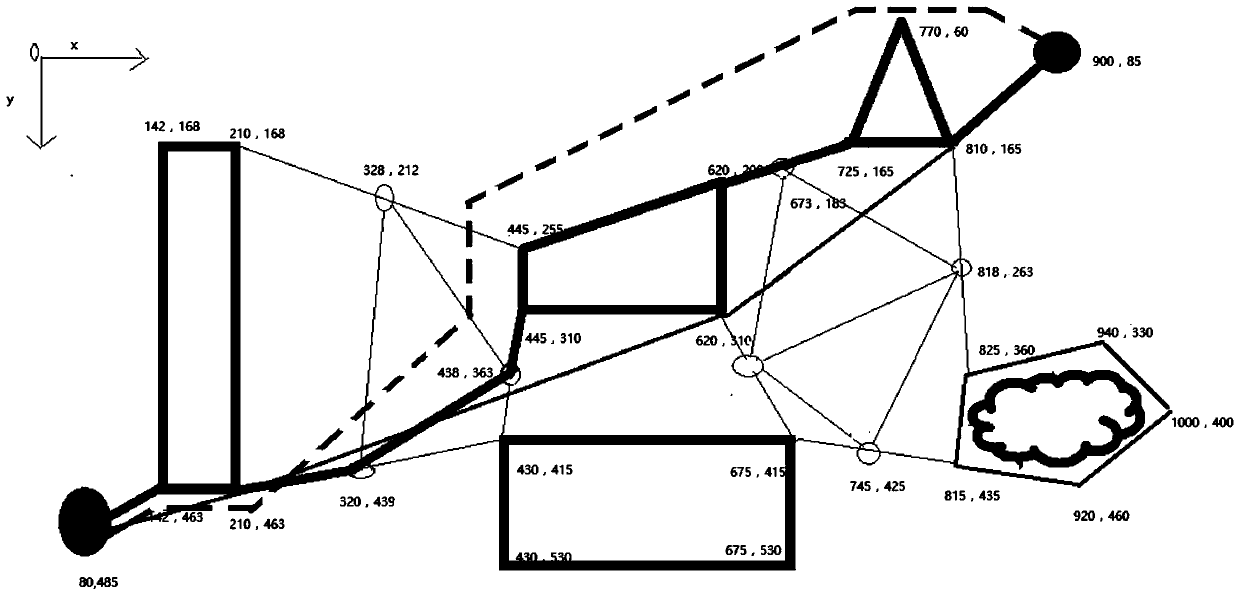
[0104] Depend on figure 1 It can be clearly seen that the number of routes that mobile robots can reach is large and complex. If this is used as the basis for the experiment, the amount of calculation and the complexity of the process will increase. Therefore, according to the node addition rules, some ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com