A minimally invasive fusion device
A cage and mesh bag technology, applied in the direction of spinal implants, etc., can solve the problems that the cage does not have mechanical support, restricts the space for bone grafting, and affects the fusion effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
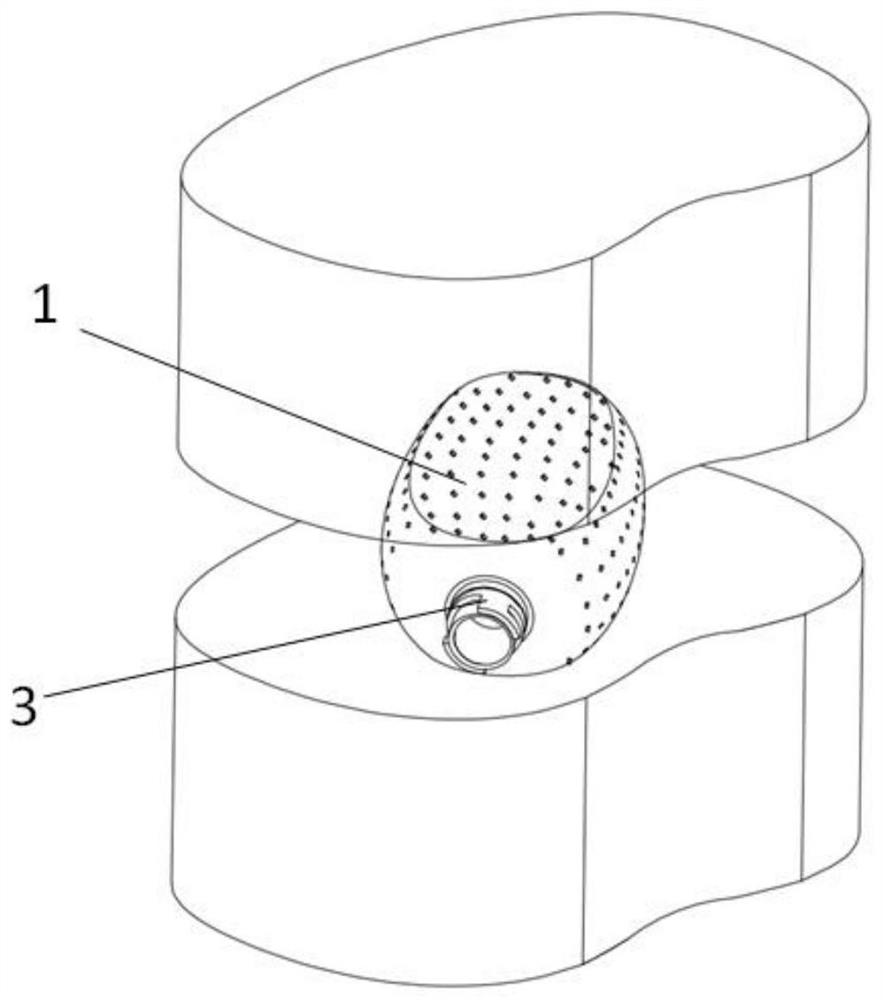
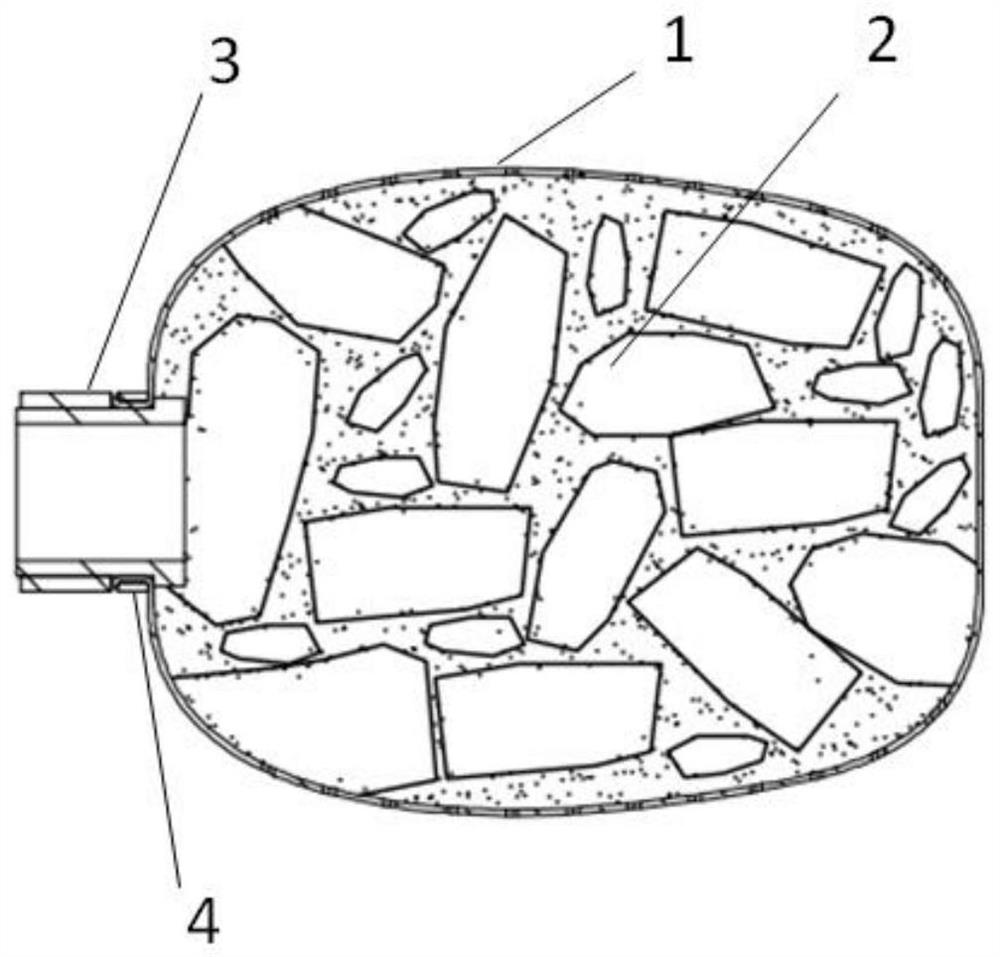
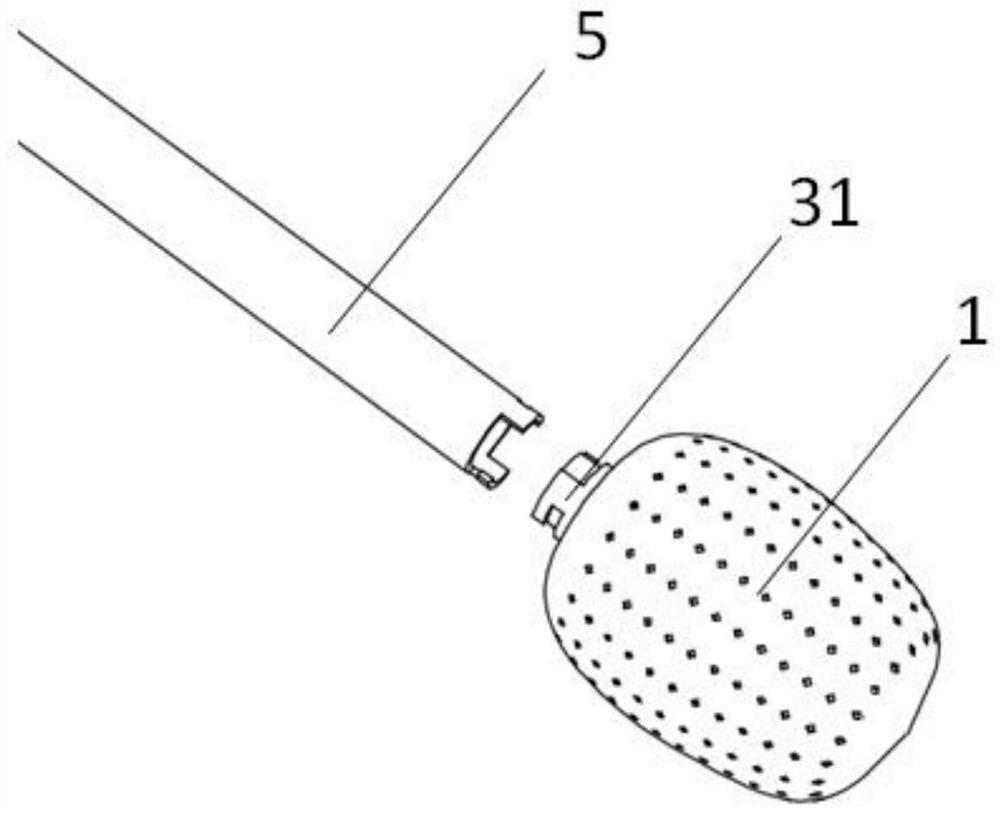
[0076] Such as figure 2 As shown, a minimally invasive fusion device includes a mesh bag 1 and a filling material 2. A connector 3 is provided at the proximal end of the mesh bag 1, and the connector 3 is extruded and connected to the mesh bag 1 through a collar 4. Such as image 3 As shown, the mesh bag 1 is connected to the connecting pipe 5 through the connecting head 3, and the mesh bag 1 is sent into the intervertebral space along the working channel through the connecting pipe 5, as shown in FIG. figure 1 shown; after reaching the working position, such as Figure 7 and 8 As shown, fill the filling tube 6 with the filling material 2 times, and use the inner push rod 7 to fill it into the inside of the mesh bag 1 until the mesh bag 1 expands to fit the contact surface of the upper and lower vertebral bodies. After filling, such as figure 2 As shown, the filling material 2 can seal the inner hole of the connector 3 and play a role of self-sealing. The inner push rod...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Such as figure 2 As shown, a minimally invasive fusion device includes a mesh bag 1 and a filling material 2. A connecting head 3 is provided at the proximal end of the mesh bag 1, and the connecting head 3 is extruded and connected to the mesh bag 1 through a collar 4. Bone filling materials 2 with different structures and particle sizes are preloaded in the filling tube 6 according to the ratio. Such as image 3 and 4 As shown, the mesh bag 1 is connected to the connecting tube 5 through the connecting head 3, and the mesh bag 1 is sent into the intervertebral space along the working channel through the connecting tube 5. After arriving at the work location, such as Figure 5 and 6 As shown, the filling pipe 6 enters the mesh bag 1 along the connecting pipe 5, and the filling material 2 in the filling pipe 6 is pushed to the inside of the mesh bag 1 by using the inner push rod 7 until the mesh bag 1 is fully expanded to the point where the upper and lower vertebr...
Embodiment 3
[0089] (The fuser has a liner without a sealing device) such as Figure 11 As shown, a minimally invasive fusion device includes a foldable mesh bag 1, a filling material 2 and a liner core 9, an outlet 10 is provided in the middle, and a connector 3 is provided at the proximal end, the mesh bag 1 and the liner The proximal end of the core 9 is extruded and connected through a collar 4 , the connecting head 3 is extruded connected with the lining core 9 , and the distal end is extruded connected with the lining core 9 through another collar 4 . The connecting tube 5 can be connected with the connector 3 of the fusion device, and the fusion device is sent into the intervertebral space along the working channel. After reaching the working position, as Figure 7 and 8 As shown, the filling material 2 is filled in the filling tube 6 several times. Use the inner push rod 7 to inject the filling material 2 into the net bag 1 through the outlet 10, and the net bag 1 can expand to f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com