Air conditioner and area control method thereof
An area control and area technology, applied in the area control method and the air conditioner field using the area control method, can solve problems such as poor adaptability of area control, and achieve the effects of improving user experience, balancing air volume, and reducing impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The principles and embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
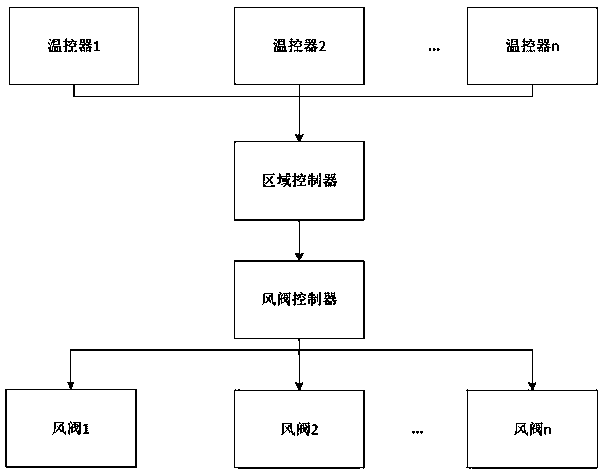
[0031] figure 1 Shows the structural block diagram of the regional control part of the air conditioner of the present invention, a set of air conditioning units of the present invention corresponds to n blocks of areas, each area is provided with a damper and a temperature controller, and each damper corresponds to a damper After the controller, the zone controller processes the temperature fed back by the thermostat, it sends a control command to the damper controller, and then the damper controller adjusts the switch and / or opening of the damper according to the control command.
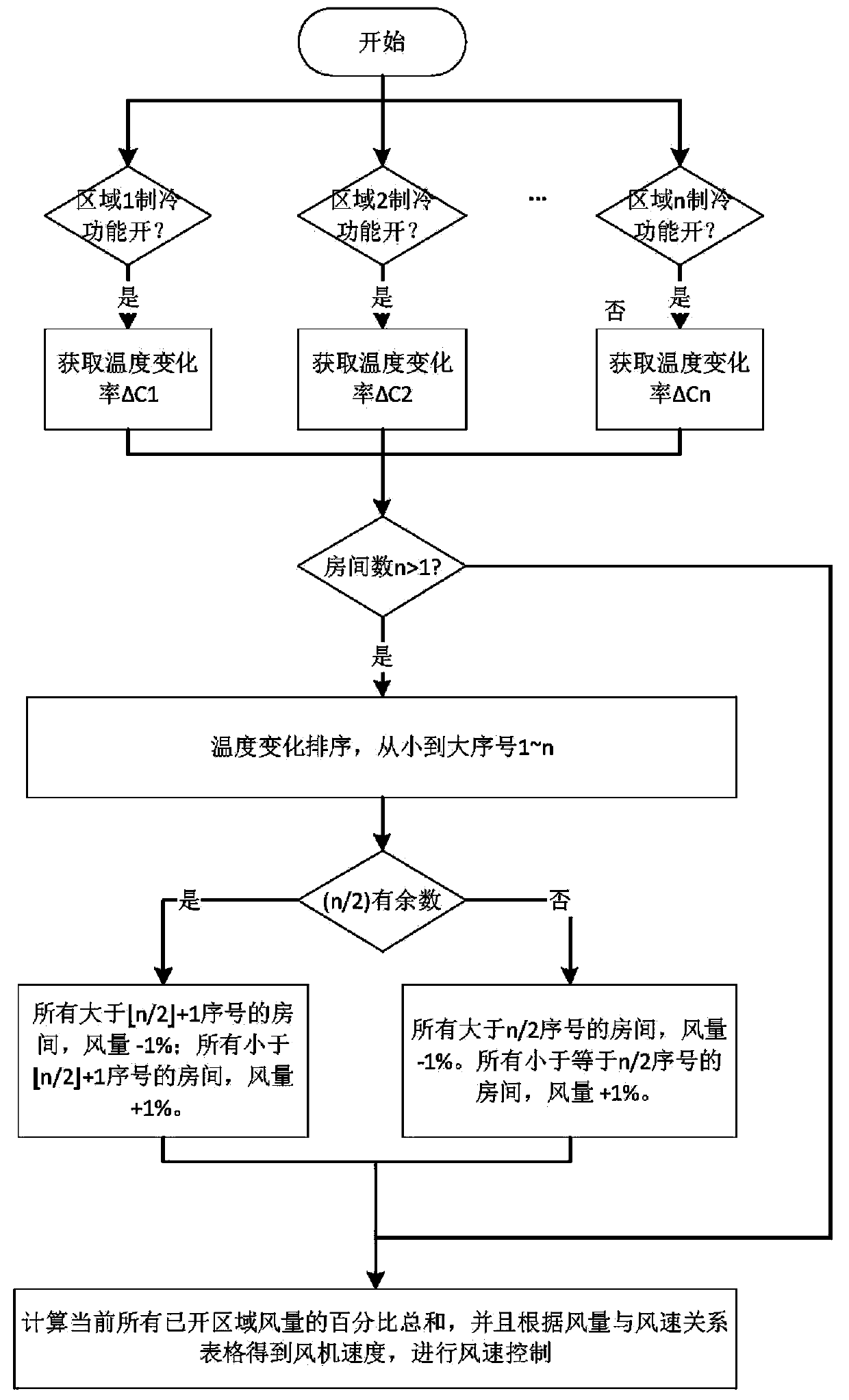
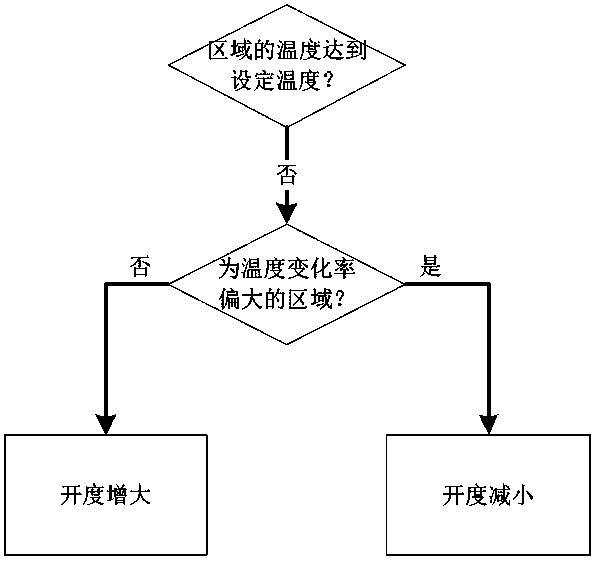
[0032] figure 2 It shows the detailed flow chart of the regional control method of the present invention. When the air conditioning function is turned on in some or all regions, that is, the cooling function, heating function or air supply function is t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com