Unmanned aerial vehicle route planning method based on improved Q-learning algorithm
A route planning and UAV technology, applied in the UAV route planning field based on the improved Q-learning algorithm, can solve the problems of increasing time complexity, dimension disaster, large computing pressure, etc., to reduce the number of exploration steps, speed up The effect of convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
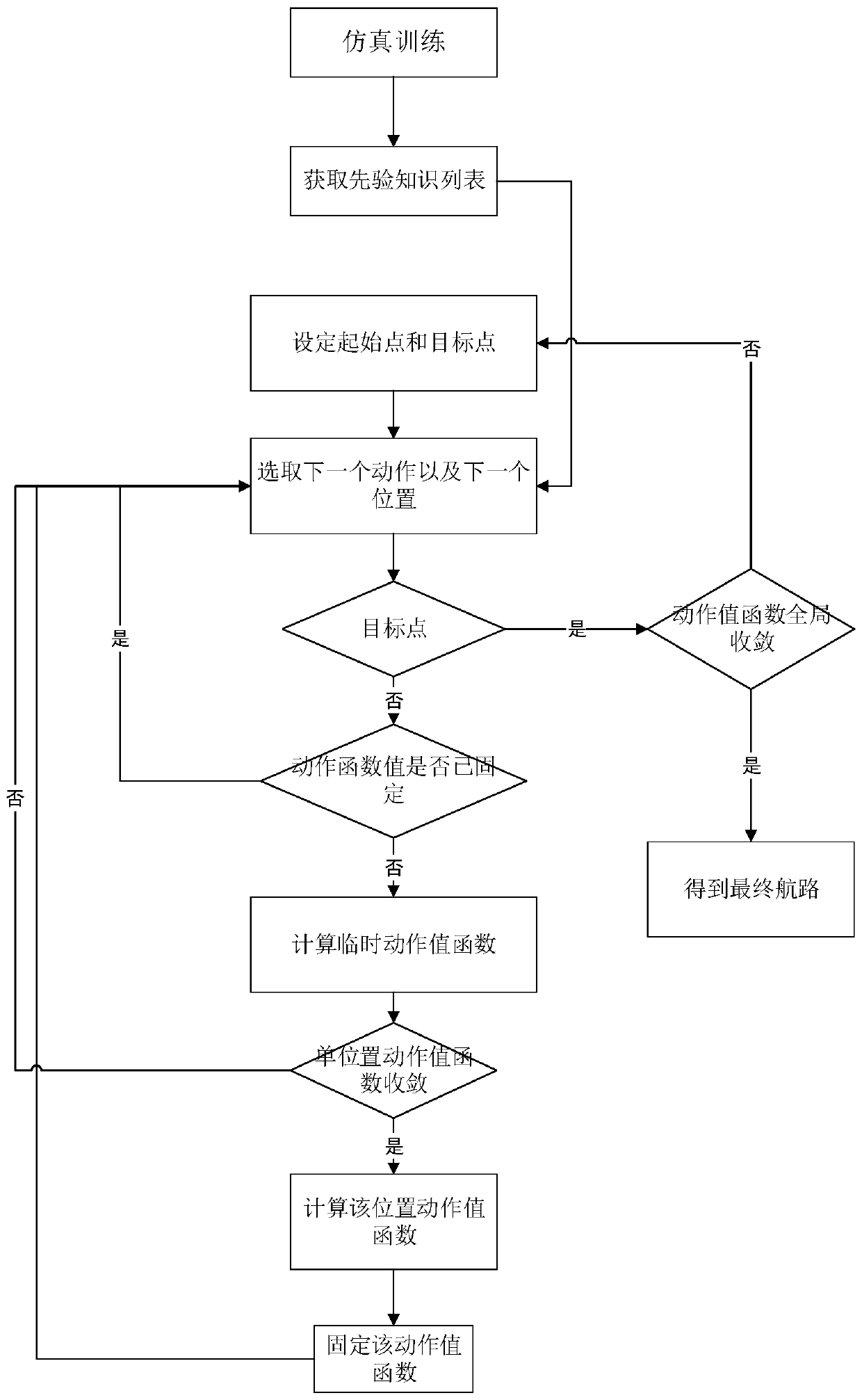
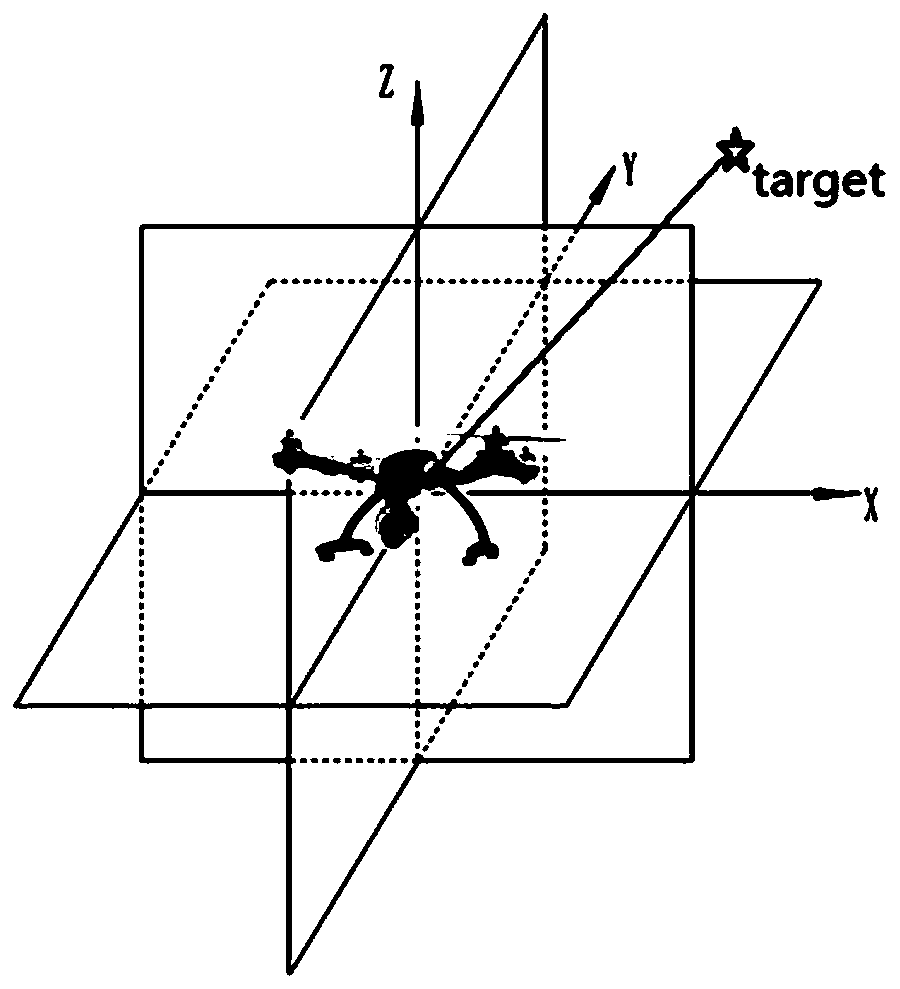
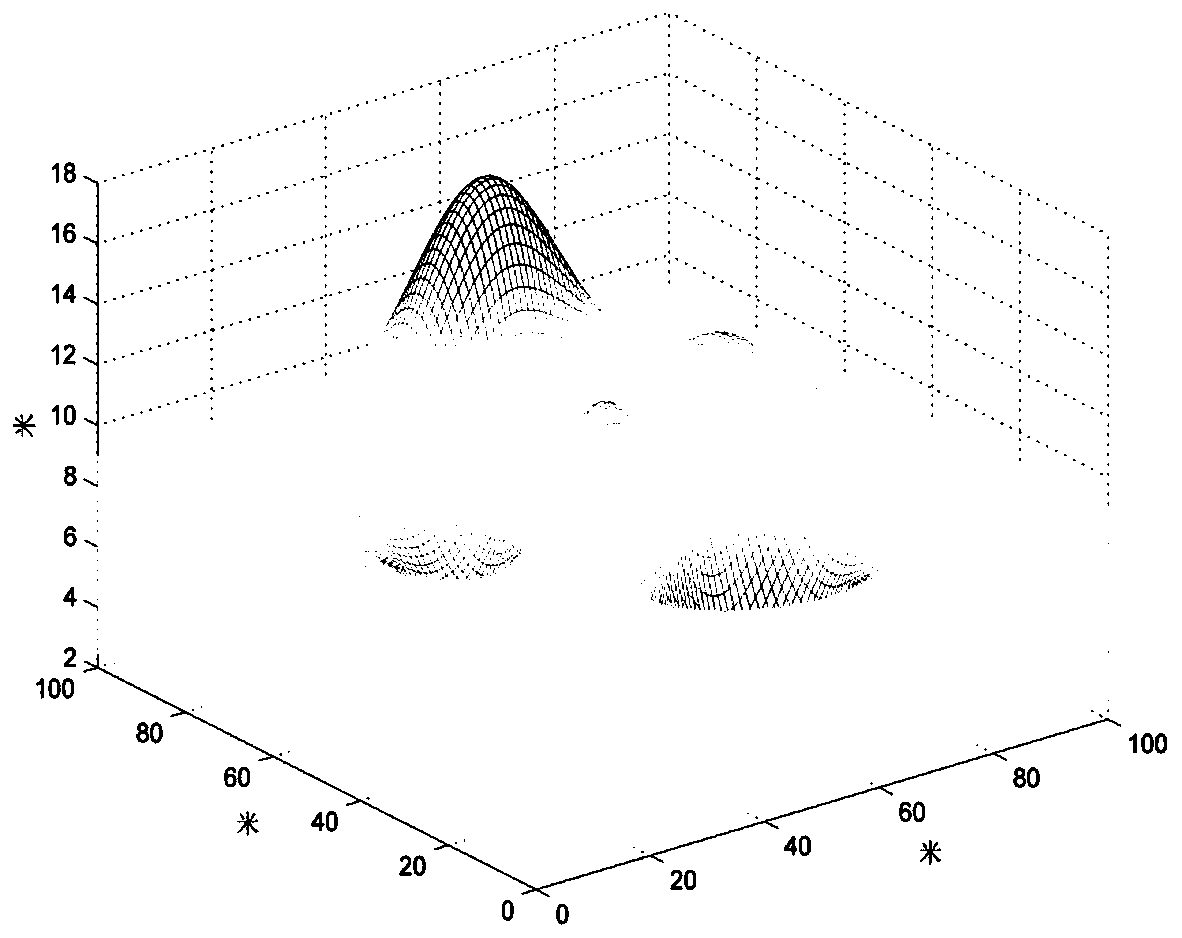
[0064] Applying the Q-learning algorithm to the route planning problem of the UAV, firstly, the flight environment of the UAV is modeled and discretely processed, and the real continuous environment is converted into a discrete environment that can be used by reinforcement learning Q-learning. In order to simulate the environment in which the UAV flies, the environment is modeled in 3D. Design a 100m*100m*20m three-dimensional grid map, where the size of each grid is 1m*1m*1m, and use the three-dimensional grid map as a virtual environment for drones to fly, such as image 3 shown. The degree of discretization of the grid map and the size of the grid have a great influence on the calculation results. Under the premise of the same size global map, the larger the grid size, the state space will be reduced, the calculation cost will be greatly reduced, and the calculation speed will be improved. , but reduces the planning accuracy. If the grid size is set smaller, although the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com