Optical path structure
A technology of light path and light, which is applied in the direction of material analysis, measuring devices, and instruments through optical means, can solve the problems of complex light path structure and low light fusion efficiency, and achieve high light efficiency, compact cavity structure design, and easy processing and adjust the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
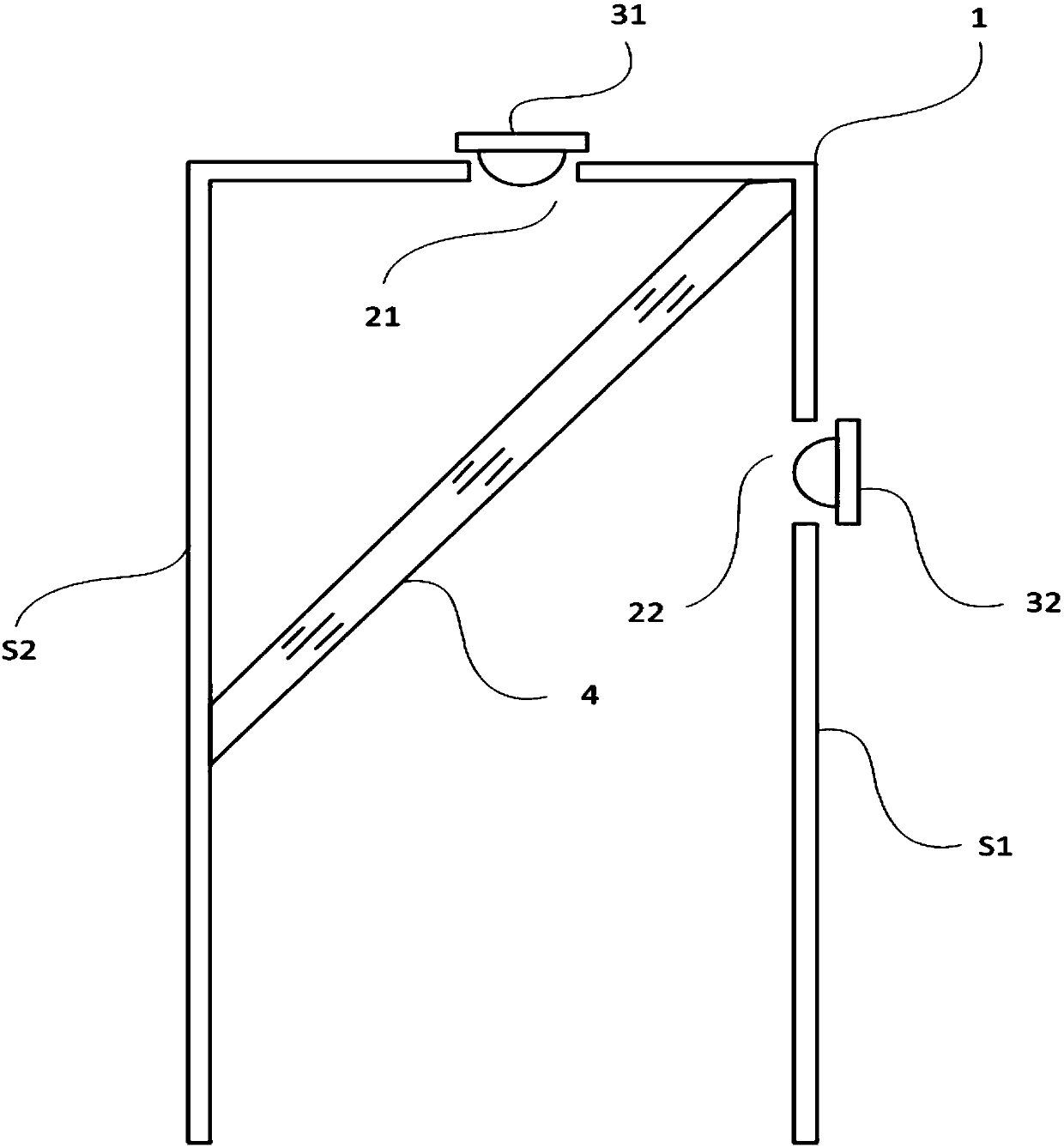
[0050] Such as figure 1 As shown, the optical path structure in this embodiment includes a cuboid cavity 1, one end of the cavity 1 is open, and a through hole 21 is arranged on the end surface of the other end, and the red LED 31 is arranged at the through hole 21, and the light emitted by the LED 31 It is emitted through the through hole 21 toward the opening of the cavity 1 .
[0051] The side S1 of the four sides of the cavity 1 is provided with a through hole 22 , and the blue LED 32 is arranged at the through hole 22 , and the light emitted by the LED 32 is emitted to the side S2 through the through hole 22 .
[0052] In cavity 1 such as figure 1 The dichroic mirror 4 is arranged as shown, and the dichroic mirror 4 described in this embodiment can allow the red light emitted by the LED31 to directly pass through the dichroic mirror 4, but the blue light emitted by the LED32 is reflected at 90°, and the red light directly transmitted Combined with the blue light reflect...
Embodiment 2
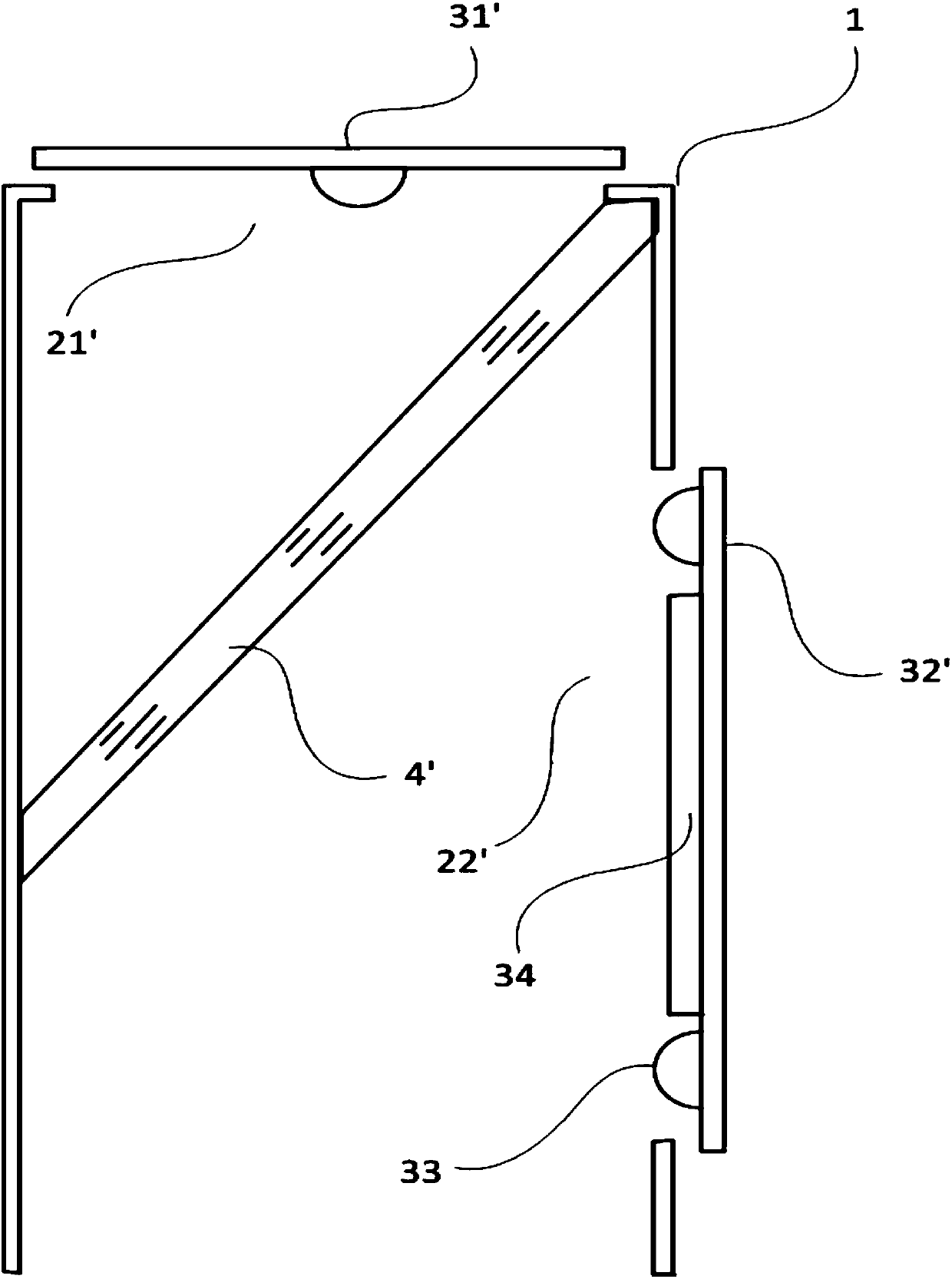
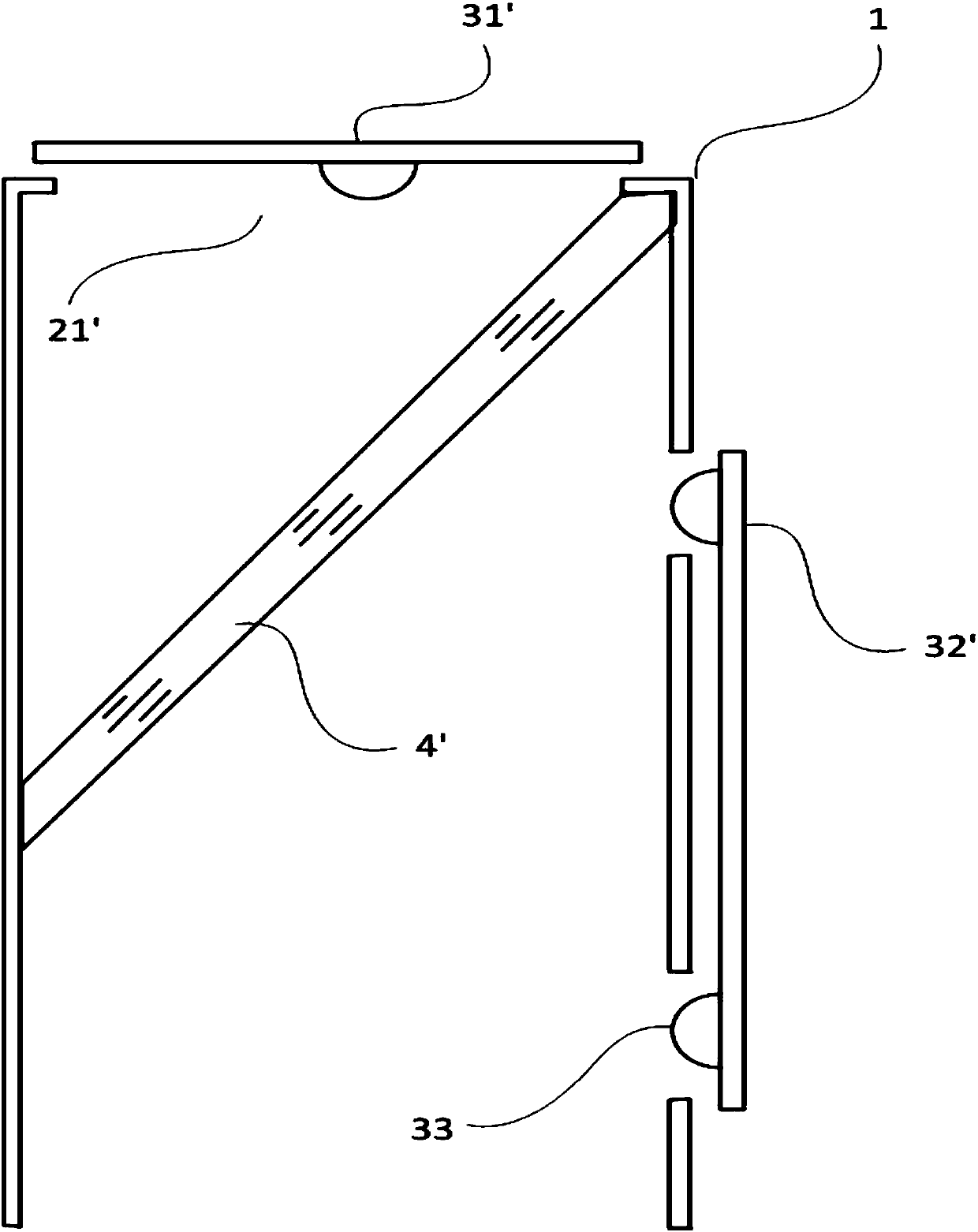
[0056] Such as figure 2 As shown, the cavity 1 in this embodiment is a cylinder, one end of the cavity 1 is open, and a strip-shaped notch 21' is provided on the end surface of the other end, the LED board 31' covers the notch 21', and the LED The light emitted by the plate 31 ′ is emitted toward the opening of the cavity 1 through the notch 21 ′.
[0057] A strip-shaped notch 22' is provided on the side of the cavity 1, and the LED board 32' covers the notch 22', and the light emitted by the LED board 32' is emitted to the other side of the cavity opposite to the notch 22' through the notch 22'.
[0058] In this embodiment, a photodiode 33 is also arranged on the LED board 32', and the photodiode 33 faces the notch 22' to collect the light intensity in the cavity.
[0059]Moreover, a light blocking member 34 is arranged between the second LED 22 and the photodiode 33, so that the light emitted by the second LED 22 cannot directly irradiate the photosensitive surface of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 lies in that a lens 5 is provided at the opening of the cavity 1 in this embodiment, and the lens 5 collimates and converts the combined light beams into parallel light or condenses light.
[0065] In a modified example of this embodiment, the lens may be a lens group to convert the combined light beam into parallel light or to condense light.
[0066] Such as Figure 5 In another embodiment shown, the lens 5 is inlaid on the threaded connector 6, the threaded connector matches the threads at the opening of the cavity 1, and the threaded connector 6 can be screwed and fixed at the opening.
[0067] In another embodiment of this embodiment, the lens or the lens group is inserted into the opening of the cavity by buckling, and can be removed from the opening of the cavity manually or with the aid of tools. The fixing of the lens lens in the opening of the cavity can be realized more conv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com