Boundary exploration autonomous mapping method based on curve fitting and target point neighborhood planning
A curve fitting, target point technique
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
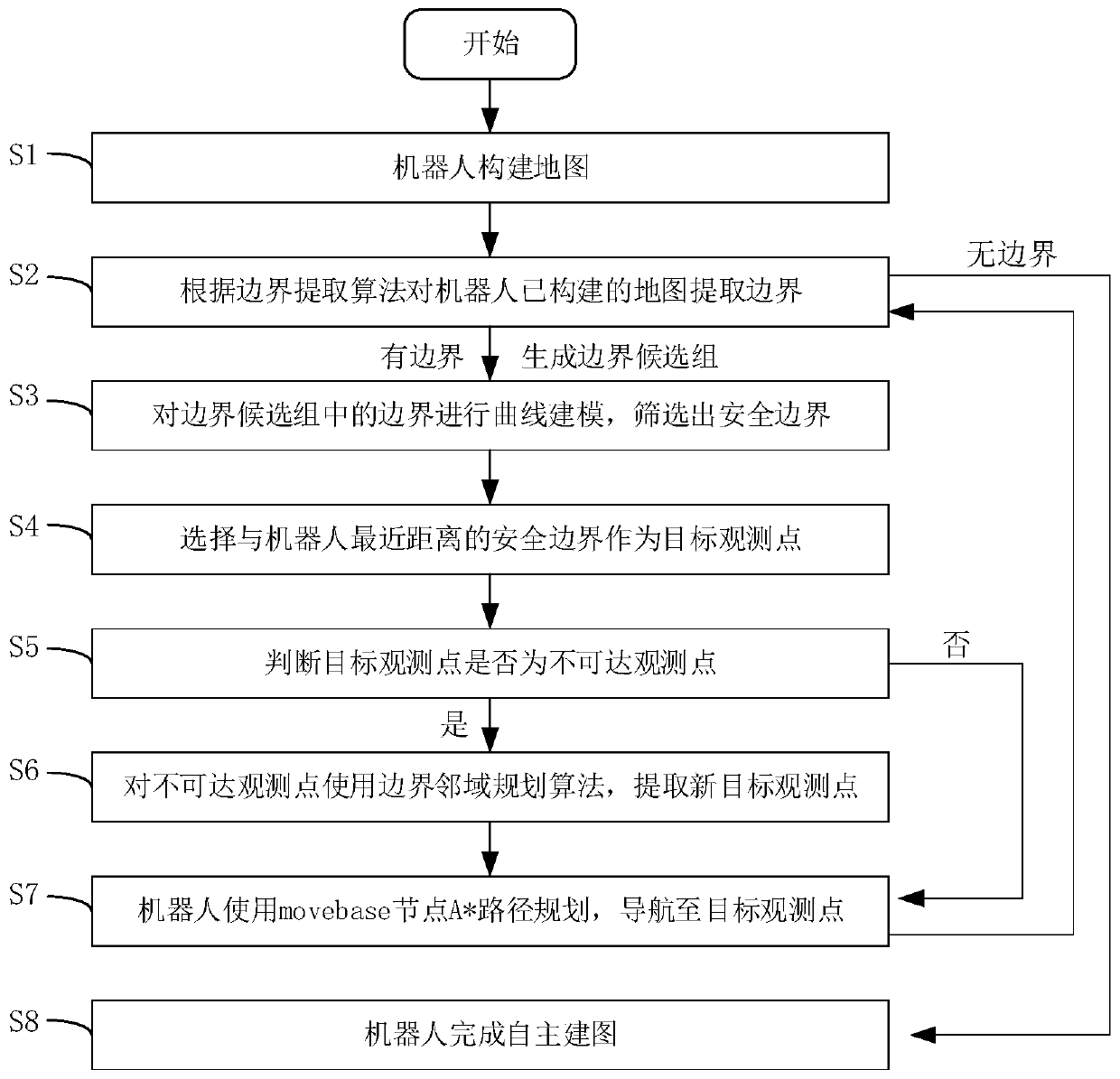
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown in , the boundary exploration autonomous mapping method based on curve fitting and target point neighborhood planning includes the following steps:
[0048] S1: The robot constructs the map;
[0049] S2: Extract the boundary from the map constructed by the robot according to the boundary extraction algorithm, and judge whether there is a boundary, and if so, generate a boundary candidate group, otherwise perform step S8;
[0050] S3: Carry out curve modeling on the boundaries in the boundary candidate group, and screen out the safety boundaries;
[0051] S4: Select the safety boundary closest to the robot as the target observation point;
[0052] S5: Determine whether the target observation point is an unreachable observation point, if so, execute step S6, otherwise execute step S7;
[0053] S6: Use the boundary neighborhood planning algorithm for unreachable observation points to extract new target observation points;
[0054] S7: The robo...
Embodiment 2
[0058] More specifically, the step S1 is as follows: In the ROS system, the odometer node is used to obtain the initial pose of the robot, and the robot uses the Gmapping algorithm to construct a map throughout the process.
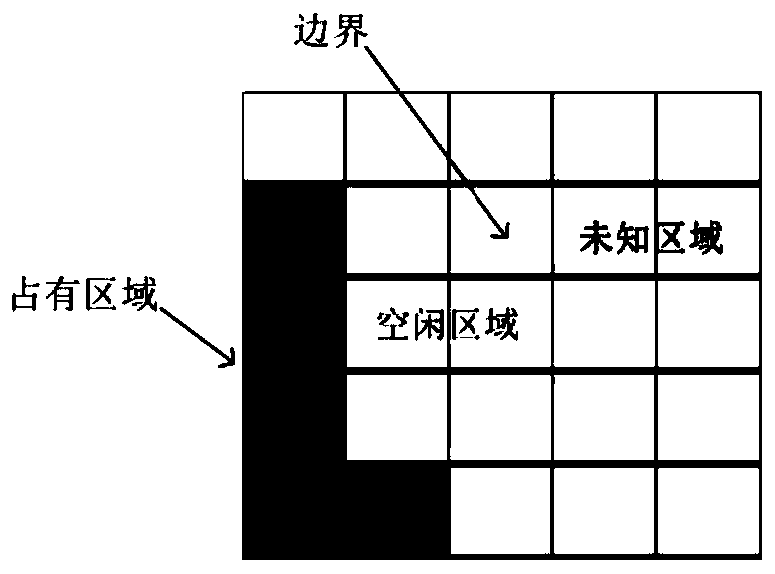
[0059] More specifically, the map model adopted by the Gmapping algorithm is a grid map; the grid map directly obtains the occupancy state of the environment through the distance information of the sensor, and provides environmental feature data; each grid in the grid map has three states , including idle state, occupied state and unknown state; where:
[0060] The idle state indicates that there is no obstacle at the grid;
[0061] The occupancy state indicates that there are obstacles at the grid, which need to be avoided during path planning of the robot;
[0062] The unknown state indicates that the grid is not perceived by the robot and belongs to an unknown environment.
[0063] In the specific implementation process, when the robot conducts auton...
Embodiment 3
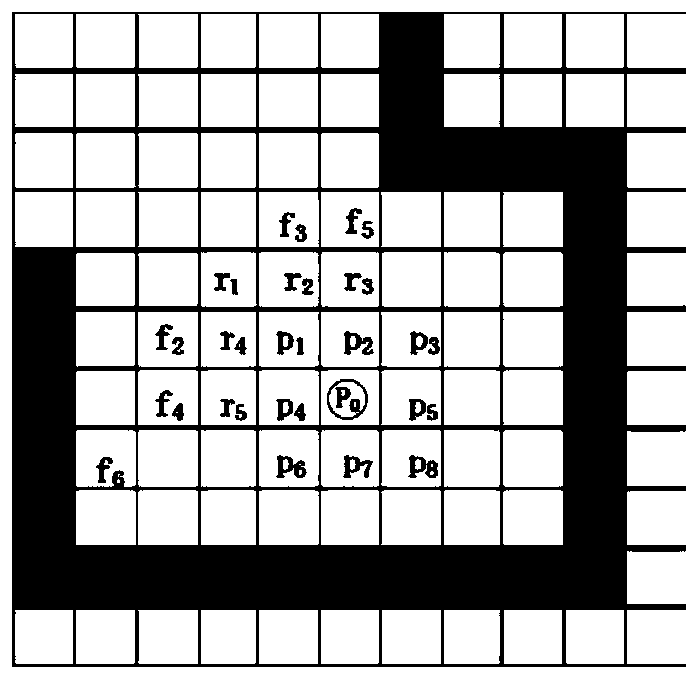
[0072] In the specific implementation process, there are many short, slender, and narrow boundaries in the candidate boundary group. These boundaries cannot accommodate the robot, causing the robot to enter the narrow area and collide, or make the robot execute path planning for a long time, but there is no path to reach. Increased autonomous map building time. Therefore, in view of the above defects, this method proposes to remove unsafe boundaries and retain safe and effective boundaries by means of curve modeling for the boundaries in the candidate boundary group, specifically:
[0073] S31: Establish the local boundary coordinate system of the boundary candidate group: the boundary in the candidate boundary group is a series of two-dimensional coordinate points based on the robot map coordinate system, which does not contain the direction information of the boundary, so the curve modeling of the boundary needs to be established first The local coordinate system of the boun...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com