A Fault Location System and Method Based on Model Hit Probability Distribution
A hit probability, fault location technology, applied in the detection of faulty computer hardware, the generation of response errors, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of narrowing the scope of troubleshooting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
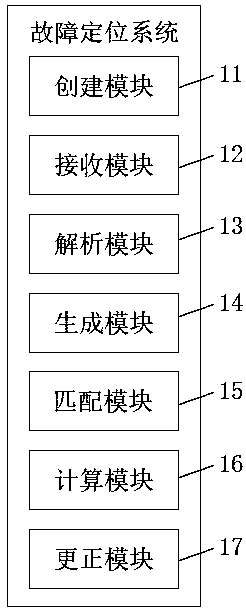
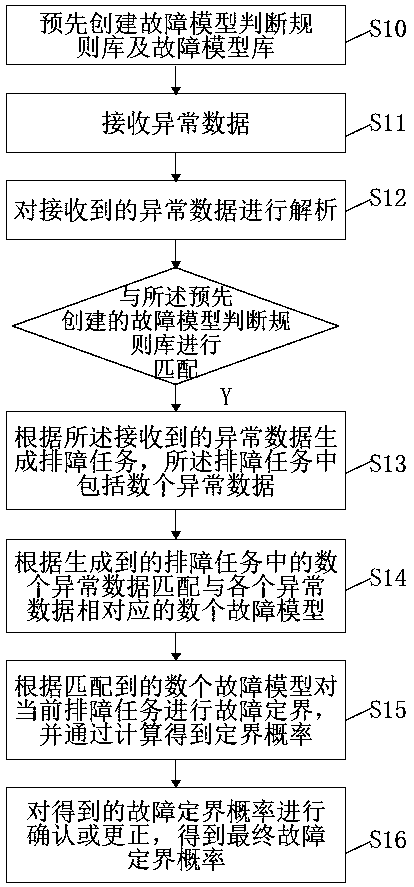
[0041] This embodiment provides a fault location system based on model hit probability distribution, such as figure 1 As shown, creating module 11, receiving module 12, parsing module 13, generating module 14, matching module 15, calculating module 16, correcting module 17;
[0042] The creation module 11 is used to pre-create a fault model judgment rule base and a fault model base;
[0043] The receiving module 12 is configured to receive abnormal data;
[0044] The parsing module 13 is configured to parse the received abnormal data and match it with the pre-created fault model judging rule base;
[0045] The generation module 14 is configured to generate a troubleshooting task according to the received abnormal data, and the troubleshooting task includes several abnormal data;
[0046] The matching module 15 is configured to match several fault models corresponding to each abnormal data according to several abnormal data in the generated troubleshooting task;
[0047] The...
Embodiment 2
[0115] A fault location system based on model hit probability distribution provided in this embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 in that:
[0116] In the generating module, a troubleshooting task is generated according to the received abnormal data, and the troubleshooting task includes several abnormal data.
[0117] Match the parsed abnormal data with the system rule base, and if it hits the rule, generate a troubleshooting task; if there are multiple abnormal data that hit the same rule, record the number of hits.
[0118] A troubleshooting task may include multiple abnormal data, such as abnormal data 1, abnormal data 2, abnormal data 3, and so on.
[0119] When new abnormal data is generated in a troubleshooting task, it is necessary to first determine whether there is an unfinished troubleshooting task that is the same as the abnormal data or associated with the device (according to the configuration item number in the abnormal data and the CMDB record If there is ...
Embodiment 3
[0122] A fault location system based on model hit probability distribution in this embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that:
[0123] This embodiment illustrates by way of example the finally obtained fault demarcation probability in a certain troubleshooting task and the correction of the obtained fault demarcation probability.
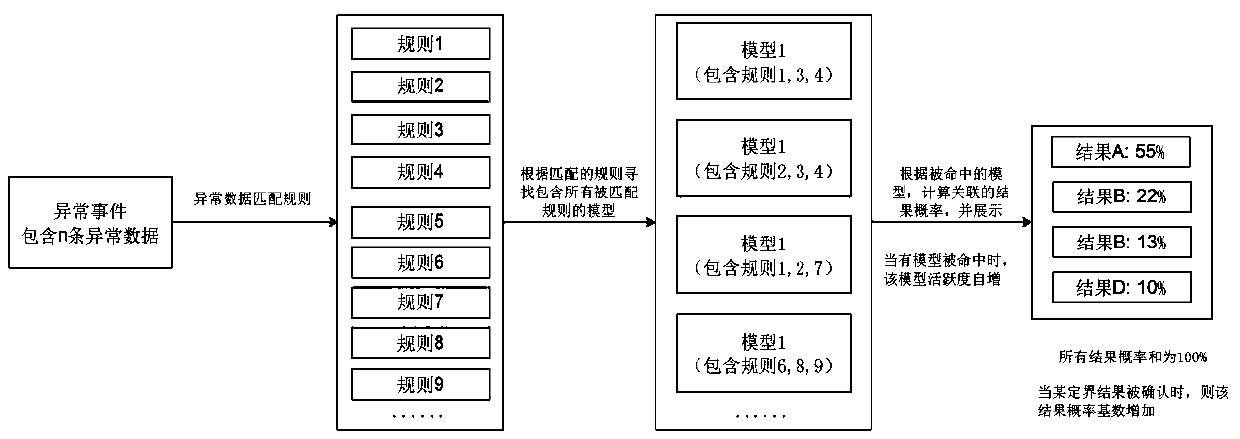
[0124] 1. Fault model delimitation probability
[0125] The rule a corresponding to abnormal event 1 in a certain troubleshooting task is matched to fault models A, B, and C, where fault model A contains rule A (a, b, c), and fault model B contains rule (a, b) , Fault model C contains rules (a, c), then the activity of fault model A, fault model B, and fault model C increases by 1 each; when the b rule corresponding to the second abnormal event 2 appears, it matches Fault models A and B, at this time, the activity of fault model A and fault model B is increased by 1 respectively; when the c rule corresponding to the third abnormal event 3 appear...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com