Shoulder joint rehabilitation exoskeleton mechanism adopting unpowered compensation joints
A compensation mechanism and exoskeleton technology, applied in passive exercise equipment, physical therapy, etc., can solve the problems of high complexity of exoskeleton and decreased joint compensation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
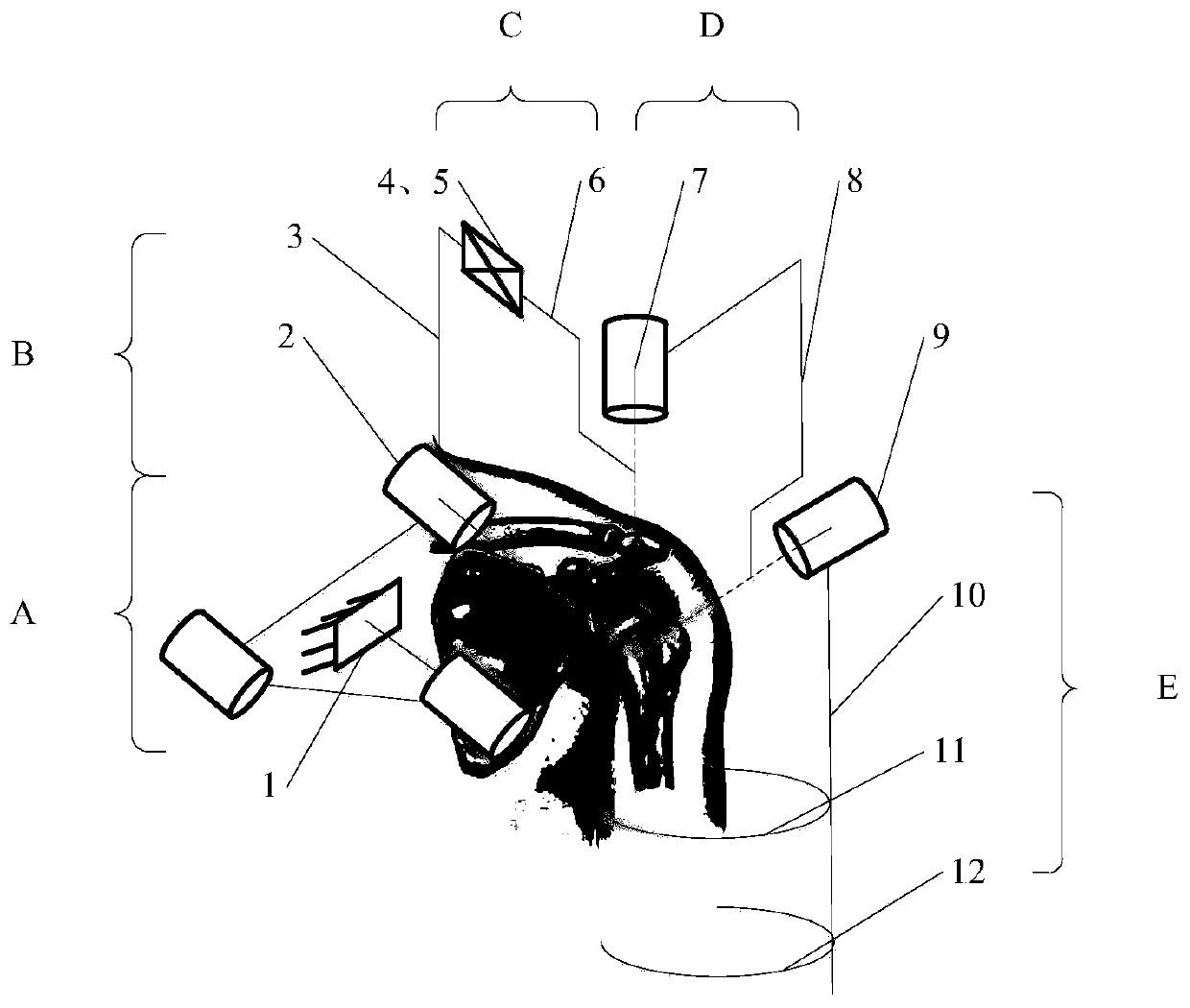
[0041] Such as Figure 1-Figure 3 A shoulder rehabilitation exoskeleton mechanism using a non-dynamic compensation joint is shown, including glenohumeral joint adaptive compensation mechanism A, exoskeleton abduction / adduction mechanism B, sagittal axis compensation mechanism C, exoskeleton internal rotation / External rotation mechanism D, exoskeleton flexion / extension mechanism E, back support (1) and two upper arm connectors, first upper arm connector (11), second upper arm connector (12). Exoskeleton abduction / adduction mechanism B, exoskeleton internal rotation / external rotation mechanism D, exoskeleton flexion / extension mechanism E realize shoulder joint abduction / adduction, internal rotation / external rotation and forward flexion / extension Basic movement; the glenohumeral joint adaptive compensation mechanism A is connected to the back support (1), providing stable support at the shoulder joint while compensating for the fluctuation of the glenohumeral joint rotation cent...
Embodiment 2
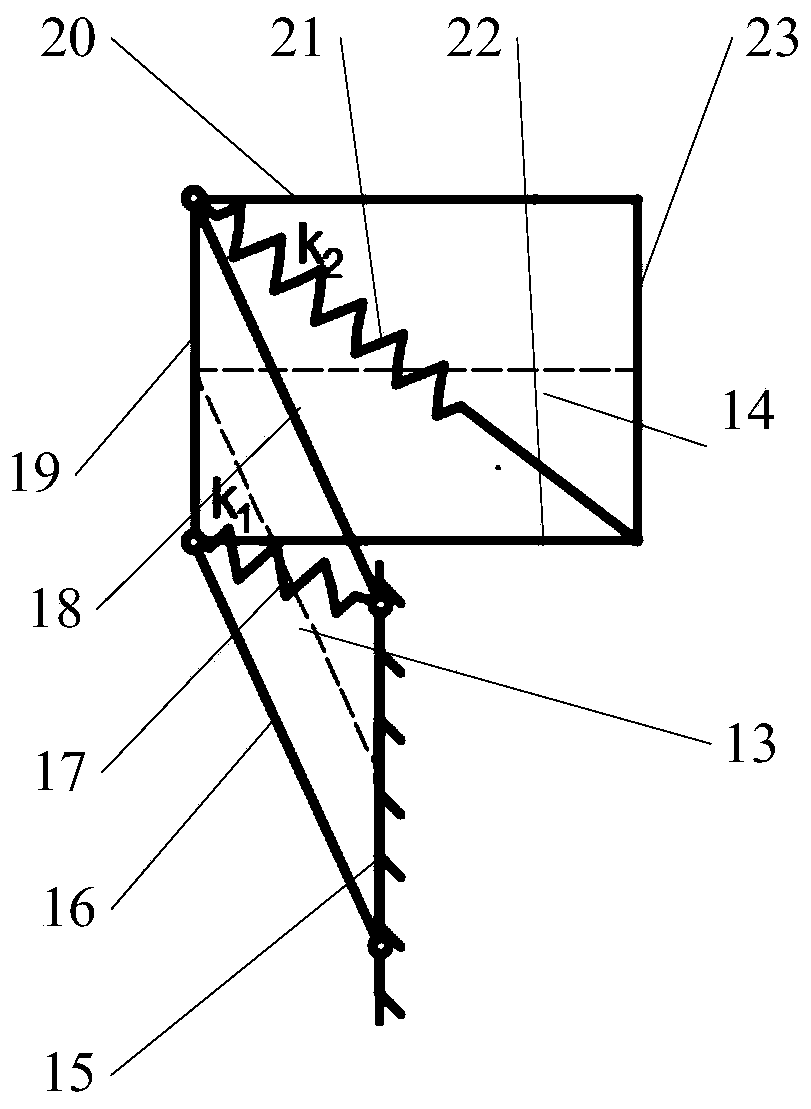
[0050] The design of the glenohumeral joint adaptive compensation mechanism A of Embodiment 1 can be divided into the following steps:
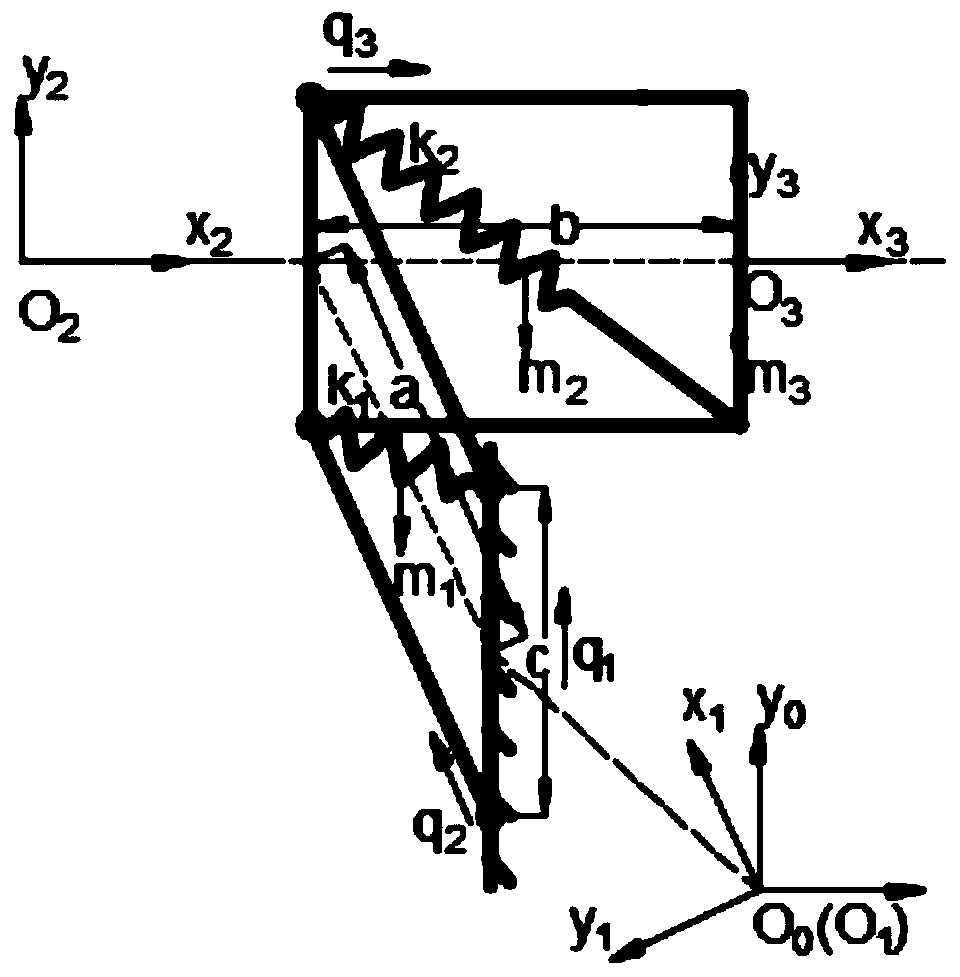
[0051] 1) Determine the length of each connecting rod, wherein the lengths of the first connecting rod (15), the third connecting rod (19) and the sixth connecting rod (23) that keep the vertical direction in motion are c=0.1m; the second The length of connecting rod (16) and the 4th connecting rod (18) is identical for length and is a=0.13m; The length of the 5th connecting rod (20) and the seventh connecting rod (22) is identical for b=0.13m;
[0052] 2) Determine the initial angle and rotation range of each parallelogram mechanism (13), (14). Let be the unit vector on link i in the institution, where q 1 is a vertically fixed chain. Establish a fixed coordinate system O at the midpoint of the first connecting rod (15) of the vertical fixed chain 0 x 0 the y 0 z 0 , x 0 The axis is parallel to the coronal axis and points from the ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com