Passive sensing circuit and control method thereof
A passive sensing and circuit technology, applied in the field of sensing, can solve the problems of large differences in sensing accuracy, unstable transmission power of readers, and inability to guarantee stability of continuous waves, so as to improve sensing accuracy and sensing distance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
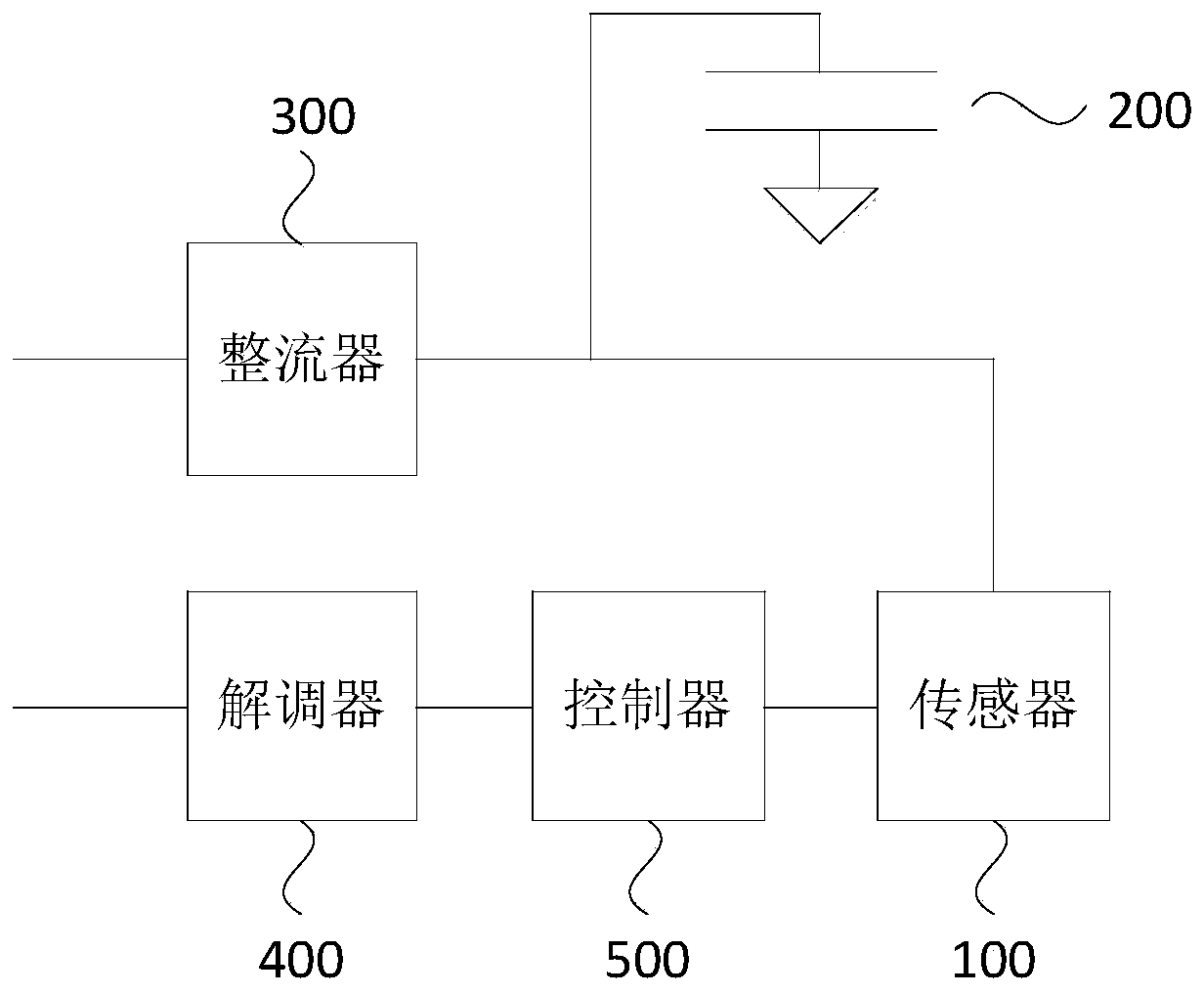
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a passive sensing circuit, which includes a sensor 100 , a first capacitor 200 , a rectifier 300 , a demodulator 400 and a controller 500 .
[0040] Specifically, the sensor 100 is used to generate sensing data according to the monitored object; the first capacitor 200 is used to provide the sensor 100 with a first working voltage; the rectifier 300 is used to convert the received induced voltage into a second working voltage to give The first capacitor 200 is charged; the demodulator 400 is used to analyze the first instruction contained in the induced voltage; the controller 500 is used to control the sensor 100 to start working according to the first instruction.
[0041] In this embodiment, the rectifier 300 is connected in series with the sensor 100 , and the first capacitor 200 is connected in parallel between the rectifier 300 and the sensor 100 . The rectifier 300 is a device that convert...
Embodiment 2
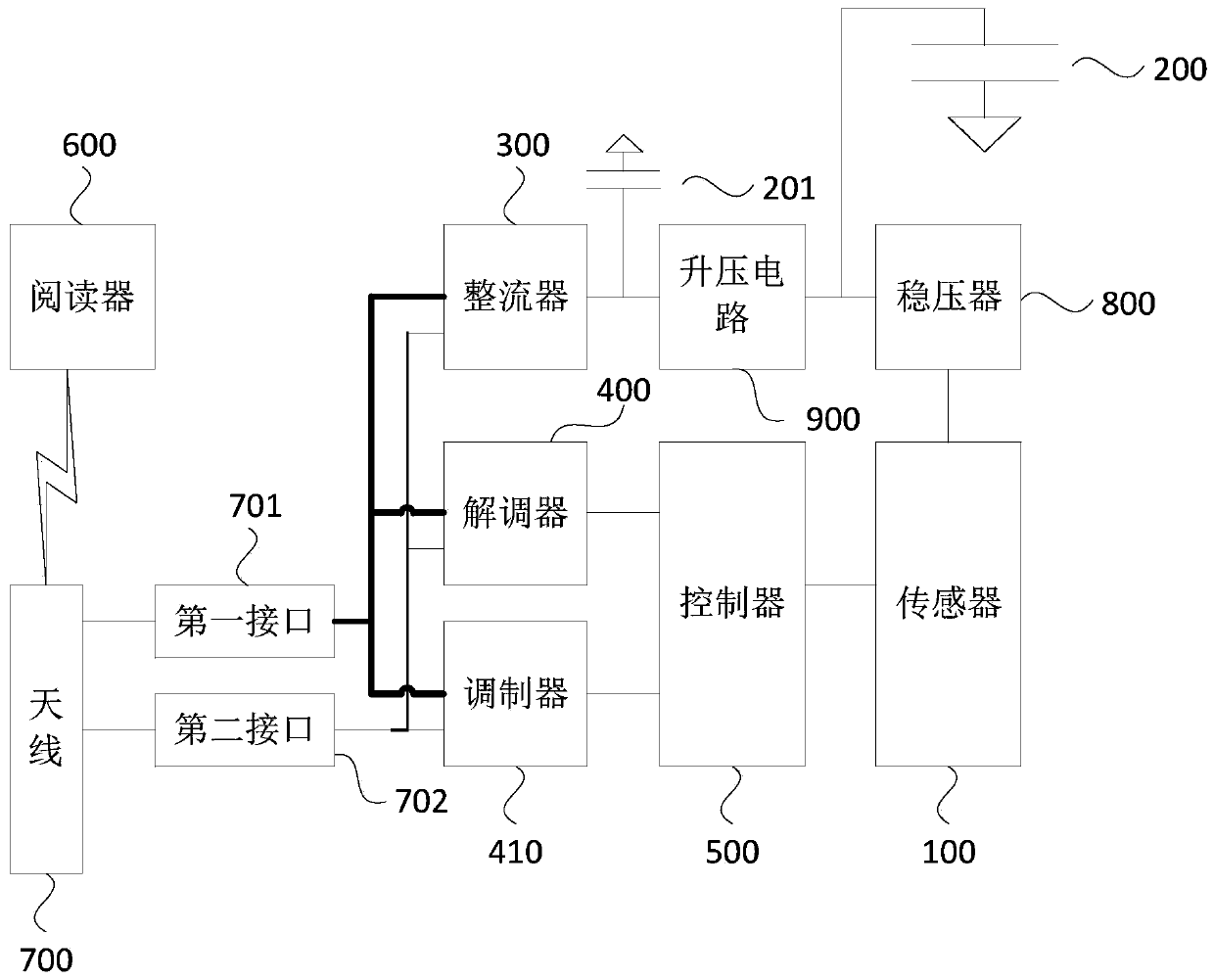
[0045] like figure 2 As shown, Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a passive sensing circuit. Embodiment 2 of the present invention is further optimized on the basis of Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The passive sensing circuit includes a sensor 100, a first capacitor 200 , rectifier 300 , demodulator 400 , controller 500 , modulator 410 , reader 600 , antenna 700 , first interface 701 , second interface 702 , voltage regulator 800 , boost circuit 900 and second capacitor 201 .
[0046] Specifically, the sensor 100 is used to generate sensing data according to the sensing object; the first capacitor 200 is used to provide the sensor 100 with a first working voltage; the rectifier 300 is used to convert the received induced voltage into a second working voltage for Charge the first capacitor 200; the demodulator 400 is used to analyze the first instruction included in the induced voltage; the controller 500 is used to control the sensor 100 to start working ...
Embodiment 3
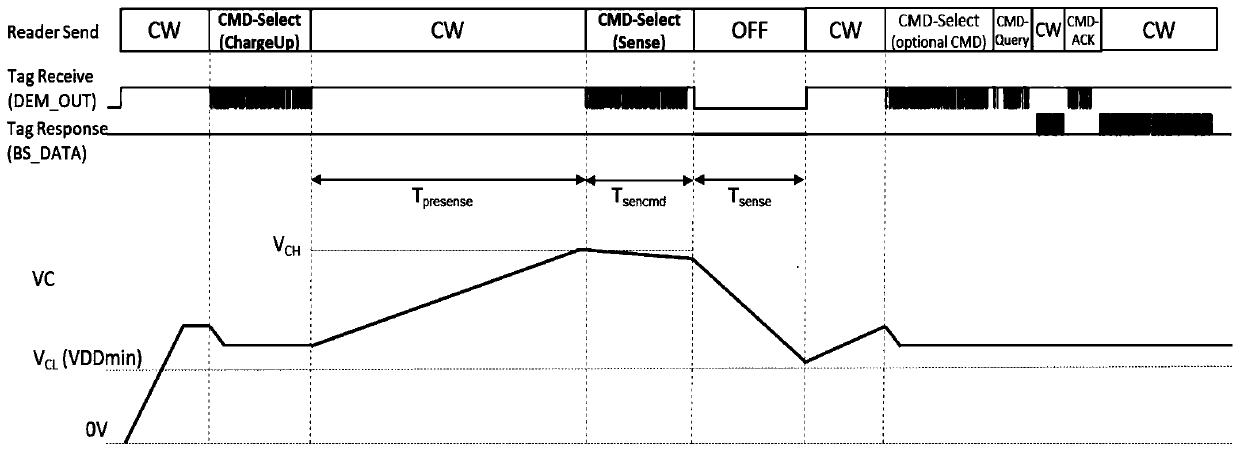
[0052] like Figure 5As shown, Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a control method of a passive sensing circuit, and the control method of the passive sensing circuit includes:
[0053] S110. Control the reader to send a radio frequency signal to charge the first capacitor in the passive sensing circuit.
[0054] S120. Based on the first capacitor as a working power source, control the reader to send the radio frequency signal to control the reader to stop sending the radio frequency signal.
[0055] S130. Control the reader to send the radio frequency signal to receive the sensing data returned by the sensor.
[0056] In this embodiment, the passive sensing circuit can be set in the chip. When the sensor sensing data is needed, firstly control the reader to send a wireless radio frequency signal to start the passive sensing circuit, that is, control the reader to send a terminal time The continuous wave placed outside the chip will generate an induced voltage af...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com