Weeding composition containing bixlozone, and applications thereof
A herbicidal composition, dichloroisoxane technology, applied in the field of pesticides, can solve the problems of reducing the amount of application, expanding the herbicidal spectrum, etc.
Active Publication Date: 2020-04-03
QINGDAO KINGAGROOT CHEM COMPOUNDS CO LTD
View PDF17 Cites 3 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
The composition can effectively prevent and control weeds such as catkins, barnyardgrass, bermudagrass,
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
 Login to View More
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
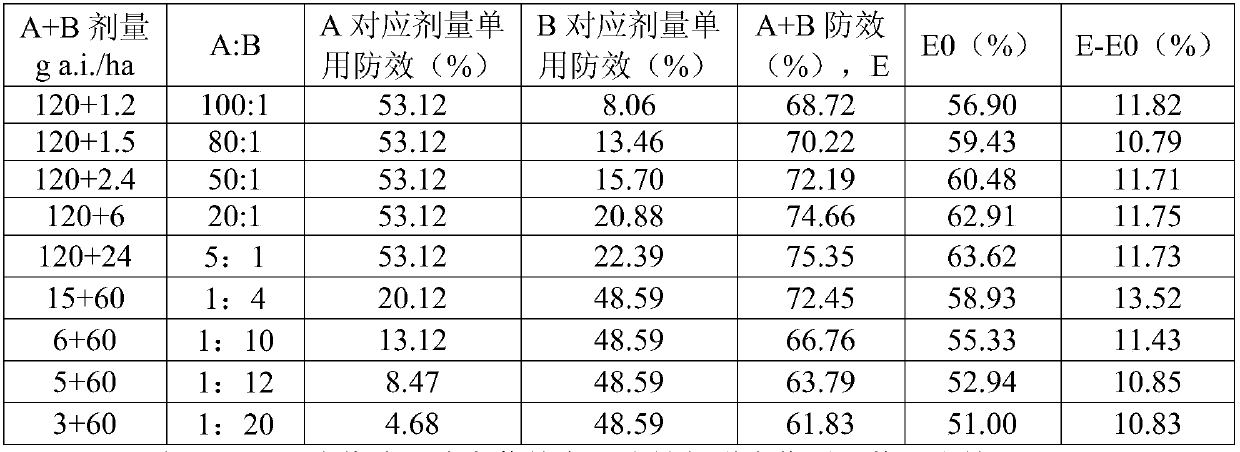
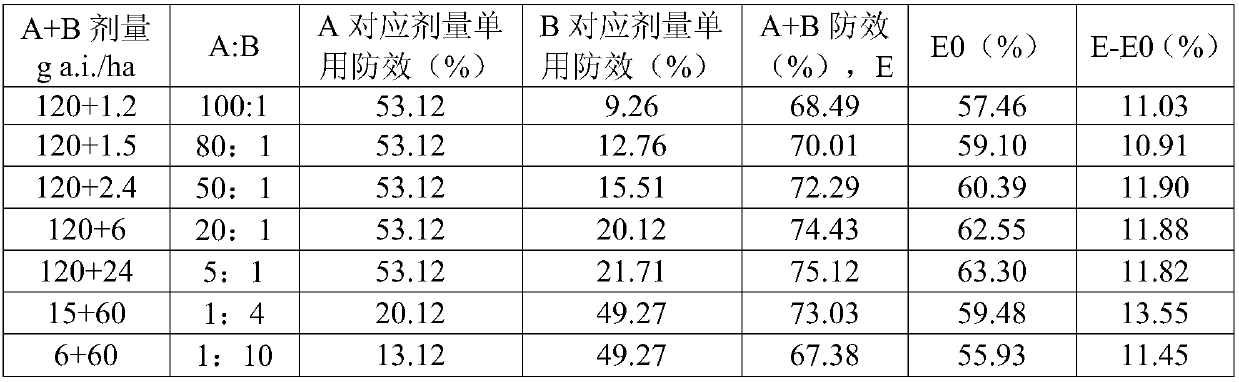
The invention belongs to the field of pesticides, and particularly relates to a weeding composition containing bixlozone, and applications thereof. The weeding composition comprises a herbicidally effective amount of an active ingredient A and an active ingredient B, wherein the active ingredient A is bixlozone, and the active ingredient B is one or a plurality of materials selected from the following compounds and salts/esters: a VLCFA inhibitor, a PPO inhibitor, a PSII inhibitor, a microtubule assembly inhibitor, an HPPD inhibitor, synthetic hormones and the like. The composition can effectively prevent and remove cardamine hupingshanesis, barnyard grass, monochoria vaginalis, amaranthus retroflexus, chenopodium album, leptochloa chinensis and other weeds, and has the characteristics ofweed control spectrum expanding, application amount reducing, synergistic effect generating, solving of resistant weeds and the like.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the field of pesticides, and in particular relates to a herbicidal composition containing clomazone and application thereof. Background technique [0002] Chemical herbicide is the most economical and effective means of controlling weeds in farmland, but long-term continuous high-dose use of a single species or single mode of action of chemical herbicides is likely to cause problems such as weed resistance and resistance evolution. Reasonable compounding or mixing of herbicide compounds has the advantages of expanding the spectrum of weeds, improving the control effect, delaying the occurrence and development of weed resistance and drug resistance, and is one of the most effective methods to solve the above problems. For example, patents CN106455569A and CN107920511A describe herbicidal compositions containing 3-isoxazolidinone compounds, but in production, it is still necessary to develop products with high safety, wide herbic...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): A01N43/80A01N57/14A01N33/22A01N43/90A01N43/70A01N43/653A01N33/18A01N43/56A01N41/10A01N43/40A01N25/04A01P13/00
CPCA01N25/04A01N33/18A01N33/22A01N41/10A01N43/40A01N43/56A01N43/653A01N43/70A01N43/80A01N43/90A01N57/14A01N43/54A01N43/66
Inventor 彭学岗赵德刘娜
Owner QINGDAO KINGAGROOT CHEM COMPOUNDS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com