Method of prognosis and follow up of primary liver cancer
A technology for primary liver cancer and liver cancer, applied in the new non-invasive quantitative testing field, can solve the problems of difficult detection of primary liver cancer and low incidence of cancer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0242] Embodiment 1. Method
[0243] Functions were obtained in a group of 9925 patients with chronic liver disease (termed the pre-inclusion population), all patients were subjected to FibroTest measurements (Fibrotest as disclosed in WO 2002 / 016949). Since the Fibrotest formula is 4.467×Log(α2 macroglobulin (g / l))-1.357×Log(haptoglobin (g / l))+1.017×Log(GGT(IU / l))+0.0281×age (years )+1.737×Log(bilirubin (μmol / l))-1.184×ApoA1(g / l)+0.301×gender (female=0, male=1)-5.540, which ensures that the measured α2 macroglobulin, Haptoglobin, GGT, age (when Fibrotest was performed), bilirubin, ApoA1 levels, and sex were all available. Furthermore, patients were pre-enrolled only if they had no previous liver transplant and had no history of PLC.
[0244] Primary liver cancer was defined as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or cholangiocarcinoma (CC) according to biopsy, or if no biopsy was available, according to Barcelona criteria or death certificate.
[0245]In the constitutive popul...
Embodiment 2
[0257] Example 2. Evaluation of functions
[0258] Determining the diagnostic capabilities of a function
[0259] In P0, AUROC = 0.915 (0.889-0.936) for the HR-Test, a combination of three proteins, one liver function test, age and sex, as shown in fl-a.
[0260] In P1, the HR test retrieved a significant AUROC = 0.828 (0.803-0.850), while in the paired cases of P2: = 0.812 (CI 0.772-0.846).
[0261] Other data as shown – Determination of functional prognostic ability
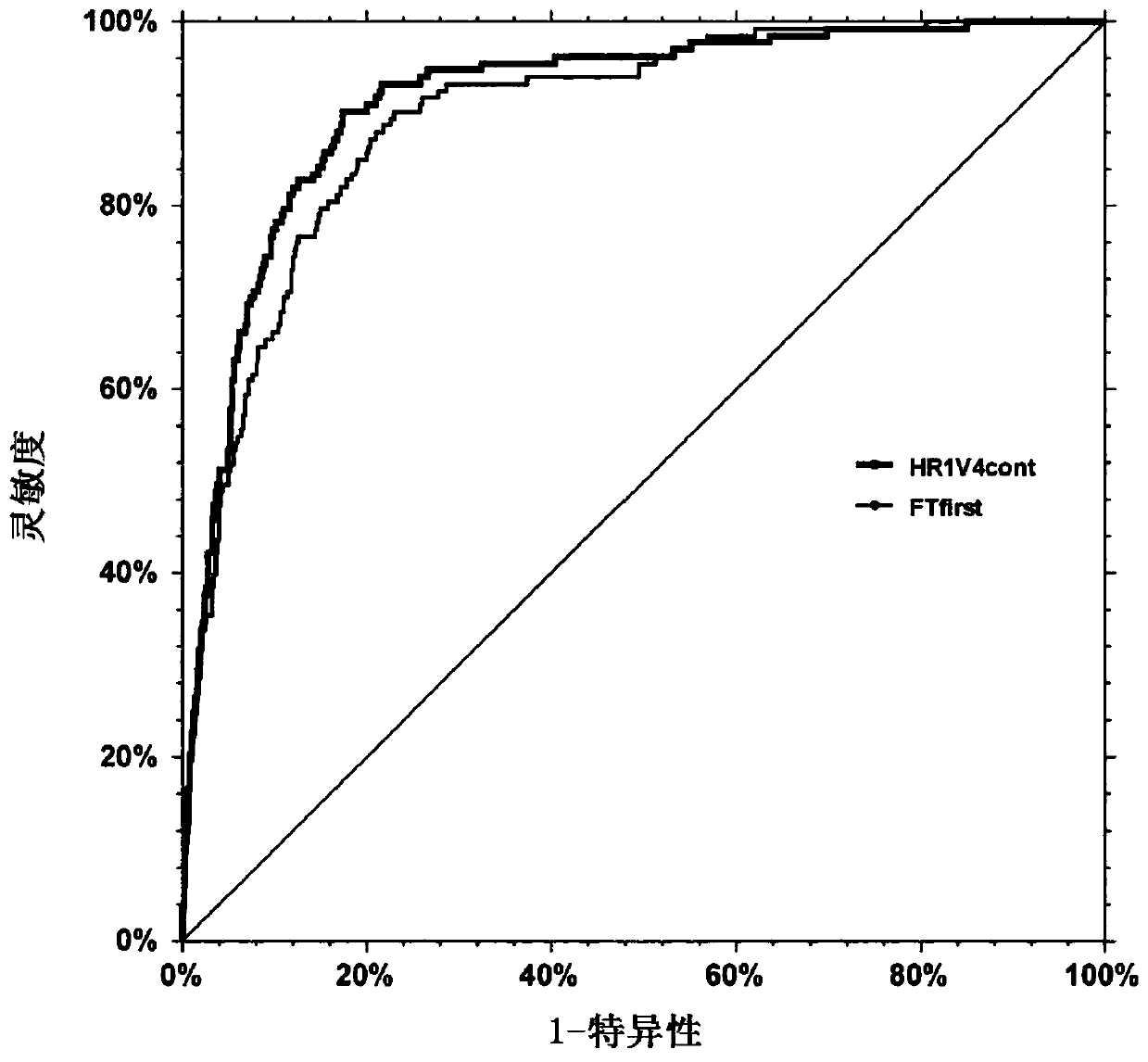
[0262] from figure 1 As can be seen in , a blood test (HR1V4) using the same markers is more sensitive and specific for detecting the presence of primary liver cancer (simultaneous liver cancer) than the Fibrotest test (which actually uses fewer biochemical markers), with a higher The AUROC proves this.
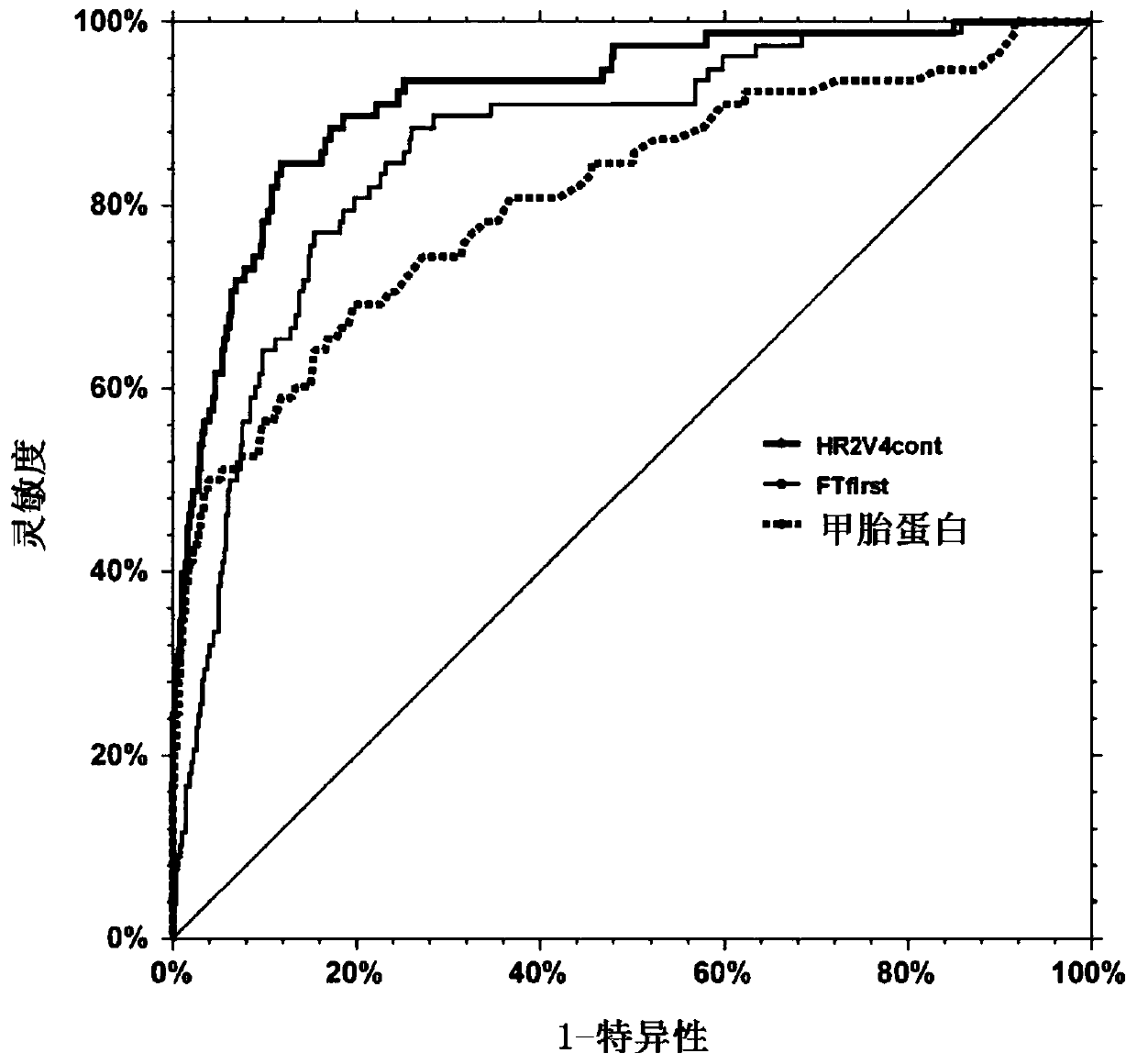
[0263] figure 2 A blood test using the fibrosis markers used in Fibrotest and AFP (a liver cancer marker) was shown to be more sensitive and specific for the presence of primary liver cancer (synch...
Embodiment 3
[0269] Example 3. Development of Cox functions
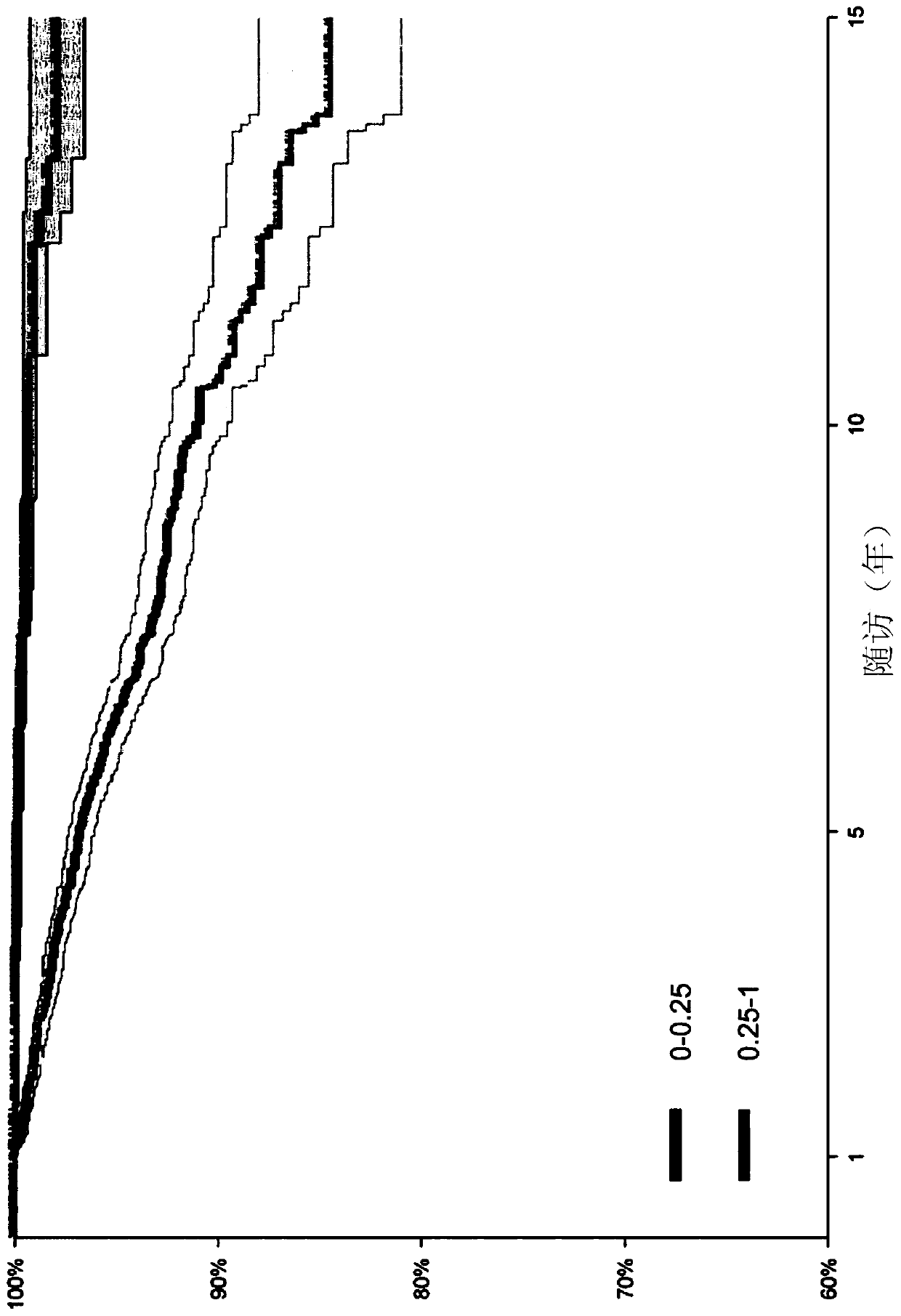
[0270] Specimens prospectively collected by an ongoing group were retrospectively analyzed. To design an early sensitive high-risk test (HR1c-test), hepatoprotective proteins (apolipoprotein A1, haptoglobin) were compared with known risk factors (sex, age, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase), and liver fibrosis marker (α2-macroglobulin) combined in the Cow model. These components were then combined with alpha-fetoprotein, a direct marker of liver cancer, in order to increase specificity (HR2c-test). The primary endpoint was the prediction of HCC by HR1 at 10 years, with HR2 having higher performance than alpha-fetoprotein at 5 years.
[0271] result. A total of 9,892 patients were included, 85.9% without cirrhosis, followed for a median of 5.9 years [IQR; 4.3-9.4]. 221 patients developed liver cancer. The time-dependent area under the ROC curve (AUROC-T) for HR1 to predict cancer was 0.874 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.838 to 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com