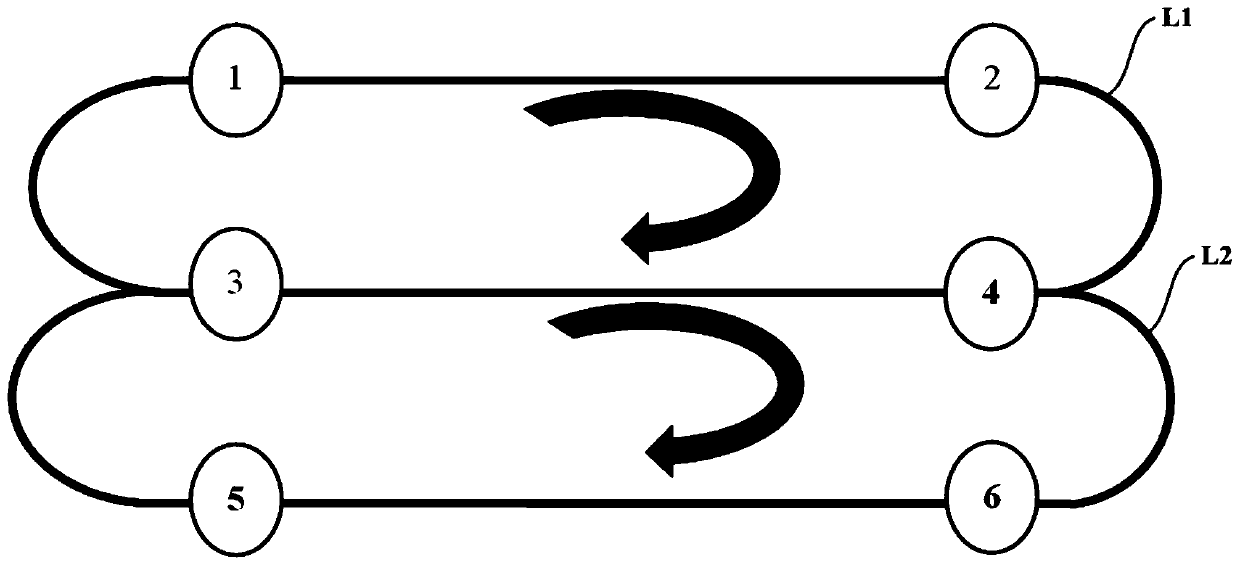
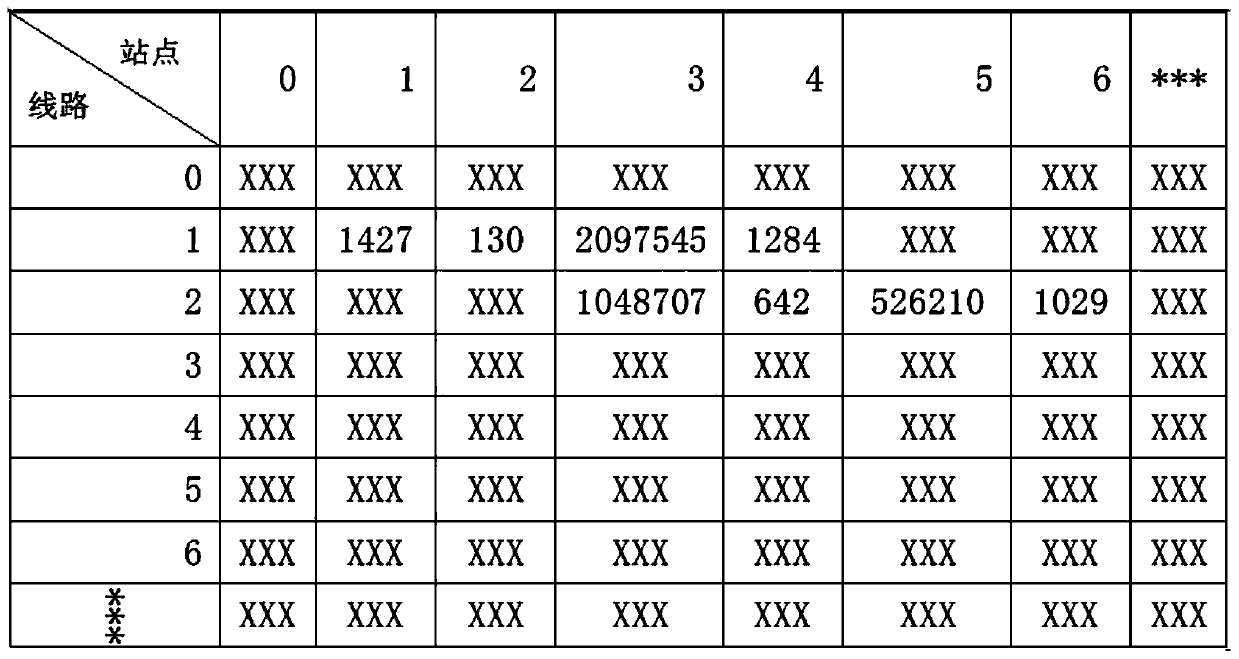
Path planning method of magnetic navigation AGV
A path planning and magnetic navigation technology, applied in the field of magnetic navigation AGV, can solve the problems of reducing on-site debugging time, non-standard design of line sites, need to change source code, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing on-site debugging time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
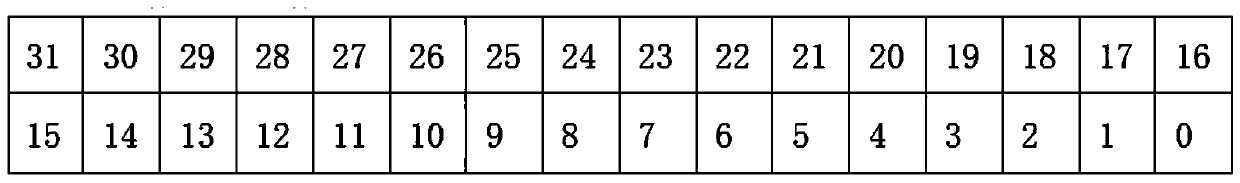
[0111] As an embodiment of the present invention, the data range of the obstacle area group control composition is 0-15, and each data is defined as follows:
[0112] 0 means no action;
[0113] 1 is obstacle area group 1;
[0114] 2 is obstacle area group 2;
[0115] 3 is obstacle area group 3;
[0116] 4 is obstacle area group 4;
[0117] 5 is obstacle area group 5;
[0118] 6 is obstacle area group 6;
[0119] 7 is obstacle area group 7
[0120] 8 is obstacle area group 8
[0121] 9 is obstacle area group 9;
[0122] 10 is obstacle area group 10;
[0123] 11 is obstacle area group 11;
[0124] 12 is obstacle area group 12;
[0125] 13 is obstacle area group 13;
[0126] 14 is obstacle area group 14;
[0127] 15 is obstacle area group 15.
[0128] As an embodiment of the present invention, the data range of the line jump control is 0-254, and each data is defined as follows:
[0129] 0 means no action;
[0130] 1-254 is the corresponding jump line.
[0131] A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com