Wireless Internet-of-Things resource allocation method based on probability transfer deep reinforcement learning
A technology of reinforcement learning and probability transfer, applied in the directions of instruments, character and pattern recognition, electrical components, etc., it can solve the problems that the decision cannot reach the optimal solution, the decision delay increases, and the real-time performance of the system cannot be guaranteed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0065] Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that the preferred embodiments are only for illustrating the present invention, but not for limiting the protection scope of the present invention.
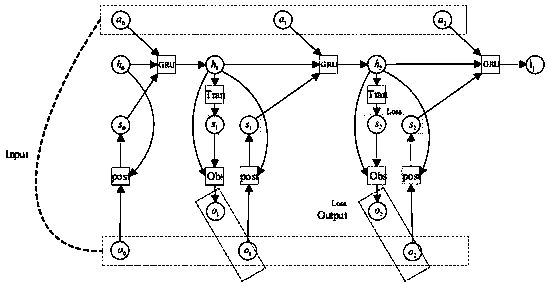
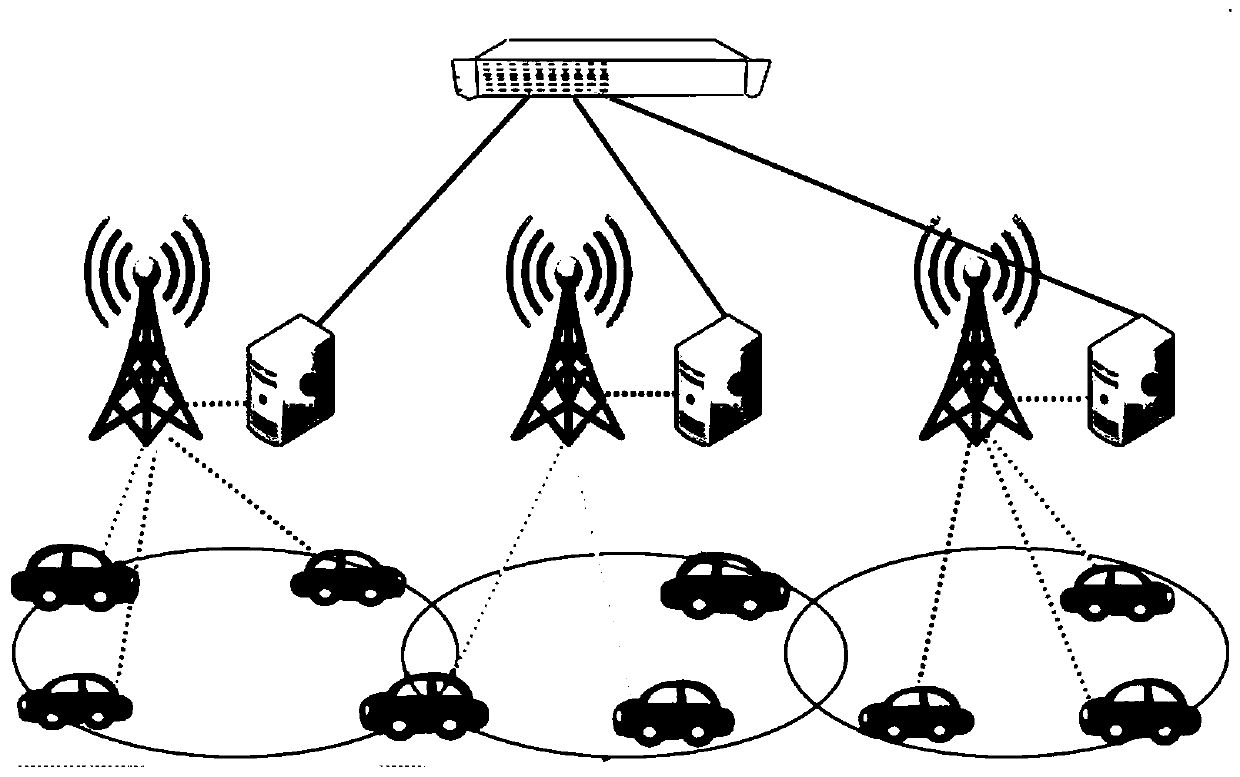
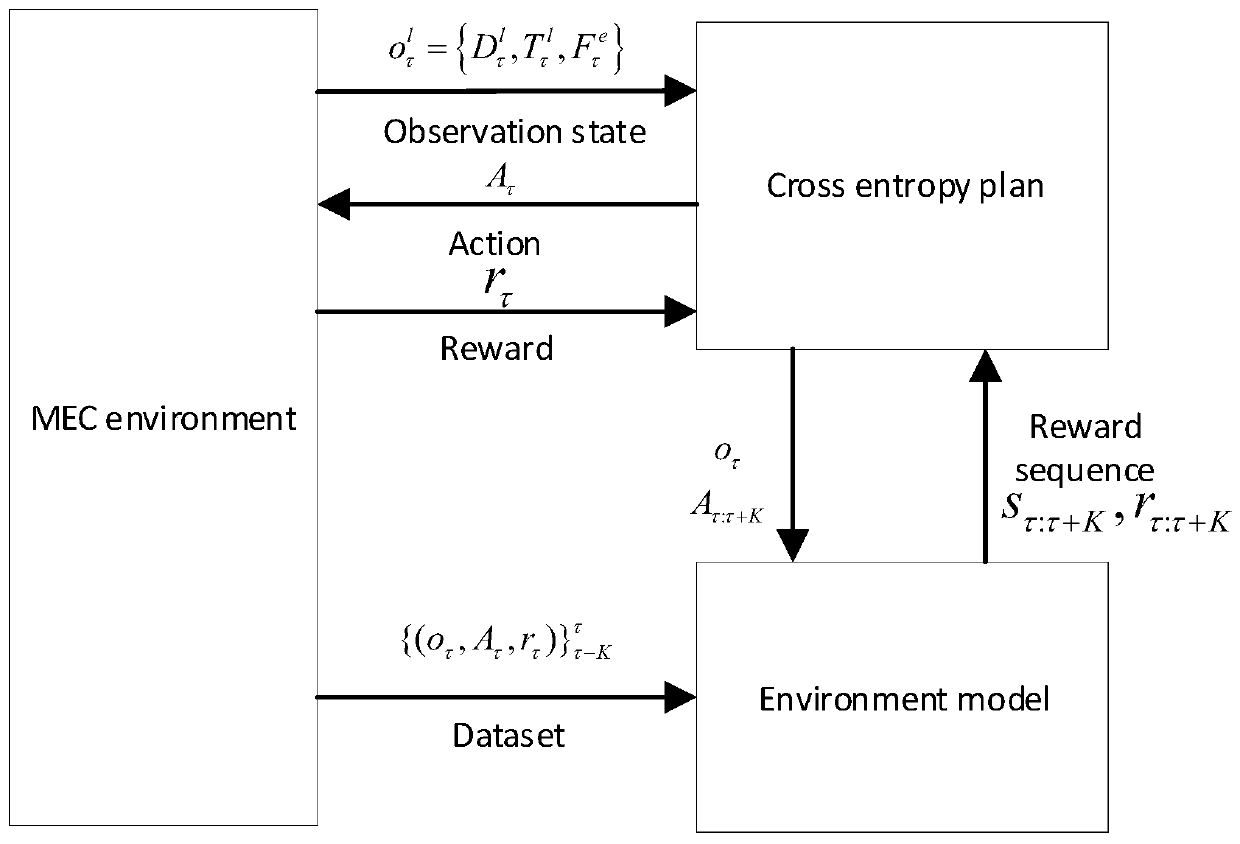
[0066] Such as figure 1 As shown, in this scenario, the task unloading model is considered to be partial unloading, that is, a task is unloaded at a rate of a i (η) Offloaded to the edge server e l , the remaining 1-a i (η) part of the tasks are in the user u at the same time i Local processing is complete. The task computation and transfer models to consider are as follows:
[0067] 1) Local computing model:
[0068]
[0069] 2) Task offloading model:
[0070] The task offloading action for each user is defined as a i ={a i (IP), a i (f e ),a i (η)}, where a i (IP) is defined as user u i The address of the server that provides edge computing services....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com