Orthopedic walker
A technology of orthopedic and receiving parts, applied in the field of orthopedic walking aids, can solve the problem that the device is difficult to adapt to the user's personal needs and size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0099] A. Introduction to Examples and Definitions of Terms
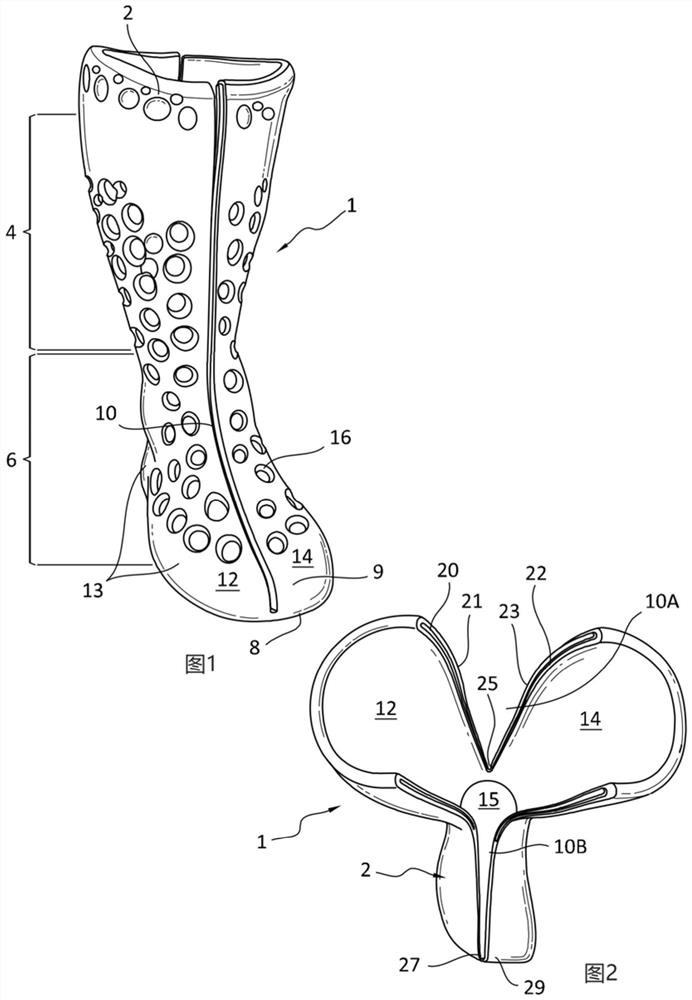
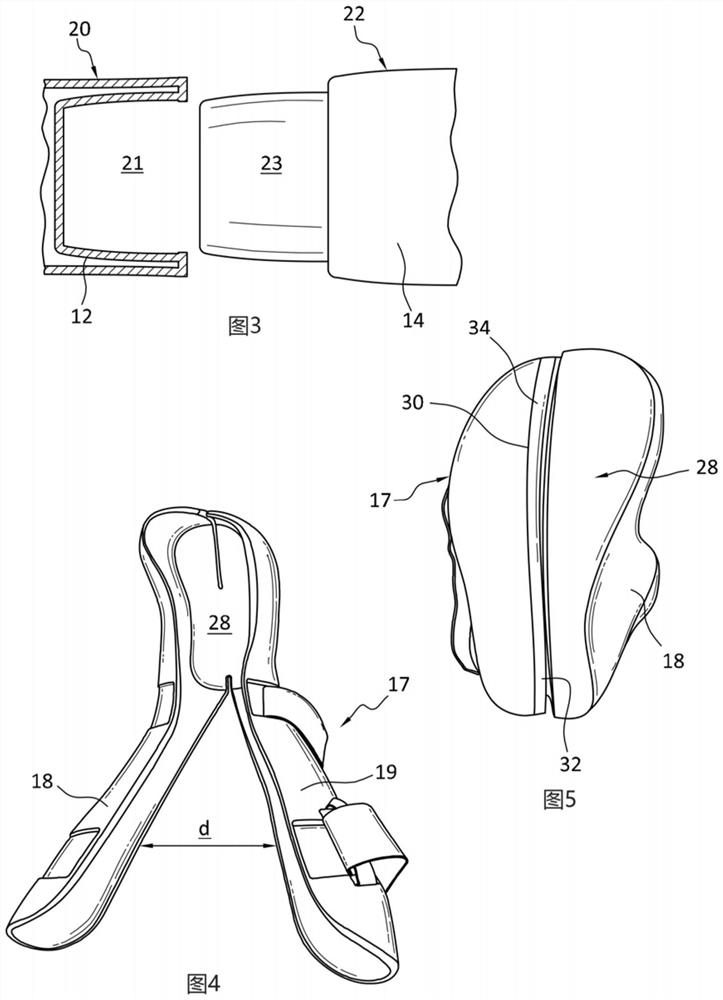
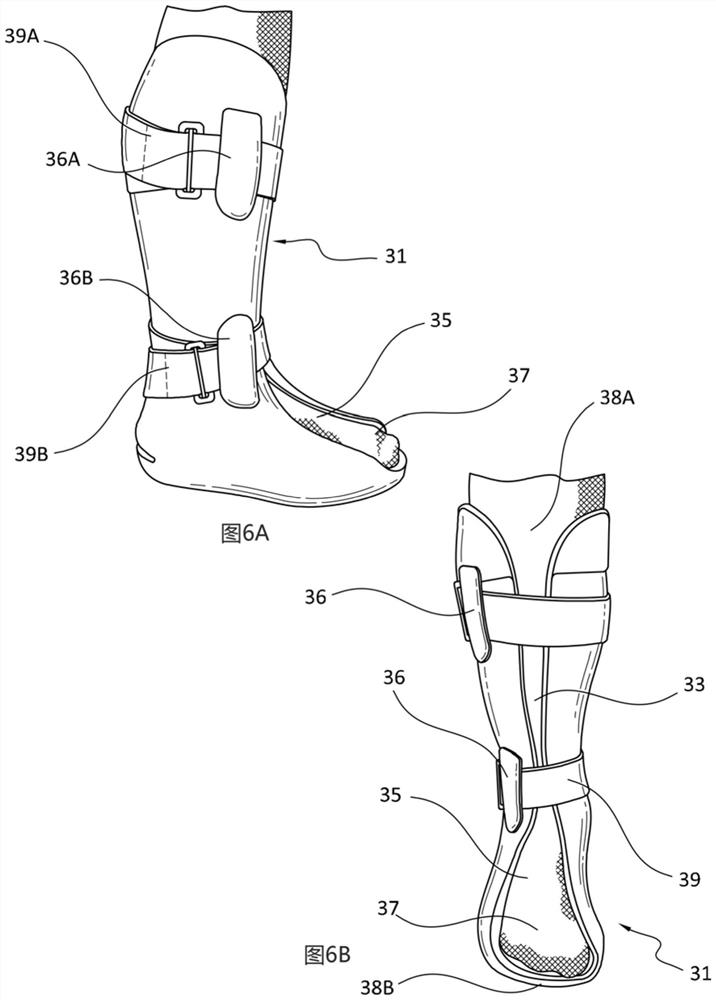
[0100] Embodiments of the orthopedic walking aid are adapted to be donned and doffed relative to a user and configured to stabilize and support a user's body part (eg, the user's lower leg, ankle, and foot).
[0101] The walking aid has a semi-rigid or rigid body material to reduce the complexity, cost and weight of the walking aid. The semi-rigid nature of the main body material provides rigid support when the walking aid is worn on the limb and allows the walking aid to elastically retain or return to its original shape, while the walking aid has some degree of flexibility or elasticity , in order to facilitate regular put on and take off. Unlike conventional orthopedic walking aids, the preferred embodiment of the body of the walking aid described above is constructed of a single material and eliminates the need for different materials of construction. Walking aids that eliminate the need for adhesives and fast...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com