Tobacco bio-enzyme inactivation device and method
A technology for biological enzymes and tobacco materials, applied in the field of tobacco biological enzyme inactivation devices, can solve problems such as inability to adapt to biological enzyme inactivation treatment and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
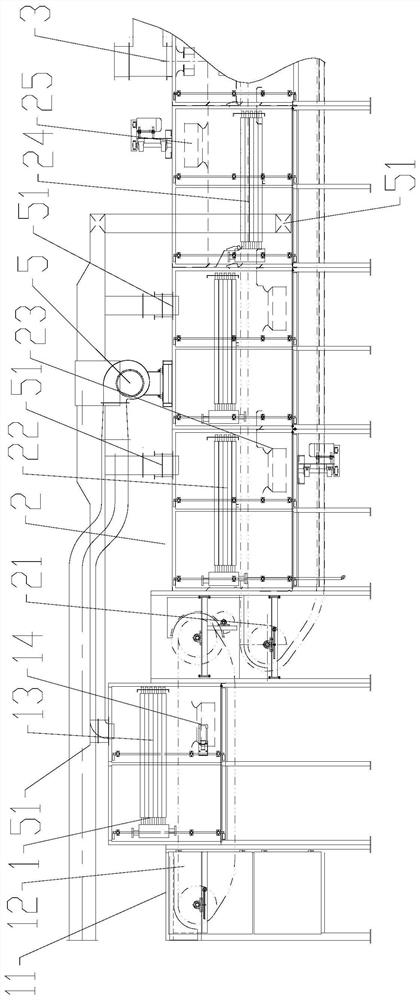
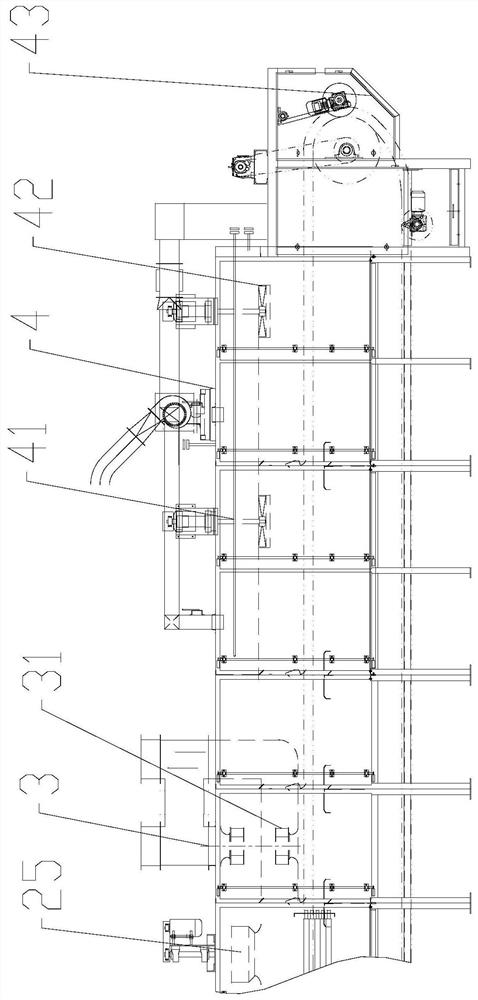
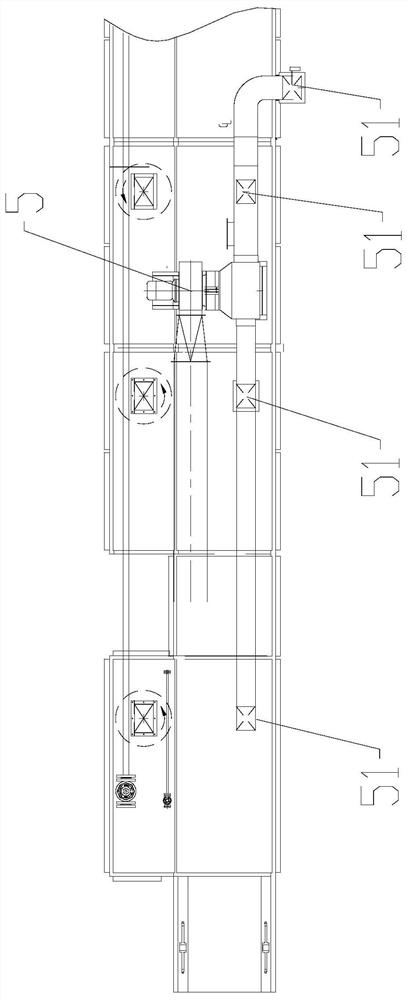
[0044] Such as figure 1 , figure 2As shown, a tobacco biological enzyme inactivation device disclosed in this embodiment includes a casing and an inactivation zone 1, a drying zone 2, a cooling zone 3 and a dampening zone 4 arranged in series in the casing, and the inactivation zone 1 A material inlet 11 is provided, and a material outlet 43 is provided in the resurgence zone 4 . In the prior art, the inactivation of biological enzymes is only achieved through the drying area. Due to the low temperature in the drying area, the complete inactivation of the tobacco material cannot be completed. However, when the temperature in the drying area is increased, the tobacco material will be deactivated for a long time. At high temperature, the quality of the tobacco material is affected and the aroma is lost. In the present invention, the tobacco material is quickly inactivated at high temperature and short-term through the additional inactivation zone 1, which can ensure the compl...
Embodiment 2
[0054] A kind of tobacco bio-enzyme inactivation method disclosed in this embodiment uses a kind of tobacco bio-enzyme inactivation device disclosed in Example 1, comprising the following steps:
[0055] S1 Tobacco material uniformly enters the inactivation zone 1 through the feed port 11, and runs with the first conveyor belt 12 at a speed of 5m / min;
[0056] S2 During the 40s period when the tobacco material passes through the inactivation zone 1, the first fan 14 blows hot air at 110°C from the bottom of the first conveyor belt 12 to the tobacco material at a speed of 8m / s until the temperature of the tobacco material increases to 25-40°C ;
[0057] S3 Tobacco materials are poured from the first conveyor belt 12 in the inactivation zone 1 into the second conveyor belt 21 in the drying zone, and run at a speed of 7m / min along with the second conveyor belt 21, and are sequentially blown up and dehydrated at 80°C The process and the blowing drying and dehydration process are ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] A kind of tobacco bio-enzyme inactivation method disclosed in this embodiment uses a kind of tobacco bio-enzyme inactivation device disclosed in Example 1, comprising the following steps:
[0065] S1 Tobacco material uniformly enters the inactivation zone 1 through the feed port 11, and runs with the first conveyor belt 12 at a speed of 8m / min;
[0066] S2 During the 30s period when the tobacco material passes through the inactivation zone 1, the first fan 14 blows hot air at 125°C from the bottom of the first conveyor belt 12 to the tobacco material at a speed of 10m / s until the temperature of the tobacco material increases to 25-40°C ;
[0067] S3 Tobacco materials are poured from the first conveyor belt 12 in the inactivation zone into the second conveyor belt 21 in the drying zone, and run with the second conveyor belt 21 at a speed of 5m / min, and carry out the upward blowing drying and dehydration process at 60°C in sequence And blow drying and dehydration process...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com