Power grid probabilistic load flow analysis method based on generalized semi-invariants and maximum entropy method
A semi-invariant, probabilistic power flow technology, applied to AC networks, electrical components, circuit devices of the same frequency with different sources, etc., can solve the problems of system voltage, frequency over-limit risk level increase, and randomness of new energy sources. , to achieve the effect of optimal scheduling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0075] The present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
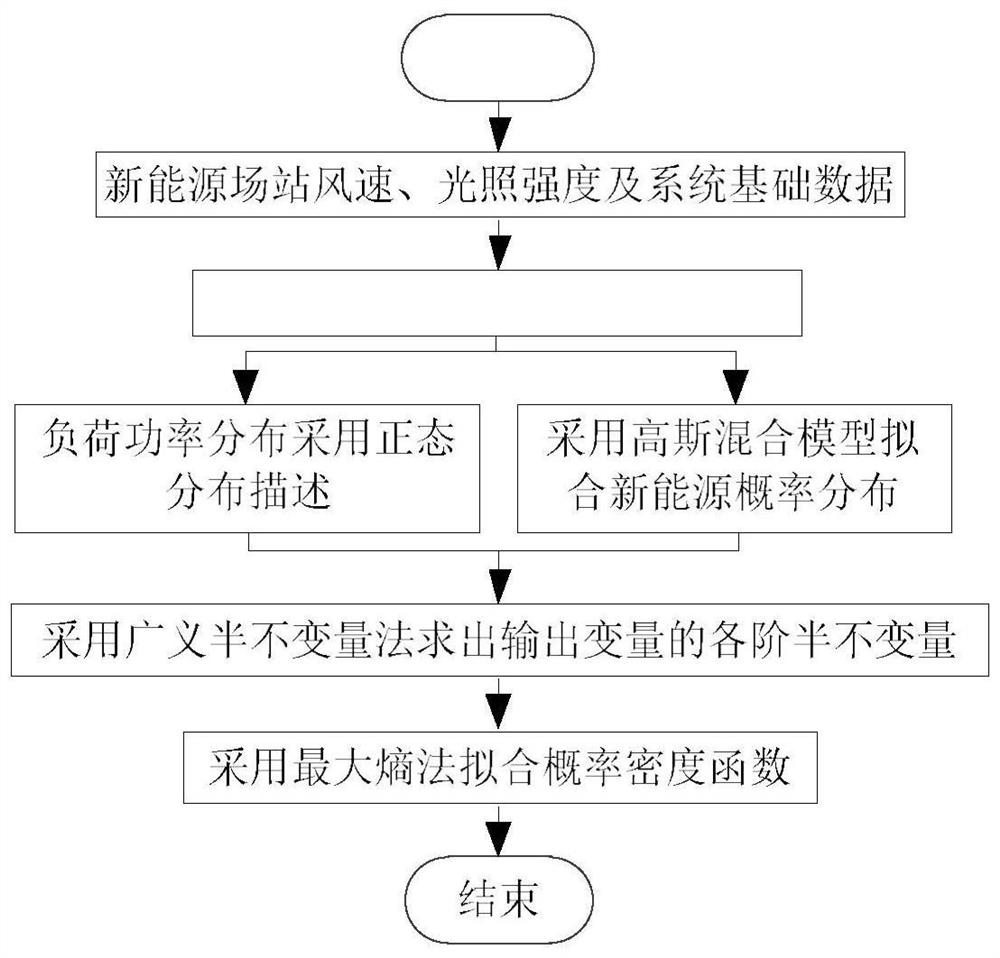
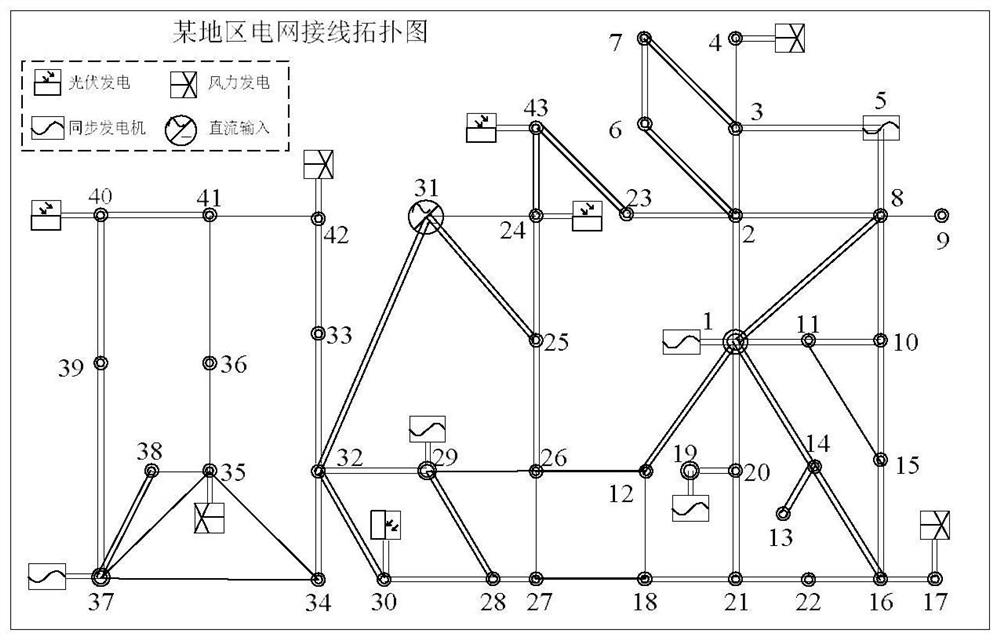
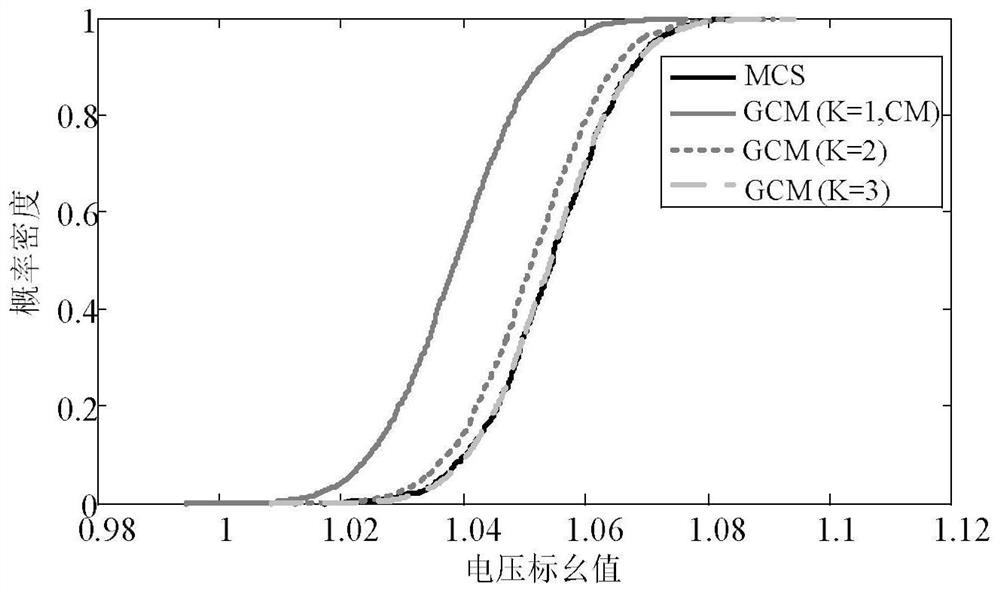
[0076] In this embodiment, the method of the present invention is applied to the power system, such as figure 1 As shown, the specific calculation method steps are as follows:
[0077] S1: Establish a power system power flow model considering frequency, including the following models:
[0078] The primary frequency regulation characteristics of the generator can be expressed as:
[0079] P Gi =-K Gi (f-f N ) i=1,2,...,g
[0080] In the formula: P Gi is the active power of the i-th generator; K Gi is the primary frequency modulation coefficient of the i-th generator set; f N is the rated frequency of the system under normal conditions; f is the system frequency.
[0081] The primary frequency regulation characteristics of grid load can be expressed as:
[0082] P Di =P DNi +K Di (f-f N )
[0083] In the formula: P Di and P DNi R...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com