Processing method for making sandalwood yellow tea from tender tip leaves of symplocos paniculata
A processing method, the technology of white sandalwood leaves, is applied in the field of processing sandalwood yellow tea from the young shoots of white sandalwood, which can solve the problems of insufficient sandalwood aroma, sweet fragrance, failure to control the temperature, and color difference of sandalwood yellow tea soup, etc., to achieve the taste Good, convenient processing and operation, strong taste and sweet aftertaste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
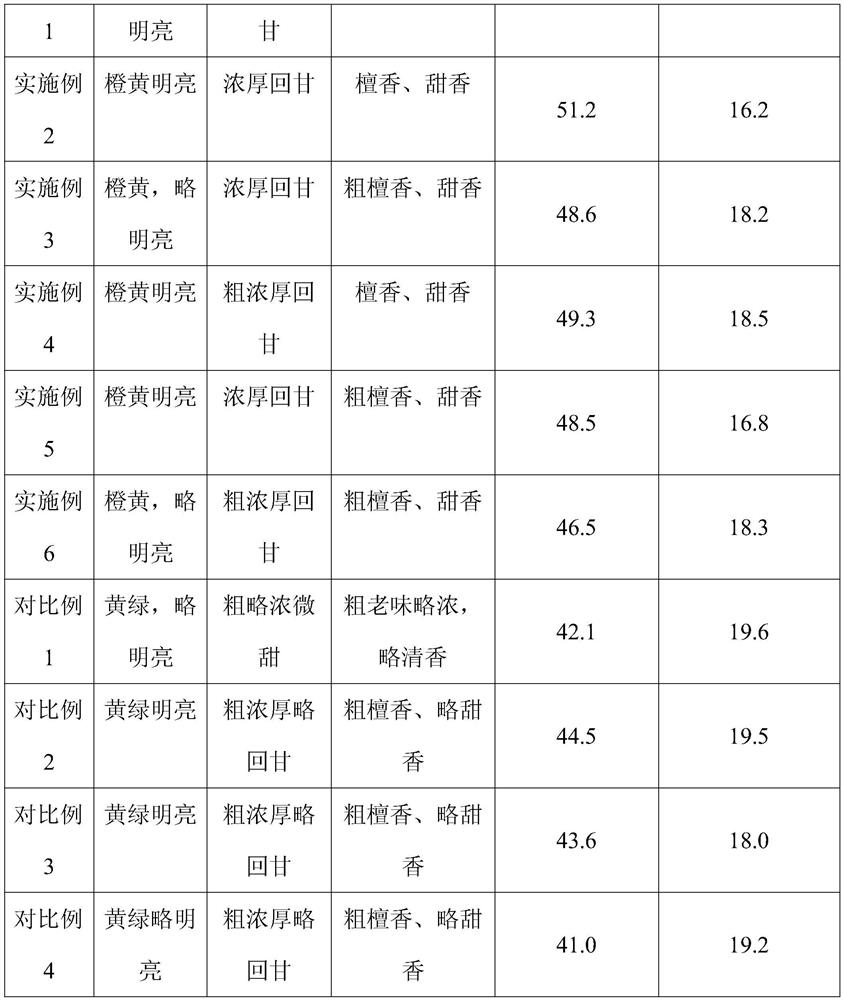
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054]A kind of processing method of making sandalwood yellow tea from white sandalwood young tip leaf, comprises the following steps:
[0055] S1. Select raw materials of white sandalwood tender leaves, and cool them for the first time: the raw materials of white sandalwood leaves are fresh green leaves on young shoots. It is better to have one bud and one leaf or one bud and two leaves. Put it into the dustpan and spread it to cool, the thickness of the spread is 0.4cm, and the cool time is 30min;
[0056] S2, withering for the first time: withering the young tip leaves of white sandalwood after cooling for the first time in step S1 at a temperature of 25° C. for 13 hours until the water loss rate reaches 30%;
[0057] S3, greening: put the young white sandalwood leaves withered in step S2 into a pot with a temperature of 252-277° C. and stir-fry for 7 minutes to turn them green until the leaves are slightly prickly to the hands, and the scent of green grass subsides;
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0071] A kind of processing method of making sandalwood yellow tea from white sandalwood young tip leaf, comprises the following steps:
[0072] S1. Select raw materials of white sandalwood tender leaves, and cool them for the first time: the raw materials of white sandalwood leaves are fresh green leaves on young shoots. It is better to have one bud and one leaf or one bud and two leaves. Put it into the dustpan and spread it to cool, the thickness of the spread is 0.5cm, and the cooling time is 25min;
[0073] S2, withering for the first time: withering the young tip leaves of white sandalwood after cooling for the first time in step S1 at a temperature of 26° C. for 12 hours until the water loss rate reaches 30%;
[0074] S3, greening: put the white sandalwood young shoot leaves withered in step S2 into a pot with a temperature of 250-280° C. and stir-fry for 5 minutes to turn them green until the leaves are slightly prickly to the hands, and the scent of green grass subsid...
Embodiment 3
[0088] A kind of processing method of making sandalwood yellow tea from white sandalwood young tip leaf, comprises the following steps:
[0089] S1. Select raw materials of white sandalwood leaves and cool them for the first time: the raw materials of white sandalwood leaves are fresh green leaves on the young shoots. It is better to have one bud and one leaf or one bud and two leaves. Put it on the dustpan and spread it to cool, the thickness of the spread is 0.6cm, and the cool time is 30min;
[0090] S2, withering for the first time: withering the young tip leaves of white sandalwood after cooling for the first time in step S1 at a temperature of 25° C. for 12 hours until the water loss rate reaches 31%;
[0091] S3, greening: put the young white sandalwood leaves withered in step S2 into a pot with a temperature of 260-280° C. and stir-fry for 6 minutes to turn them green until the leaves are slightly prickly to the hands, and the scent of green grass subsides;
[0092] S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com