Rail hand-cranking sightseeing vehicle
A technology for sightseeing cars and tracks, applied in the field of rail sightseeing cars, can solve the problems of lack of tourist fun and inconvenience in electricity consumption, and achieve the effects of avoiding excessive speed, improving efficiency and obvious deceleration effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
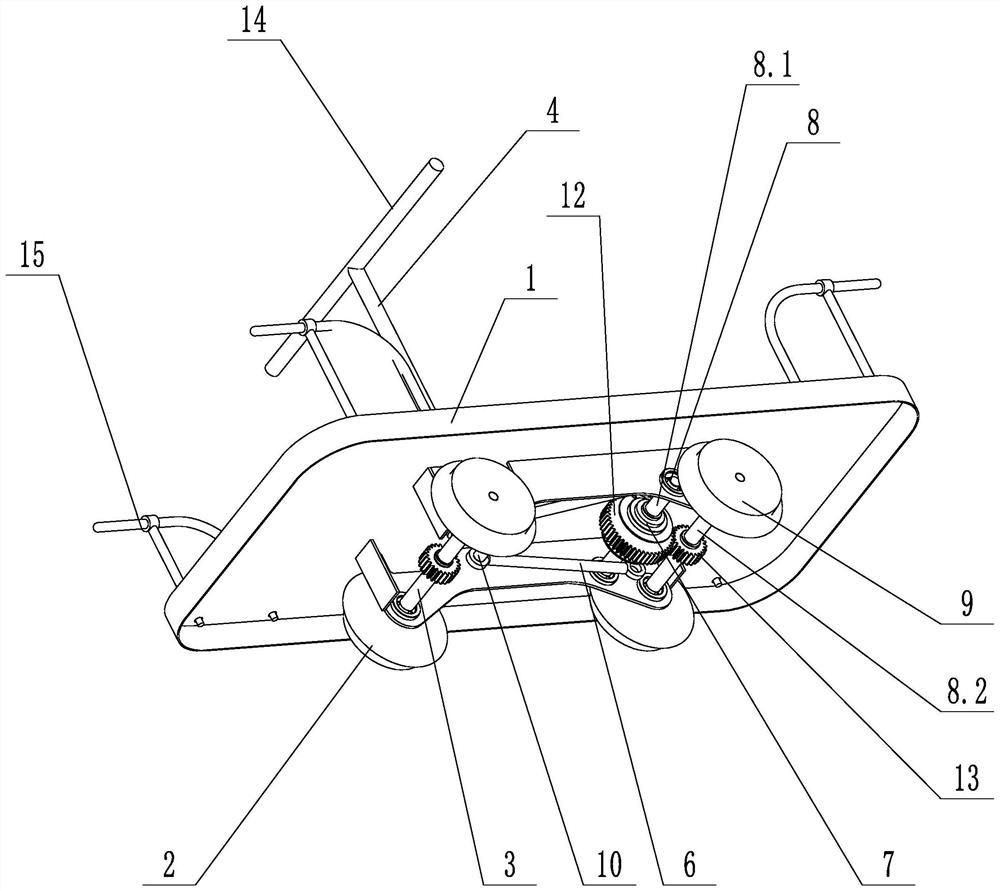
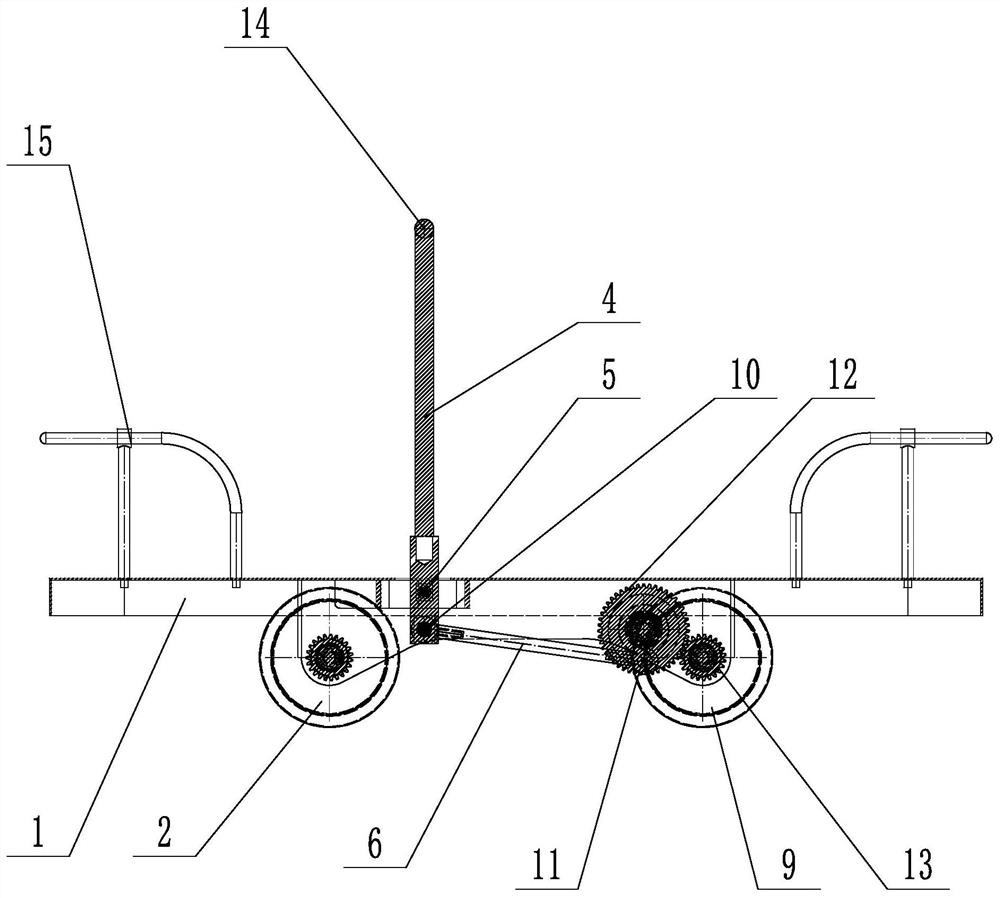
[0027] like figure 1 and figure 2 shown ( figure 1 The second pin shaft 11 is not shown), a rail hand sightseeing car, including a platen 1, a front wheel 2, a front wheel shaft 3, a rocker 4, a first rotating shaft 5, a connecting rod 6, a ratchet mechanism 7, a Second rotating shaft 8, rear wheel 9, driving gear 12 and driven gear 13, the diameter of driving gear 12 is greater than driven gear 13; , the rear wheel shaft 8.2 is rotationally connected with the platen 1; the driving gear 12 and the ratchet mechanism 7 are fixed on the transition shaft 8.1, the rear wheel 9 and the driven gear 13 are fixed on the rear wheel shaft 8.2, and the driving gear 12 meshes with the driven gear 13; The wheel 2 is rotationally connected with the platen 1 through the front axle 3, the rocking bar 4 is rotationally connected with the platen 1 through the first rotating shaft 5, the upper end of the rocking bar 4 is provided with a handle 14, and the lower end of the rocking bar 4 is conn...
Embodiment 2
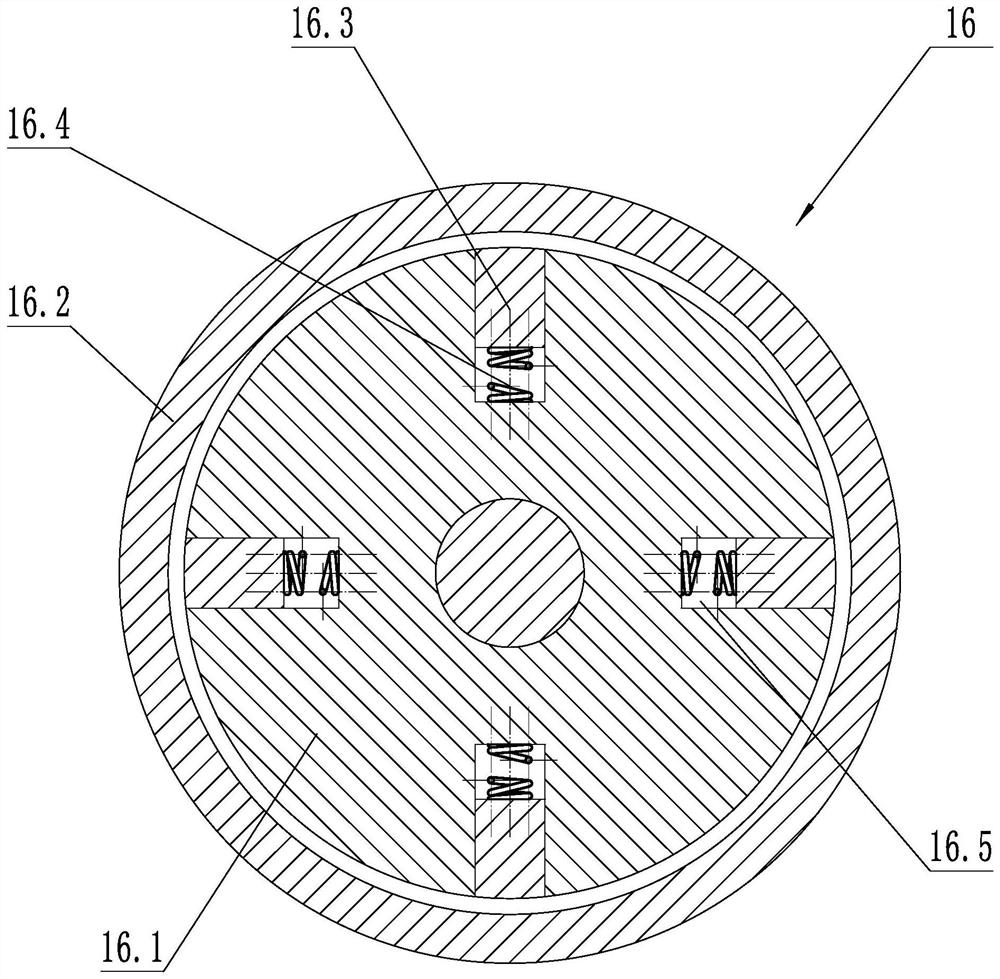
[0030] like image 3 As shown, on the basis of Embodiment 1, a speed-limiting mechanism 16 is also included. The speed-limiting mechanism 16 includes a rotating wheel 16.1, a friction wheel cover 16.2, a friction block 16.3 and a telescopic spring 16.4, and the rotating wheel 16.1 is coaxially fixed with the front wheel shaft 3 , the front axle 3 is provided with a chute 16.5 arranged radially, the friction block 16.3 is slidably connected with the rotating wheel 16.1 through the chute 16.5, one end of the telescopic spring 16.4 is connected with the friction block 16.3, and the other end of the telescopic spring 16.4 is connected with the rotating wheel 16.1 The friction wheel cover 16.2 is fixed to the platen 1, and the friction wheel cover 16.2 is coaxially arranged with the rotating wheel 16.1, and the friction block 16.3 contacts with the inner side wall of the friction wheel cover 16.2 when extending out.
[0031]The speed limiting mechanism 16 can play a very good role ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] like Figure 4 As shown, on the basis of Embodiment 1, a brake mechanism 17 is also included. The brake mechanism 17 includes a brake pad 17.1, a connecting block 17.2, a brake spring 17.3, a brake disc 17.4, a connecting rod 17.5 and a hand brake lever 17.6; The plate 1 is connected in rotation, the hand brake lever 17.6 is fixed to the upper end of the connecting rod 17.5, the brake disc 17.4 is fixed to the lower end of the connecting rod 17.5, the connecting block 17.2 is slidingly connected to the platen 1, one end of the connecting block 17.2 is fixed to the brake pad 17.1, and the connecting block The other end of 17.2 is in contact with brake disc 17.4; the section of brake disc 17.4 is oval; one end of brake spring 17.3 is connected with platen 1, and the other end of brake spring 17.3 is connected with connecting block 17.2. The number of the brake pads 17.1, connecting blocks 17.2 and brake springs 17.3 is 2 respectively, and the brake pads 17.1, connecting b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com