Spatial autocorrelation clustering method for remote correlation mode
A technology of spatial autocorrelation and correlation pattern, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, data processing applications, etc., to achieve the effect of facilitating horizontal comparison
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
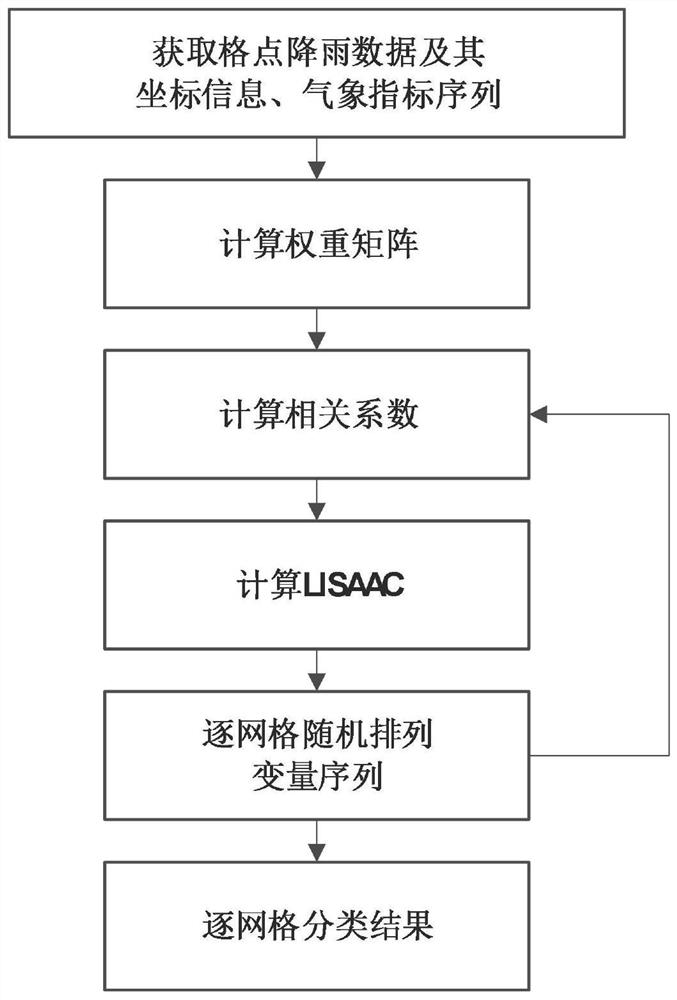
[0051] Such as figure 1 As shown, a spatial autocorrelation clustering method for teleconnection mode, including the following steps:
[0052] S1: Obtain the spatial grid coordinate information of the research area, and calculate the spatial weight matrix according to the coordinate information;
[0053] S2: Obtain grid-scale rainfall data in the study area and large-scale meteorological factor indicators in the same time range, and obtain the time series of rainfall-meteorological indicators;
[0054] S3: According to the obtained time series of rainfall-meteorological indicators, calculate the correlation coefficient r of rainfall-meteorological indicators grid by grid;
[0055] S4: Calculate the grid-by-grid spatial autocorrelation local index LISAAC according to the correlation coefficient r and the spatial weight matrix;
[0056] S5: Rearrange the time series of rainfall and meteorological indicators in step S2 to obtain a new time series of rainfall-meteorological indi...
Embodiment 2
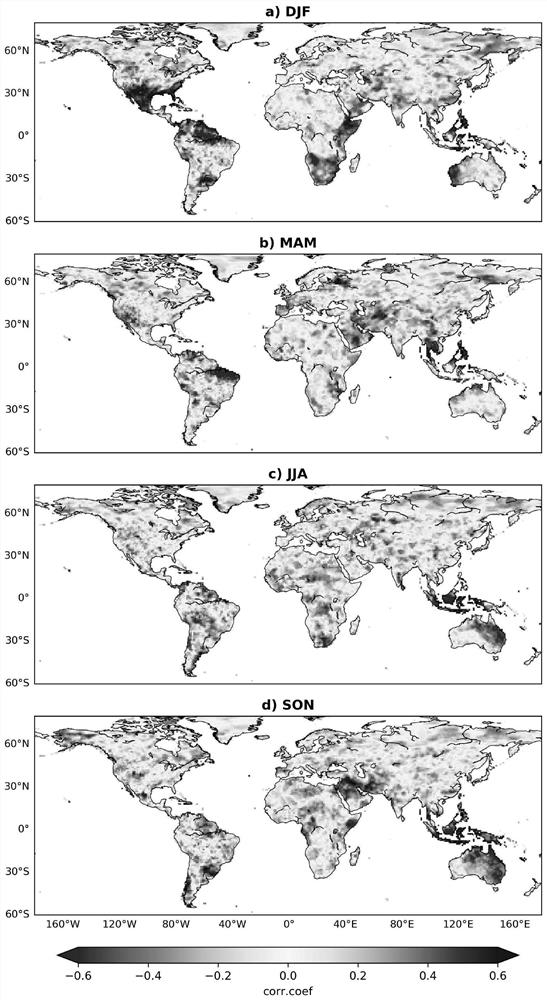
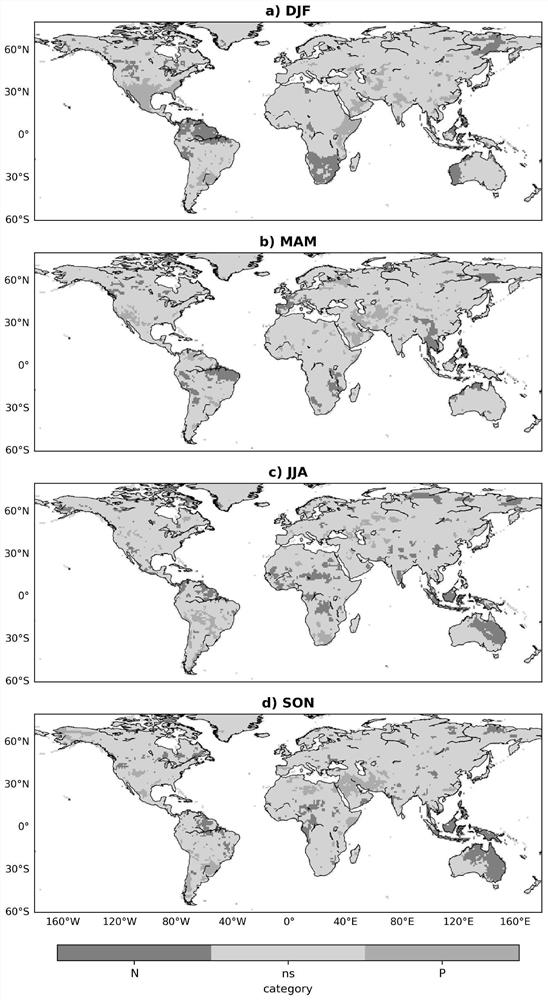
[0085] More specifically, on the basis of Example 1, this example illustrates the effect of the method through experiments, using the US Climate Prediction Center (CPC) 1982-2010 global seasonal grid precipitation data and Take the indicator as an example, calculate the spatial autocorrelation clustering of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and the global seasonal precipitation teleconnection model, take the significance level α as 0.10 as an example, calculate LISAAC, and compare the grid without considering the spatial autocorrelation Significance classification results and results calculated using local Moran indices.
[0086] Such as figure 2 as shown, figure 2 The spatial distribution of teleconnection coefficients in the northern hemisphere in winter, spring, summer and autumn (denoted as DJF, MAM, JJA and SON, respectively) is given. If the spatial autocorrelation relationship is not considered, and only the significance of the correlation coefficient of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com