Method and system for identifying water quality hidden danger points of multi-water-source water supply pipe network
A technology for water supply pipe network and hidden danger points, which is applied in the field of identifying water quality hidden danger points of multi-water source water supply pipe network, and can solve problems such as the inability to accurately determine the location of water quality hidden danger points.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
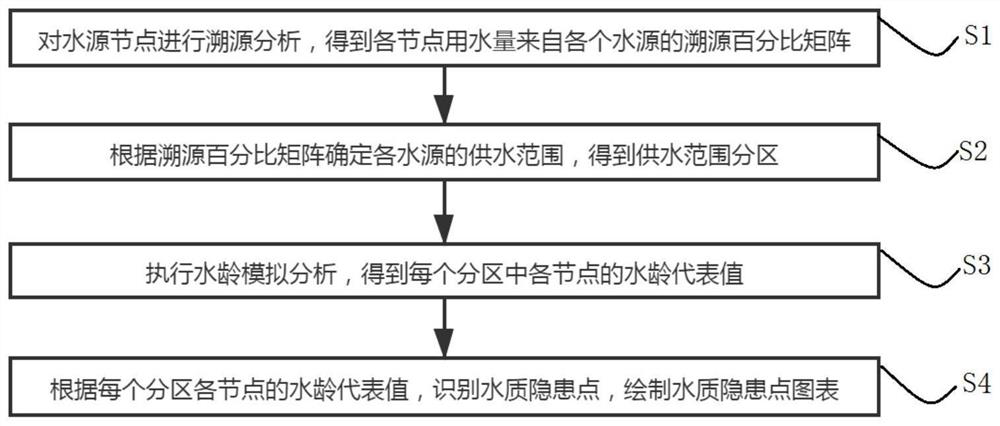
[0061] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for identifying hidden dangers of water quality in a multi-source water supply network includes the following steps:
[0062] S1: Conduct traceability analysis on the water source nodes, and obtain the traceability percentage matrix of the water consumption of each node from each water source;
[0063] S2: Determine the water supply range of each water source according to the traceability percentage matrix, and obtain the division of the water supply range;
[0064] S3: Perform water age simulation analysis to obtain the water age representative value of each node in each partition;
[0065] S4: According to the water age representative value of each node in each zone, identify water quality hidden danger points, and draw a chart of water quality hidden danger points.
[0066] In the above scheme, the method traces the source of the water supply network, and divides the water supply range of each water source by analyzing the tracea...
Embodiment 2
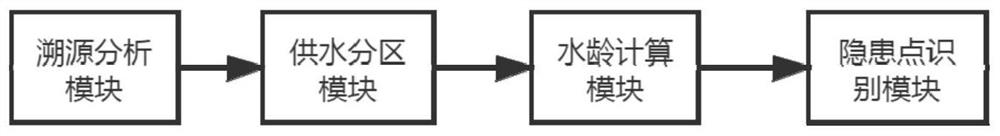
[0090] Such as figure 2 As shown, a system for identifying hidden dangers of water quality in a multi-source water supply network uses a method for identifying hidden dangers of water quality in a multi-source water supply network, including a traceability analysis module, a water supply zoning module, a water age calculation module, and identification of hidden dangers module; the output end of the traceability analysis module is electrically connected to the input end of the water supply partition module, the output end of the water supply partition module is electrically connected to the input end of the water age calculation module, and the output end of the water age calculation module is connected to the The input terminals of the hidden danger point identification module are electrically connected.
[0091] The traceability analysis module includes the following algorithms:
[0092] S11: Import the water supply network model to be analyzed into EPANET software, and ch...
Embodiment 3
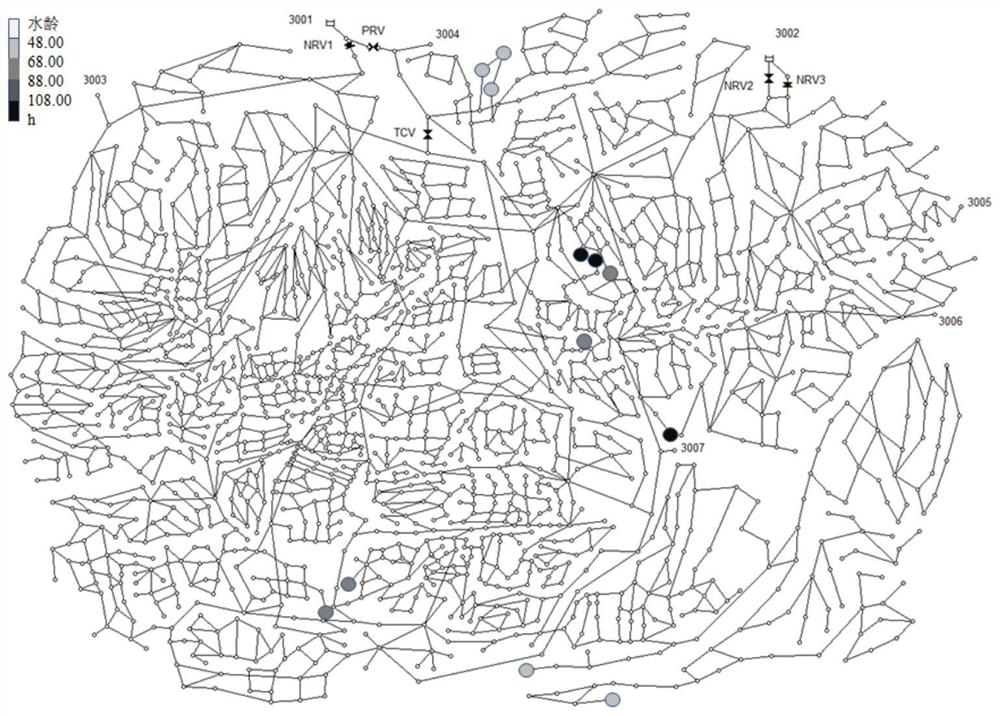
[0110] Such as image 3 As shown, the specific implementation effect of the present invention is illustrated by taking the water supply network of Exeter City, England as an example. There are 1,837 water demand nodes, 2,507 pipe sections, and 7 water sources in the pipeline network. The total water supply is 281,300 tons / day. The default simulation duration of the pipeline network is 24 hours. The analysis of the hidden water quality points of the pipe network includes the following steps:
[0111] Step 1: First, import the water supply network model file of Exeter City into EPANET2.2 software, and change the node water demand simulation method to pressure-driven analysis. Secondly, set the type of water quality simulation to Trace, and set the total simulation time to 168 hours. Then, set the water source node numbered 3001 as the target node for tracking, and obtain the percentage of available water in each node in the pipe network from the water source 3001 when the wate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com