Molecular marker for identifying subspecies of northern sea track of sika deer, identification method and application
A technology of molecular markers and sika deer, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, measurement/inspection of microorganisms, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems that there is no molecular marker identification method for sika deer subspecies, and achieve low cost and low cost. Cost and time saving effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1. Acquisition of specific SNP markers for identifying the Hokkaido subspecies of sika deer
[0024] 1. Screening of specific SNP loci of sika deer Hokkaido subspecies
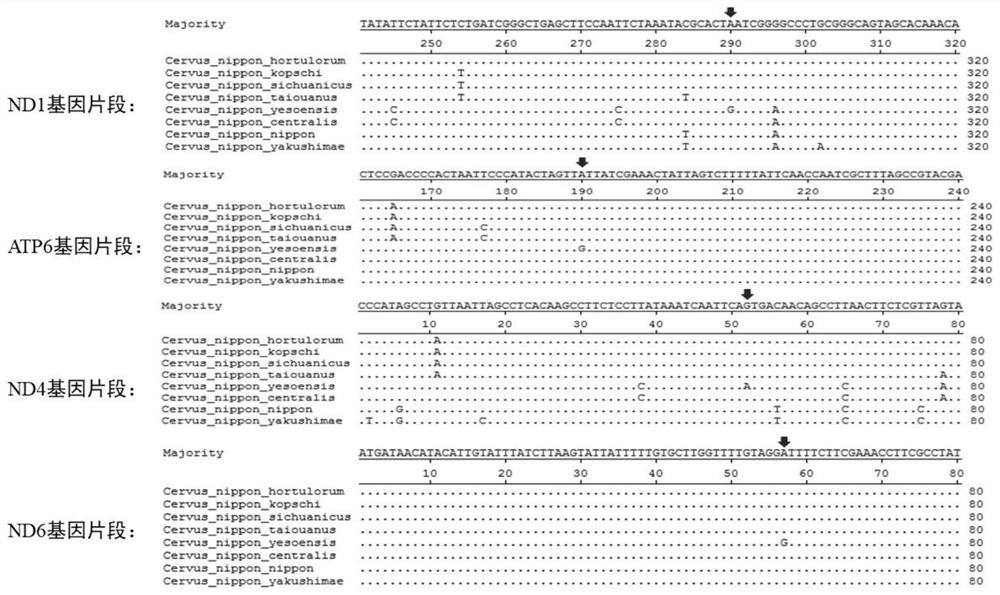
[0025] Combining the mtDNA sequences of different subspecies samples of sika deer, such as the Northeast subspecies, Sichuan subspecies, South China subspecies, Taiwan subspecies, Hokkaido subspecies, Honshu subspecies, nominated subspecies and Yakushima subspecies, were compared by Mega6.0. For the analysis, the screening is mainly aimed at the loci shared by the same subspecies and specific to other subspecies, and 4 differential SNP loci are screened, such as figure 1 shown. The ND1 gene fragment, ATP6 gene fragment, ND4 gene fragment and ND6 gene fragment were intercepted with Mega6.0, and the sequence length was about 500bp, which was used to design identification primers.
[0026] 2. Primer design
[0027] Based on the intercepted target gene fragments, primers for identification were ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2, the establishment of the method for identifying sika deer Hokkaido subspecies
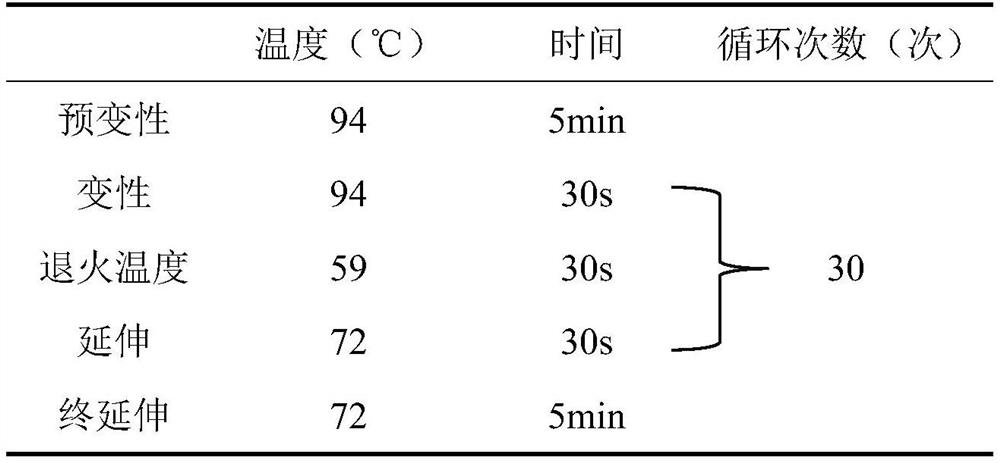
[0042] According to the primer pair shown in the above SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.8, PCR experiments were carried out to establish a method for identifying the Hokkaido subspecies and other subspecies of sika deer. The PCR amplification conditions are shown in Table 2.
[0043] Table 2 PCR amplification conditions
[0044]
[0045] The PCR reaction system is shown in Table 3.
[0046] Table 3 PCR system
[0047]
[0048] The PCR amplification process is: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes; 30 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 59°C for 30 sec, and extension at 72°C for 30 sec; extension at 72°C for 5 min, and storage at 4°C.
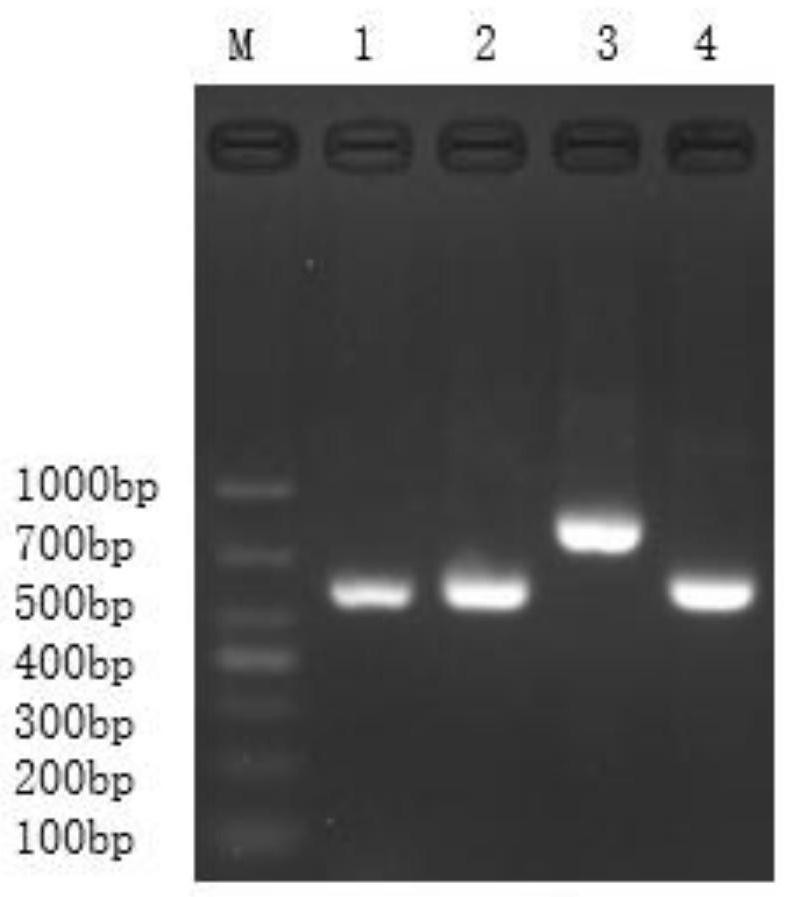
[0049] PCR results such as figure 2 , the PCR results of primer pair 1, primer pair 2, primer pair 3 and primer pair 4 have single and bright electrophoresis bands, and the experimental results show that the present invention...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3. The specific application of the method for identifying the Hokkaido subspecies of sika deer and other subspecies of the present invention
[0051] A total of 100 samples were selected from China and Japan, and genomic DNA was extracted respectively. Experimenter A randomly mixed these samples and renumbered them. Experimenter B used the primers designed by the present invention to carry out PCR amplification on these samples, and the amplified product Sent to Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. for sequencing. View the sequencing peak map through Bioedit7.0, the peak and valley of the sequencing result map are separated, there is no overlap, and there is no misreading, indicating that the sequencing result is reliable. The sequences were aligned using Mega6.0, and the bases of the specific SNP sites of the Hokkaido subspecies of sika deer were used as the basis for determination.
[0052] It is judged according to the mtDNA-specific SNP molecular m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com