Orbital parameter and constellation configuration design method based on omnibearing angle observation
A technology of orbital parameters and omnidirectional angle, applied in the field of radar, which can solve the problems of shortening the minimum omnidirectional angle observation time, limited observation azimuth span, and inability to monitor.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
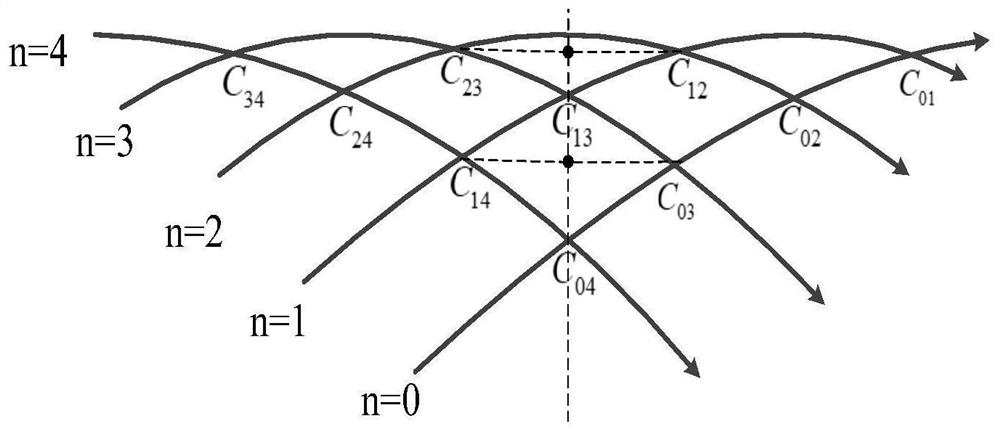
[0051] The invention discloses an orbit parameter and constellation configuration design method based on omnidirectional observation, and relates to the number of low-orbit satellite orbits, omnidirectional observation units, omnidirectional observation unit periodicity, and omnidirectional observation unit coverage .
[0052] Satellite orbital elements:
[0053] When describing satellite orbit parameters, a group of integral constants with clear meaning and independent of each other are often selected to represent the basic quantities of the orbit, which are called orbital elements. The orbital elements commonly used in elliptical orbits are six numbers σ=(a, e, i, Ω, ω, τ), where a is the semi-major axis of the orbit, indicating the size of the orbit; e is the eccentricity, indicating the shape of the orbit; i is the orbital inclination, Ω is the right ascension of the ascending node, i and Ω indicate the orientation of the orbital plane in space; ω is the argument of perig...
Embodiment 2
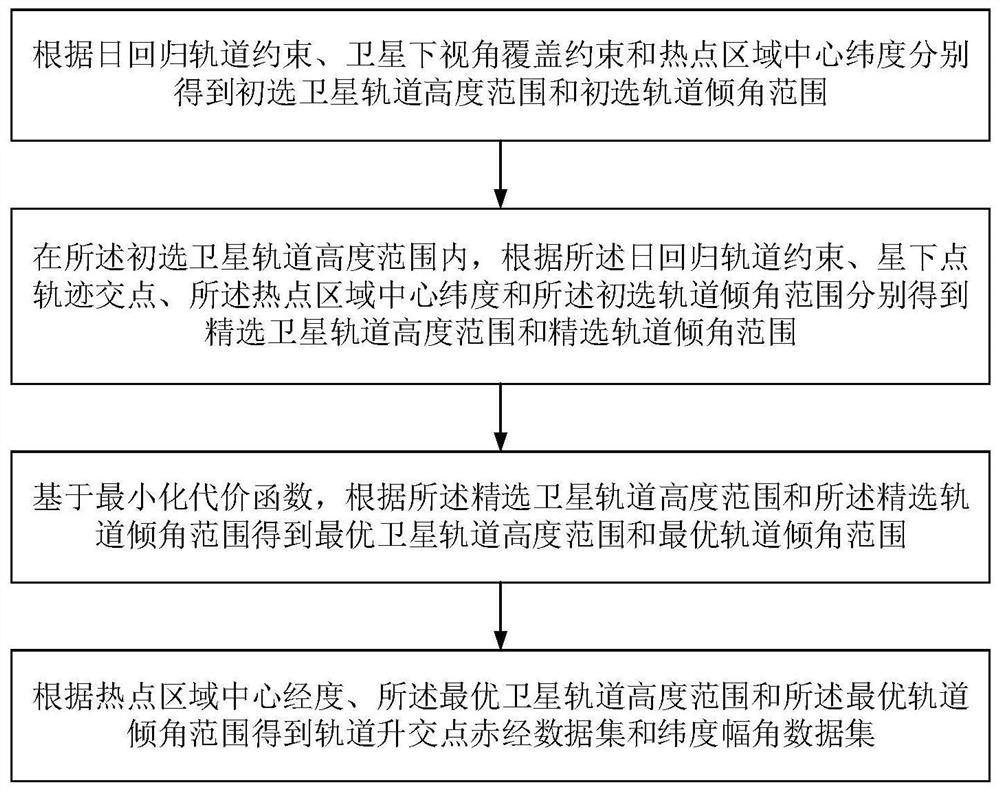
[0148] On the basis of Example 1, please refer to figure 1 , figure 1 It is a flowchart of a method for designing orbit parameters and constellation configurations based on omnidirectional observation provided by an embodiment of the present invention. A method for designing orbital parameters and constellation configurations based on omnidirectional observations, comprising:
[0149] Step 1. Obtain the altitude range of the primary satellite orbit and the inclination range of the primary orbit according to the orbit constraint of the diurnal return, the coverage constraint of the satellite's down-view angle, and the central latitude of the hotspot area, respectively.
[0150] Specifically, when the location of the hotspot is known, the satellite orbit altitude range and primary orbit that meet the conditions are preliminarily selected by using the daily return orbit constraint of the spaceborne SAR system, the satellite viewing angle coverage constraint, and the central lati...
Embodiment 3
[0201] The effect of the present invention can be verified by the following simulation.
[0202] Simulation conditions:
[0203] Utilize the STK simulation experiment to verify the orbit parameters and constellation configuration design method based on omnidirectional angle observation proposed by the present invention, the longitude and latitude of the center of the target hotspot area selected by the simulation is (47 ° 36'21 "N, 122 ° 19' 56 "W ).
[0204] Simulation content:
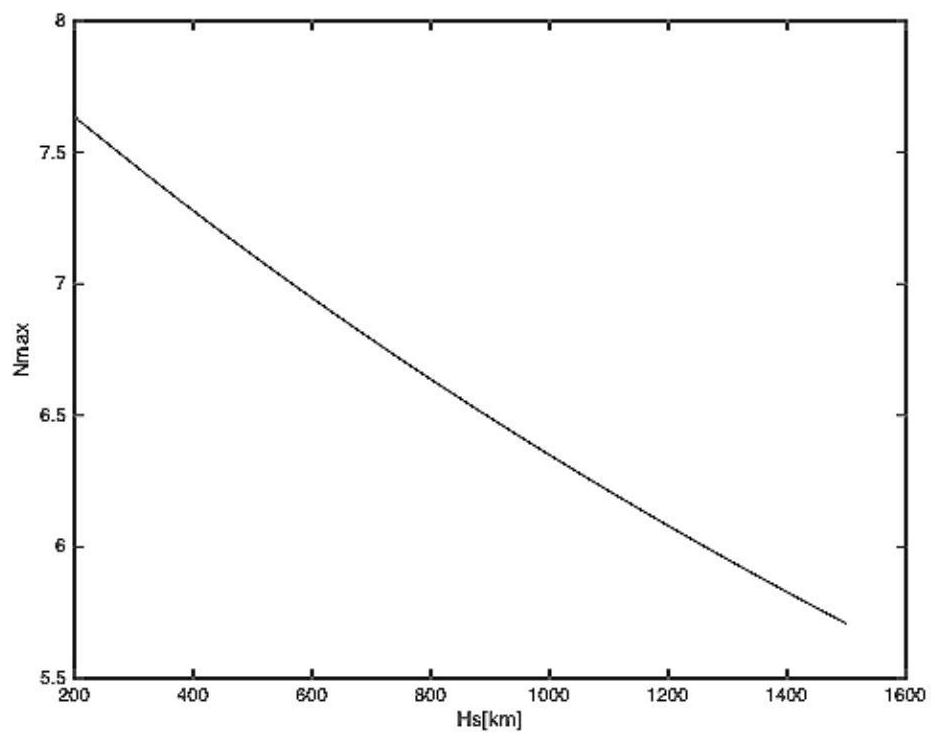
[0205] See Figure 6 and Figure 7 , Figure 6 It is a schematic diagram of the results of the primary orbit height and the primary orbit inclination provided by the embodiment of the present invention, and the abscissa H s is the orbital height, and the ordinate Inclination[°] is the orbital inclination; Figure 7 is a schematic diagram of the results of the selected orbit height and the selected orbit inclination provided by the embodiment of the present invention, in Figure 7 Among them, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com