Forest fire identification method based on multi-view robust bilateral twin vector machine
A recognition method, multi-perspective technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, computer parts, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to minimize structural risk, outliers or noise, and influence the results of classification, to minimize structural risk The effect of generalization and improvement of generalization performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
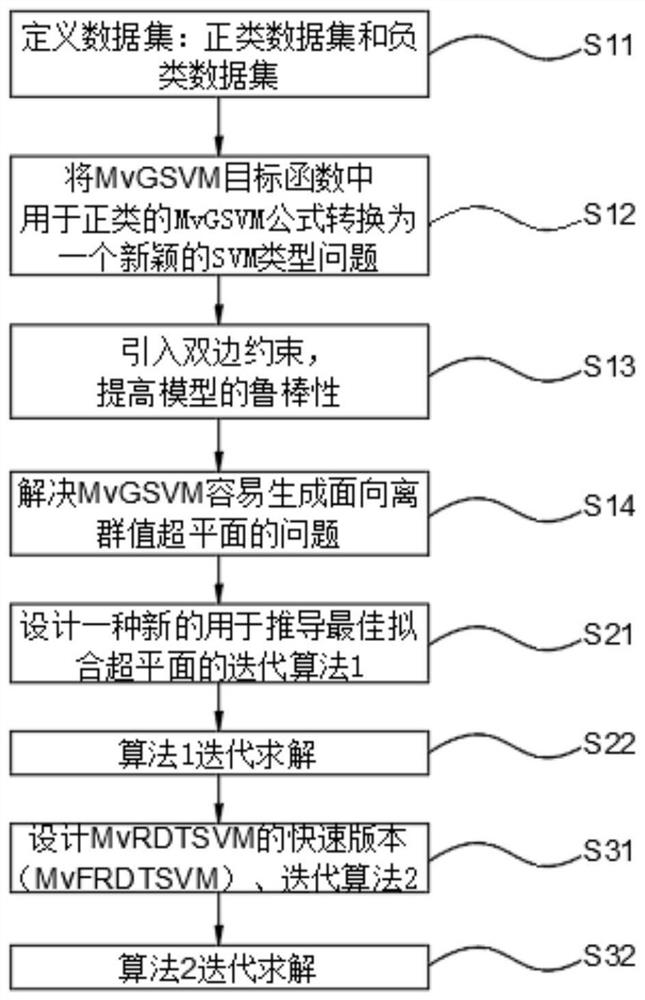
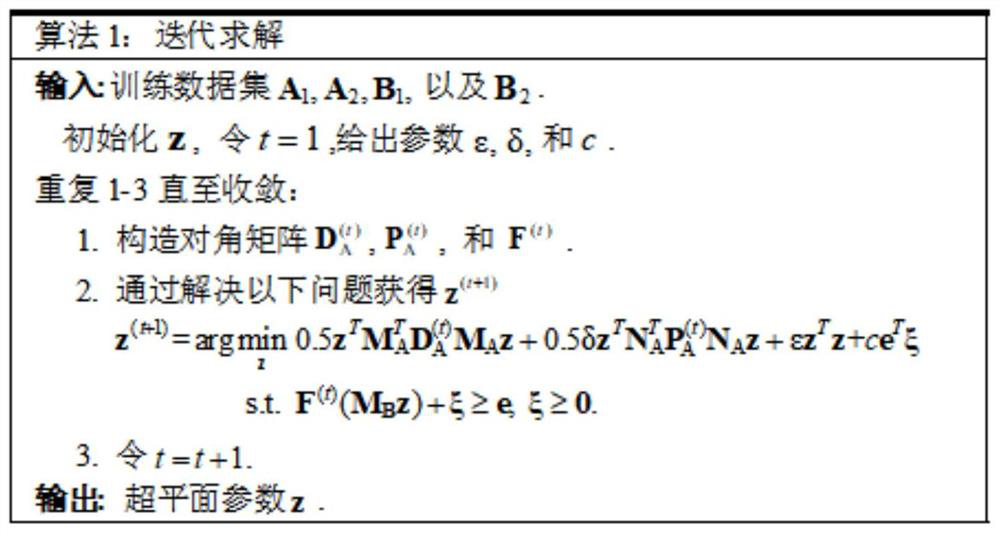
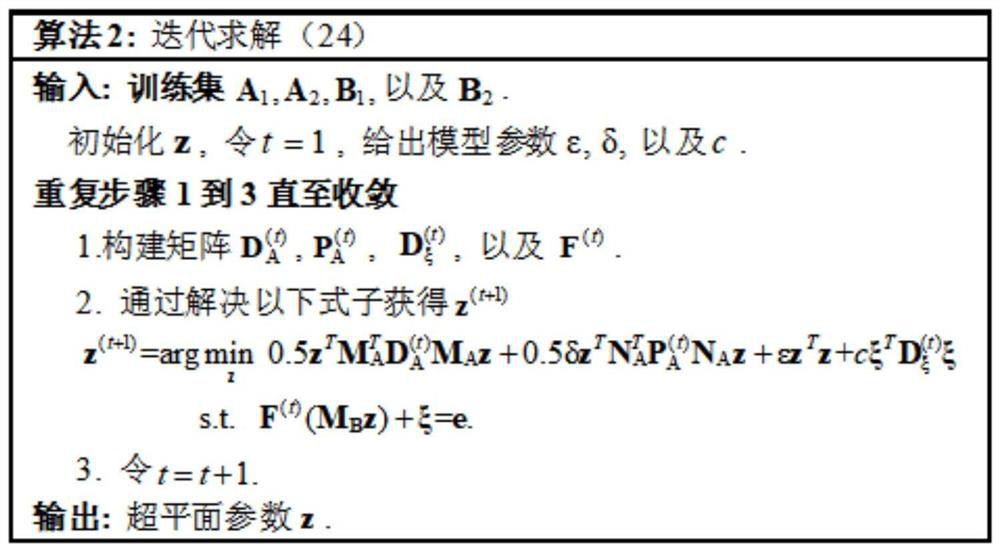
[0138] Embodiment one: for the generalization performance of a new multi-view learning method (the multi-view learning method of robust bilateral twin SVM (MvRDTSVM)) proposed for verification and the advantages in the field of forest fire recognition, the present invention uses a forest fire database (SmokeImg) for comparative experiments: the comparison method includes four single-view methods: TMSVM, WLSTSVM, L1-GEPSVM and L1-TWSVM, single-view TWSVM is divided into view figure 1 (TWSVM1) and View figure 2 (TWSVM2), and four multi-view methods: MvTSVM, MvGSVM, MvIGSVM and MvNPSVM, 150 real images of black smoke and 150 non-smoke were selected in the SmokeImg database to evaluate the classification performance of MvRDTSVM and MvFRDTSVM, and the original RGB The metric serves as the first view, and the SIFT features extracted from it serve as the second view.
[0139] Firstly, the single-view and multi-view learning methods are implemented on the original data set, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com