Robot-assisted fracture reduction path planning method and planning system and robot
A path planning and robot technology, applied in the field of surgical robots, can solve the problems of insufficient precision and safety, easy collision, insufficient or excessive rotation, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing secondary injuries, fast and accurate reset, and reducing collisions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
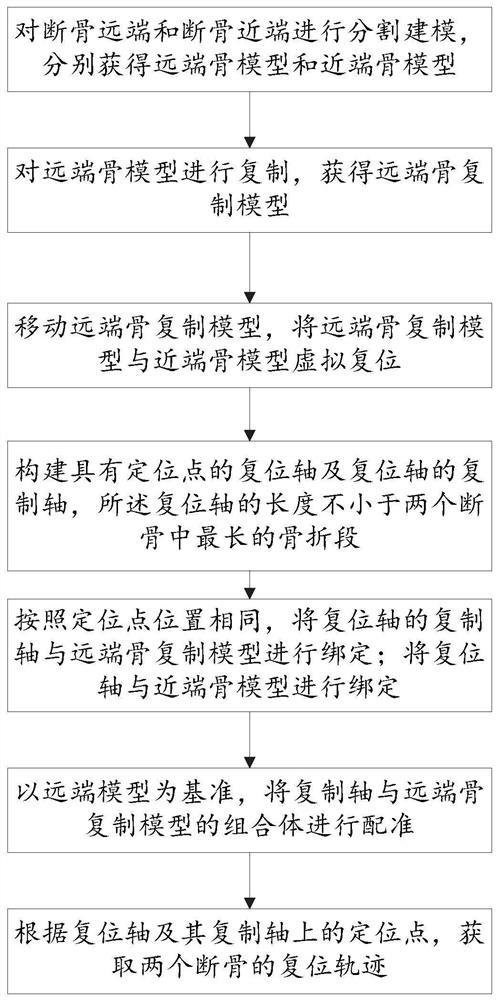
[0050] In the technical solutions disclosed in one or more embodiments, such as Figure 1-11 As shown, a robot fracture reduction path planning method is used to realize the reduction of two broken bones, including the following steps:
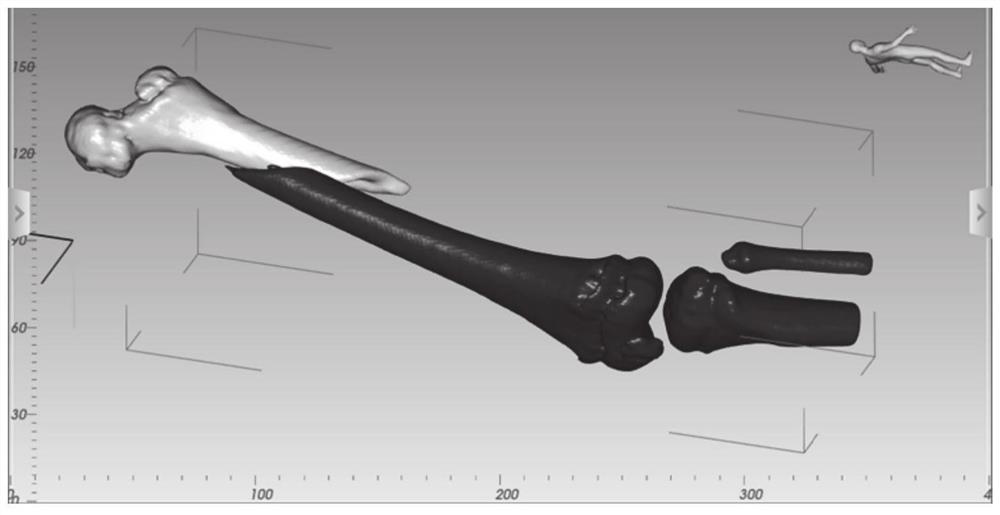
[0051] Step 1. Obtain a CT scan image of the fractured bone, segment and model the distal end of the broken bone and the proximal end of the broken bone, and obtain the distal bone model and the proximal bone model respectively;
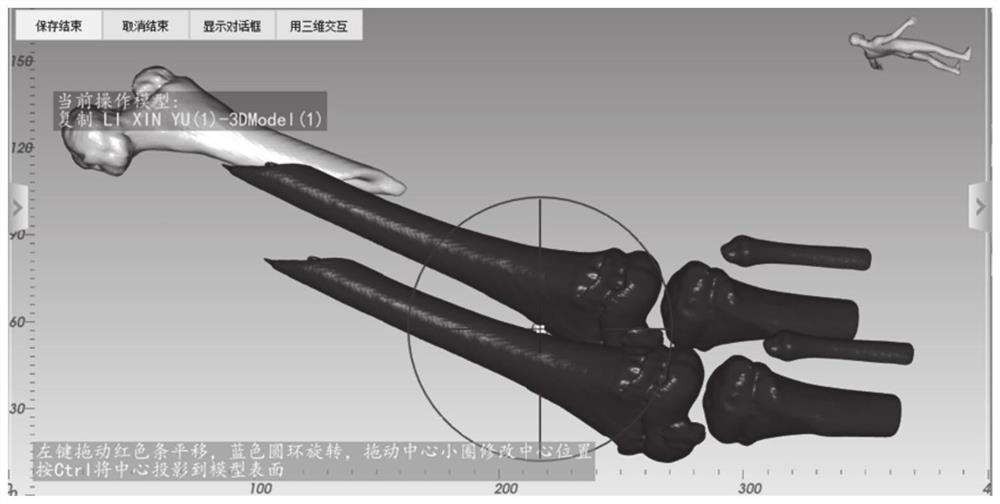
[0052] Step 2, duplicating the distal bone model to obtain the distal bone duplication model;
[0053] Step 3, move the distal bone replica model, and virtual reset the distal bone replica model and the proximal bone model;
[0054] Step 4, constructing a reduction axis with an anchor point and a copy axis of the reduction axis, the length of the reduction axis is not less than the longest fracture segment among the two broken bones;
[0055] Step 5. According to the same position of the anchor point, bind the copy...
Embodiment 2
[0090] This embodiment provides a robot fracture reduction path planning method, which is used to realize the reduction of multiple broken bones. Each segment of the distal bone model is connected in sequence according to the proximal bone model. When one of the distal bones and the proximal bone are reset As the current proximal bone and the next distal bone are reset, the robot fracture reduction path planning method described in Embodiment 1 is used for the reduction of the current proximal bone and the distal bone.
[0091] Specific steps are as follows:
[0092] (1) take the proximal end bone as the current proximal end bone, and use the broken bone adjacent to it as the current distal end bone, and use the method described in Embodiment 1 to carry out path planning;
[0093] (2) the current distal bone is reset;
[0094] (3) The combination of the current proximal bone and the current distal bone is used as the current proximal bone, and the adjacent broken bone is used...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Based on the method described in Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a robot fracture reduction path planning system, including:
[0099] Segmentation modeling module: configured to obtain a CT scan image of a fractured bone, segment and model the distal end and the proximal end of the fractured bone, and obtain a distal bone model and a proximal bone model respectively;
[0100] Model replication module: configured to replicate the distal bone model to obtain a distal bone replication model;
[0101] Virtual reduction module: configured to move the distal bone replication model, virtual reset the distal bone replication model and the proximal bone model to obtain a combined reset model;
[0102] A reduction axis generating module: configured to construct a reduction axis having an anchor point and a copy axis of the reduction axis, the length of the reduction axis is not less than the longest fracture segment among the two broken bones;
[0103] Binding module: con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com