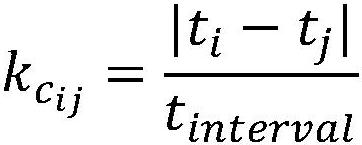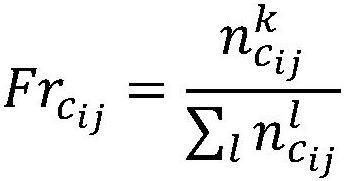Multi-mode fused unsupervised pedestrian re-identification rearrangement method
A pedestrian re-identification and multi-modal technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, neural learning methods, biological neural network models, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the workload of manual research and judgment, and reducing the degree of automation of video analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
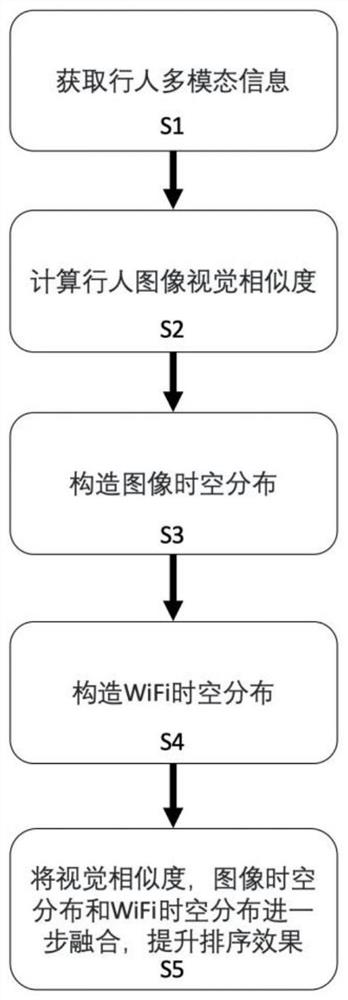
[0059] In fact, if the pedestrian image recognition results of each monitoring device on the travel path are viewed as a whole, there should be a strong spatio-temporal dependence between them. For example, it is impossible for the same pedestrian to appear in different monitoring devices that are physically far apart at the same time, and the time difference between pedestrians appearing in different monitoring devices must also have a reasonable relationship with the distance between monitoring devices and the pedestrian speed in common sense , the time for pedestrians to appear on the rear monitoring device on the travel path should not be earlier than that of the front monitoring device. However, the spatio-temporal dependencies related to pedestrian images need to know in advance which pedestrian images have been transferred across cameras, and the spatio-temporal dependencies related to pedestrian images constructed under unsupervised conditions will bring more noise.
...
Embodiment 2
[0109] This embodiment also provides a computer storage medium, the computer storage medium stores computer-executable instructions, and the computer-executable instructions can execute the fusion multimodal unsupervised pedestrian re-identification and rearrangement method in the first embodiment above . Wherein, the storage medium may be a magnetic disk, an optical disk, a read-only memory (Read-Only Memory, ROM), a random access memory (Random Access Memory, RAM), a flash memory (Flash Memory), a hard disk (Hard Disk Drive, abbreviation: HDD) or solid-state hard drive (Solid-State Drive, SSD) etc.; The storage medium may also include a combination of the above-mentioned types of memory.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com