Haloperoxidase compositions and uses thereof
A technology of haloperoxide and peroxidase, applied in drug combination, oxidoreductase, enzyme and other directions, can solve the problem of difficult to treat gram-negative bacterial infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0135] Example 1: Limulus amebocyte lysate assay
[0136] Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and lipid A were quantified using the chromogenic Limulus amoebocyte lysate (LAL) assay (LAL Endochrome-K, Charles River Endosafe). Briefly, the LAL assay is a kinetic colorimetric assay that detects and measures color development. Endotoxin activation of LAL coagulase is measured as the enzymatic (hydrolytic) cleavage of a synthetic chromogenic substrate, releasing p-nitroaniline (pNA), which can be measured by absorbance at a wavelength of 405 nm in a microplate spectrophotometer Quantify. The kinetic measurement at which the maximum color change (slope) is reached is used as a measure of the activity of the endotoxin present. Calibration standards are measured to generate standard curves and equations for calculating the endotoxin activity of assay samples. The amount of endotoxin present in a sample can be specified as Endotoxin Units (EU).
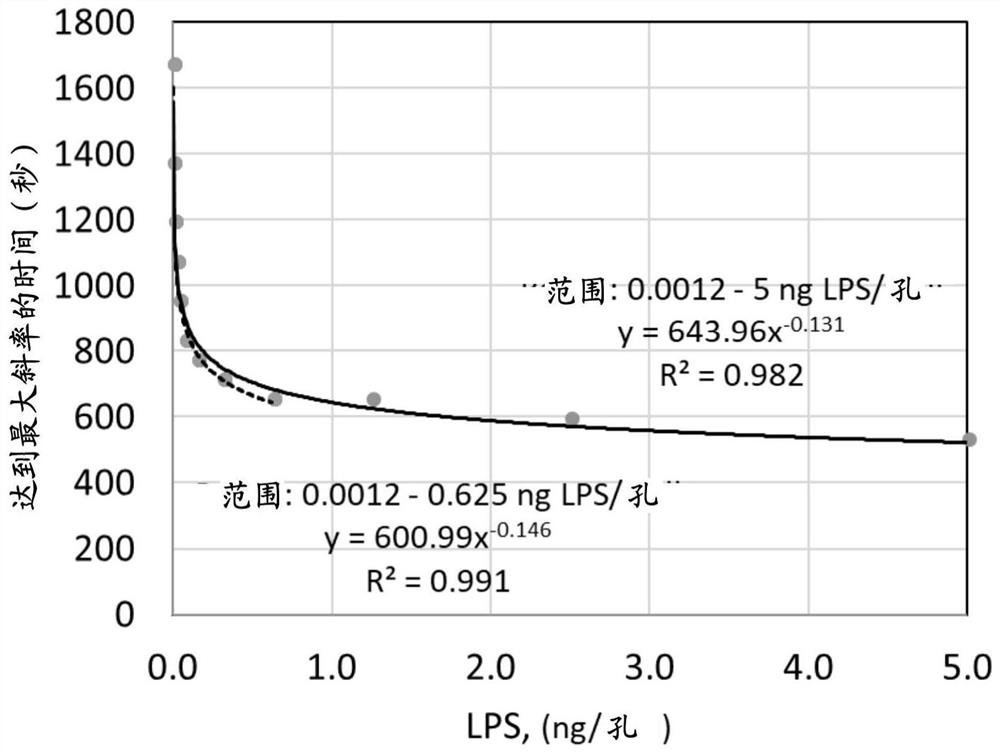
[0137] The endotoxin mass / well of a series of...
Embodiment 2
[0138] Example 2: Inhibition of LPS by haloperoxidase
[0139] MPO, EPO or GO were pre-incubated with LPS or lipid A for 30 min at 37°C. After pre-incubation, the limulus lysate solution was added and the seconds to reach the maximum color change (slope) were measured. The equation derived using the LPS standard ( figure 1 ), the time to maximum slope was converted to equivalent LPS mass and based on the difference between the activity of the expected mass (e.g., endotoxin without enzyme) and the actual measured LPS activity (e.g., endotoxin with enzyme) Calculate the inhibition rate expressed as a percentage.
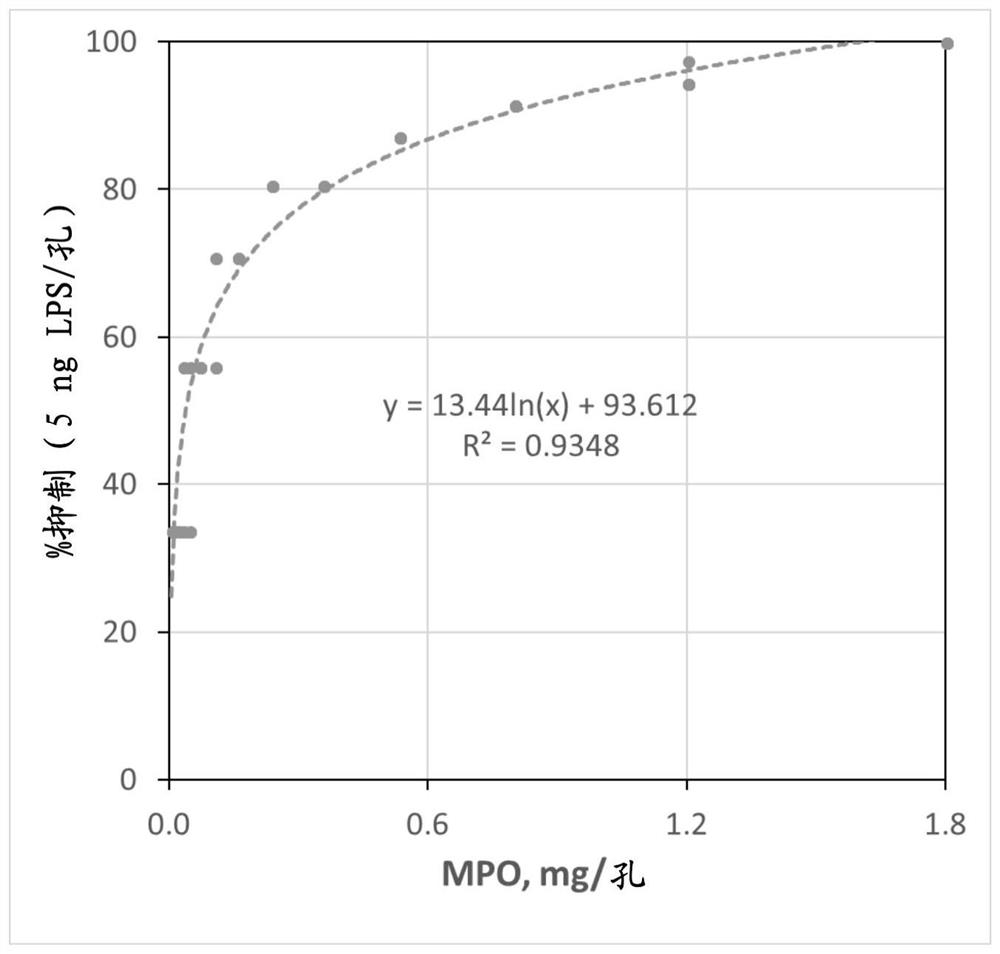
[0140] Such as figure 2 As shown, MPO significantly inhibits LPS, and the inhibition of LPS is proportional to the natural logarithm (Ln) of the mass of MPO. 1 mg MPO inhibited 90.8% of the activity of 5 ng LPS (ie 4.5 ng LPS). 0.01 mg MPO inhibited the activity of 5 ng LPS by 27.7% (ie 1.4 ng LPS). With LPS mass held constant and MPO mass varied, the percent in...
Embodiment 3
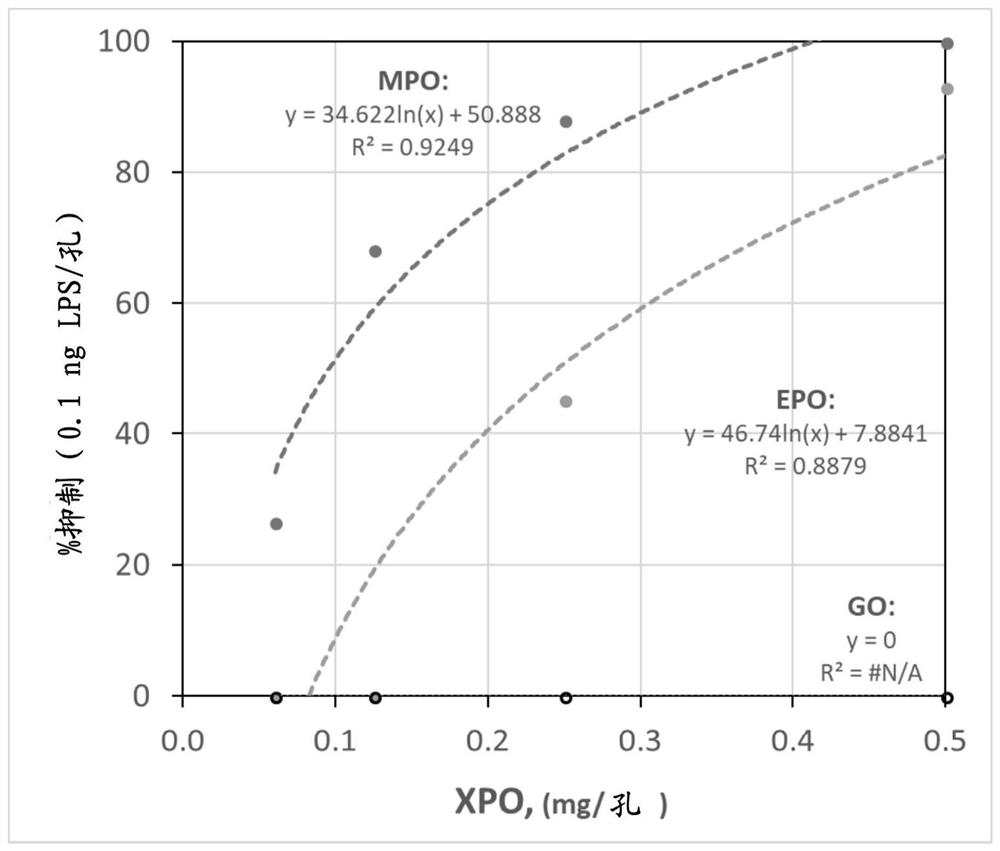
[0143] Example 3: Inhibition of Lipid A Endotoxin Activity by MPO and EPO
[0144] Lipid A, the toxic component of LPS, consists of two glucosamine units linked to phosphate groups and usually six hydrophobic fatty acids that anchor it to the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Purified lipid A is toxic and its endotoxin activity can be measured by LAL assay.
[0145] Inhibition of MPO and EPO was tested using diphosphoryl lipid A from E. coli F583 (Sigma Aldrich, L5399) and the chromogenic LAL assay described above. The hydrophobic nature of Lipid A can complicate the preparation of aqueous standards. Figure 4 The data shown in illustrates the reproducibility of aqueous lipid A standards as measured by chromogenic LAL activity up to 5.75 hours after preparation. The endotoxin unit activity per mass of lipid A was lower than that described by the manufacturer (i.e., ≥1 × 10 6 EU / mg), and the activity showed detectable degradation within hours. Therefore, LPS or Lipi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com