System for researching acute toxicity of pyralis farinalis linnaeus Chinese Litse root-bark chongcha mouse
A leopard moth, acute toxicity technology, applied in the field of insect tea research, can solve the problems of female operator's fear, mouse gnawing, mouse body damage and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
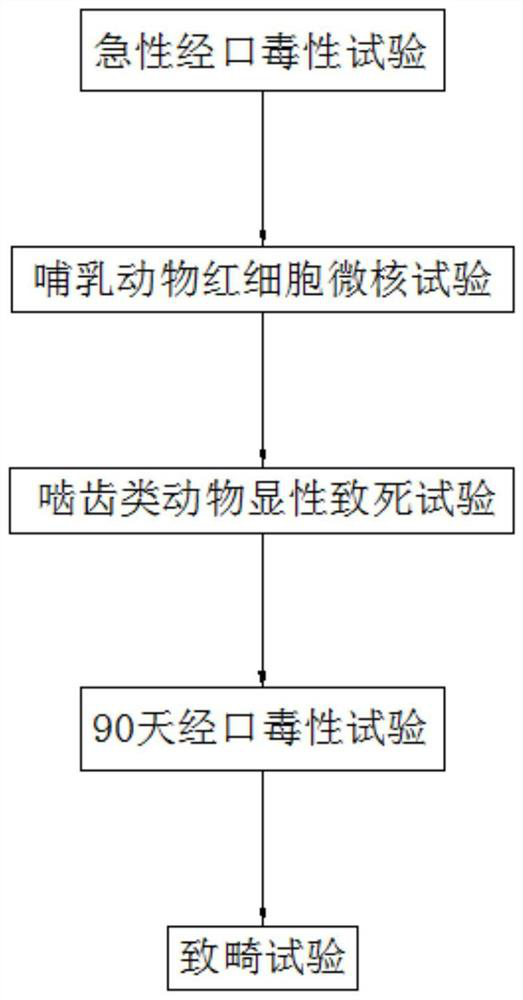
[0036] see Figure 1-7 , the present invention provides a technical scheme: a method for studying the acute toxicity of the purple spotted rice moth leopard skin camphor insect tea mouse, comprising the following steps:
[0037] S1: Acute oral toxicity test: limit method was used; 20 KM mice, half male and half male, were orally gavaged at a dose of 30 g / kg bw of the test substance, observed continuously for 14 days after gavage, and recorded The clinical sym...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com