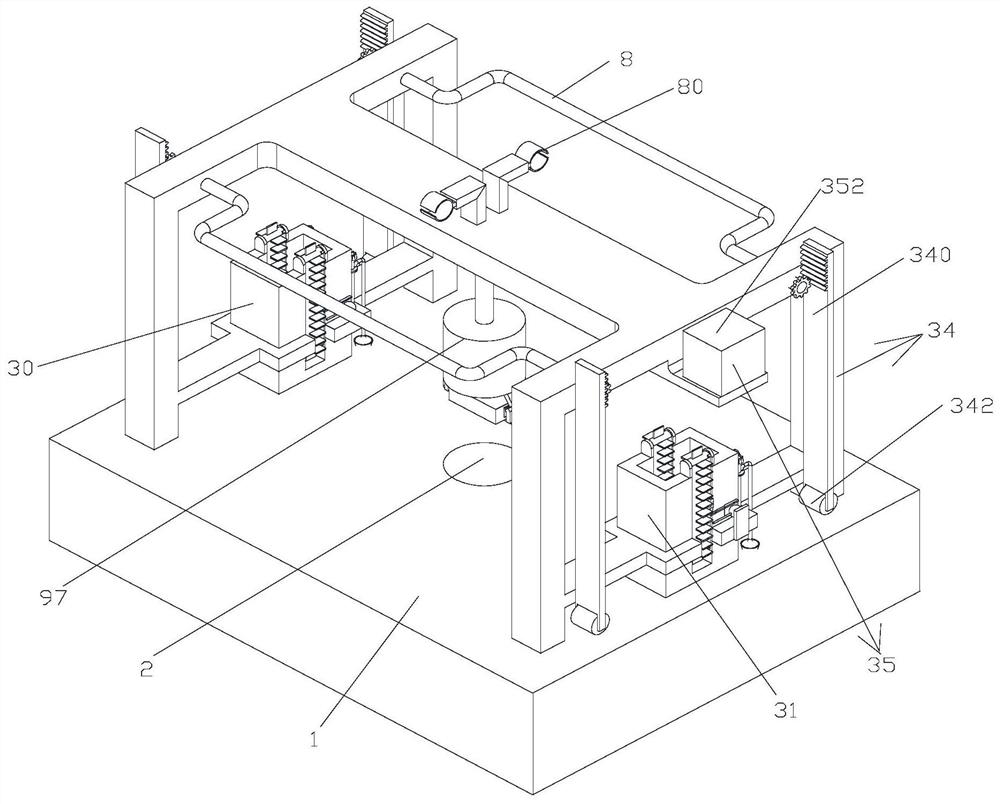
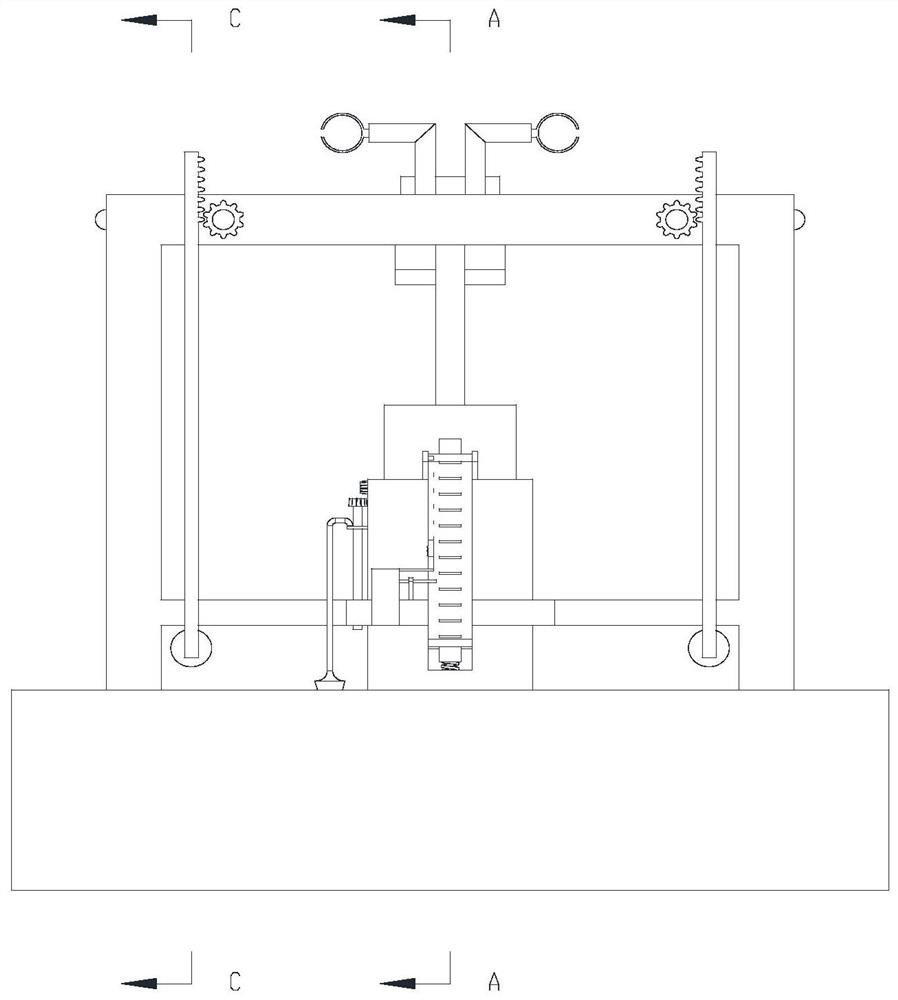
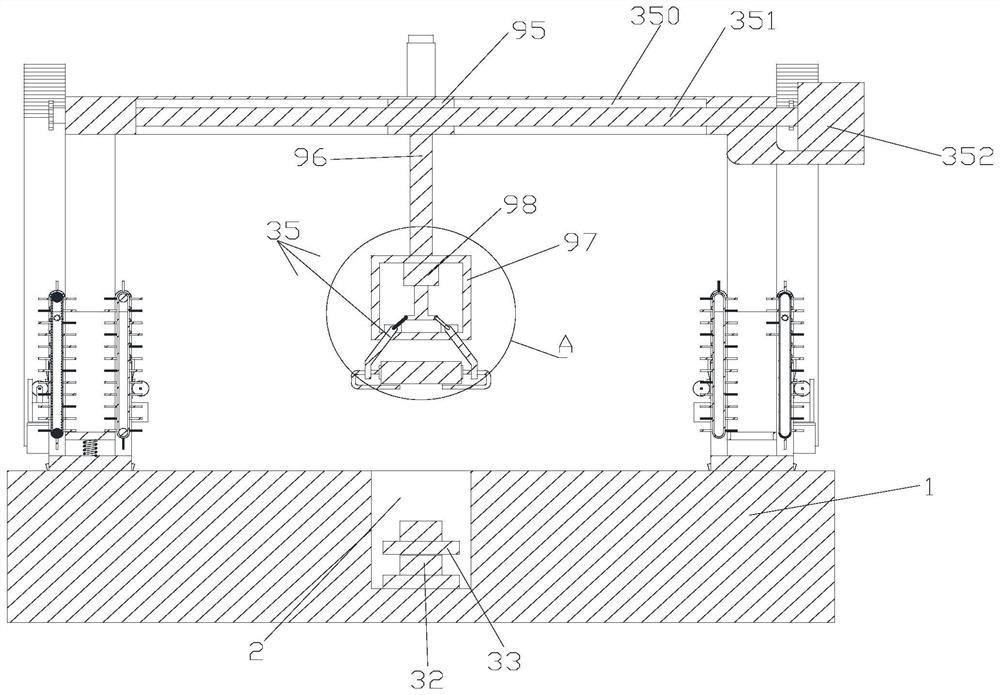
Blasting method for foundation pit excavation
A technology for foundation pits and slopes, applied in the field of blasting, which can solve problems such as inability to achieve stable discharge of explosives, adjust explosives, and a large amount of dust, achieve long-term storage of materials, prevent mutual adhesion, and improve work efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A method for excavating and blasting a foundation pit, comprising the following steps:
[0047] S1: Terrain Survey: Familiar with engineering geology and geological survey data, understand site terrain, landform, etc. Before construction, design blasthole parameters and stipulate slopes reasonably according to site terrain, cross-sectional shape of blasting area, and frozen soil distribution;
[0048] S2: Slope excavation: When excavating a side slope, a 0.4 thick protective layer is reserved during blasting excavation, and a water intercepting ditch is dug at the top of the slope along the extension direction of the slope to prevent rainwater from flowing to the side slope. The roof is sealed with cement to prevent rainwater from invading the slope, thus ensuring the quality of the slope;
[0049] S3: Slope protection: Detect whether there is a dissolved cavity in the slope structure, and excavate accordingly to form slopes located on the left and right sides of the ro...
Embodiment 2
[0076] S1: Terrain Survey: Familiar with engineering geology and geological survey data, understand site terrain, landform, etc. Before construction, design blasthole parameters and stipulate slopes reasonably according to site terrain, cross-sectional shape of blasting area, and frozen soil distribution;
[0077] S2: Slope excavation: When excavating a side slope, a 0.6m thick protective layer is reserved during blasting excavation, and a water intercepting ditch is dug at the top of the slope along the extension direction of the slope to prevent rainwater from flowing to the side slope. The top of the slope is sealed with cement to prevent rainwater from invading the slope, thereby ensuring the quality of the slope;
[0078] S3: Slope protection: Detect whether there is a dissolved cavity in the slope structure, and excavate accordingly to form slopes located on the left and right sides of the road section crossing the dissolved cavity, and use the bolt-net-spraying combined ...
Embodiment 3
[0086] S1: Terrain Survey: Familiar with engineering geology and geological survey data, understand site terrain, landform, etc. Before construction, design blasthole parameters and stipulate slopes reasonably according to site terrain, cross-sectional shape of blasting area, and frozen soil distribution;
[0087] S2: Slope excavation: When excavating a side slope, reserve a 0.7m thick protective layer during blasting excavation, and dig a water intercepting ditch along the extension direction of the slope at the top of the slope to prevent rainwater from flowing to the side slope. The top of the slope is sealed with cement to prevent rainwater from invading the slope, thereby ensuring the quality of the slope;
[0088] S3: Slope protection: Detect whether there is a dissolved cavity in the slope structure, and excavate accordingly to form slopes located on the left and right sides of the road section crossing the dissolved cavity, and use the bolt-net-spraying combined support...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com