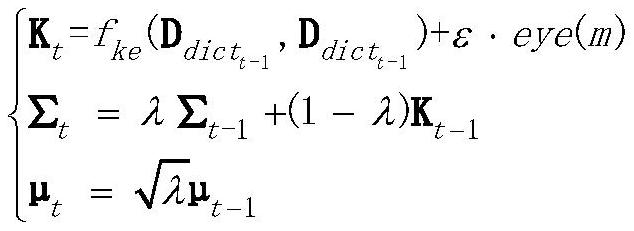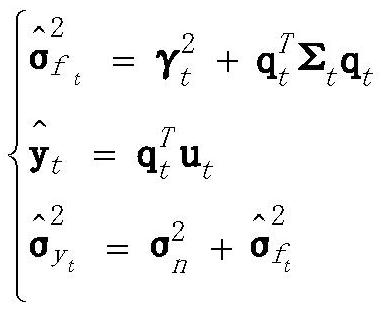Electroencephalogram signal online prediction method based on kernel recursive least square self-adaptive tracking algorithm
A recursive least squares, EEG technology, applied in the recognition, calculation, calculation model and other directions of patterns in signals, can solve the problems of missing signals, inaccurate and missing EEG signals, etc., to eliminate abnormal points and solve problems. Inaccurate measurement, effect of signal smoothing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
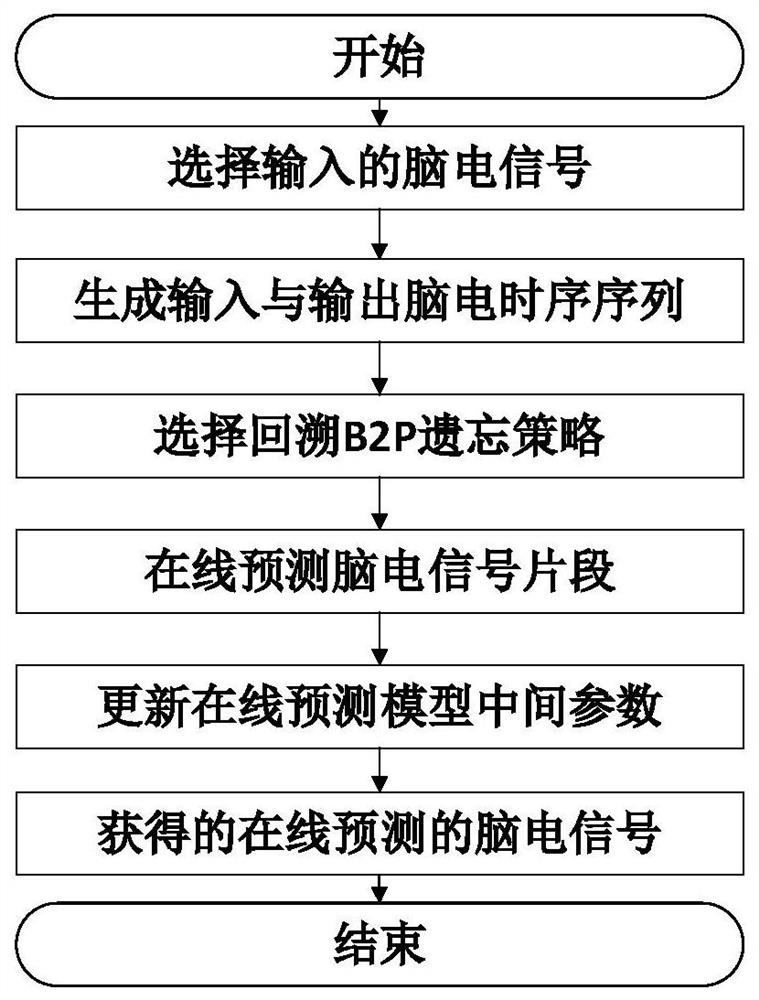
[0017] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific implementation details. This embodiment is to conduct online prediction on the brain-computer interface EEG signals actually collected in the hospital. The distribution of EEG signals is relatively complex, non-stationary and random, and the EEG signals may contain noise interference. Kernel recursive least squares The multiplicative adaptive tracking algorithm is a kernel algorithm capable of tracking nonlinear time-varying data. It includes a forgetting factor λ and a relatively cheap dictionary D dict , to enhance the ability to track complex EEG signals. For tracking non-stationary EEG signals, it provides confidence intervals and adds an uncertainty module in each iteration EEG signals may contain noise interference. In order to improve the stability and generalization ability of the algorithm in EEG signal tracking, the concept of regularization is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com