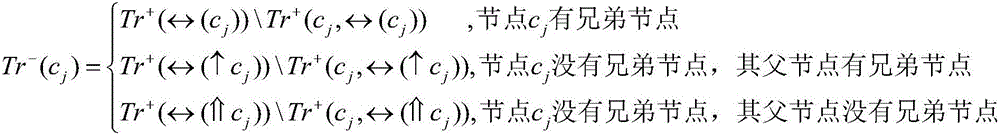Hierarchical multi-label classification method for protein function prediction
A protein function and classification method technology, which is applied in the field of hierarchical multi-label classification for protein function prediction, achieves far-reaching practical application significance, saves experimental costs, and compresses expenses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0044] Specific Embodiments 1. A hierarchical multi-label classification method for protein function prediction described in this embodiment is carried out in the following steps:
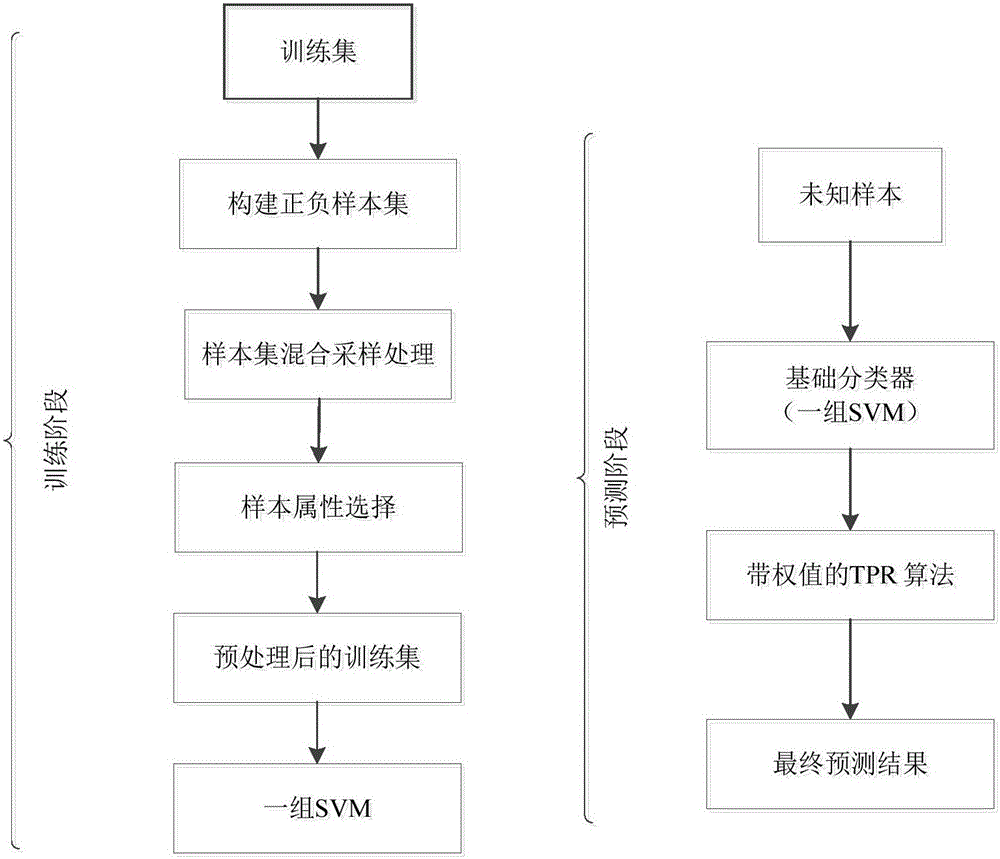
[0045] The hierarchical multi-label classification method for protein function prediction is divided into two stages: training and prediction:
[0046] 1. Training stage
[0047] In the training phase, an SVM classifier is used to train the data set of each node in the class label hierarchy to obtain a set of SVM classifiers, which are called basic classifiers, where SVM is a support vector machine;
[0048] 1.1. Use proteins with known functions as training samples to form a training set, and express each protein as a multidimensional vector, and each element in the vector is called an attribute;
[0049] The content in this vector is a digital representation of real experimental results taken from standard biological databases;
[0050] In the field of machine learning, attributes refer to the ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
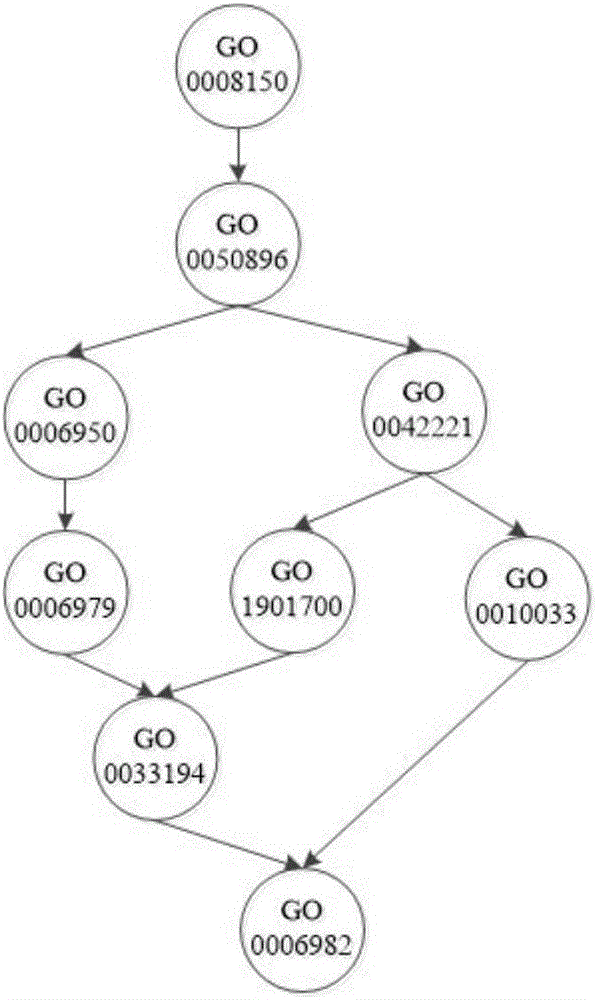
[0071] Specific embodiment 2. This embodiment is a further description of a hierarchical multi-label classification method for protein function prediction described in specific embodiment 1. The positive sample set is constructed according to the improved sibling principle as described in step 1.2. The specific process of negative sample set is as follows:
[0072] For each node in the GO annotation scheme, in the training set, the samples belonging to the node are used as positive samples, and the samples belonging to the sibling nodes of the node are used as initial negative samples, and at the same time, the negative samples that belong to the positive sample set are eliminated in the initial negative sample set. , and take it as the final negative sample set, that is, the negative sample set; among them, if a node has no sibling nodes, trace upwards and select samples belonging to the sibling nodes of its parent node as negative samples;
[0073] Specific symbols indicate:...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0077] Specific embodiment three. This embodiment is a further description of a hierarchical multi-label classification method for protein function prediction described in specific embodiment one or two. The specific process is as follows:
[0078] The oversampling method for few-class samples described in the present invention is a hierarchical SMOTE few-class sample oversampling method;
[0079] Let X be a training set containing n samples, X={x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x n}, the number of sample labels is m in total, that is, there are m nodes in total. For a node i (1≤i≤m), the positive sample set is a few-class sample, that is, a sample with the function represented by the node. The sample The collection of POS is marked as POS; the negative sample set is a multi-class sample, that is, the sample that does not have the function represented by the node, and is marked as NEG; there are a total of pn samples in POS, recorded as POS={x pos1 ,x pos2 ,...x pospn}; There are nn samples...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com