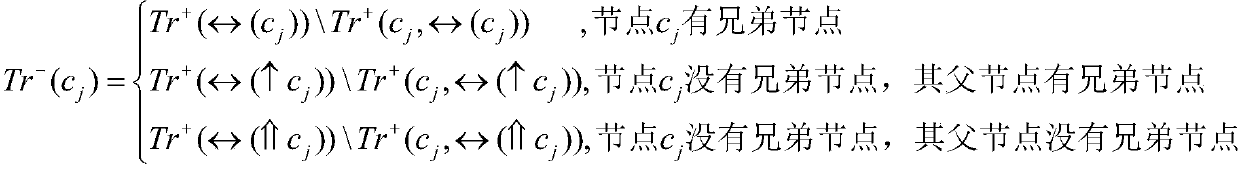Gene function prediction method based on r-svm and tpr rules
A technology of gene function and prediction method, applied in the field of data mining of bioinformatics, can solve problems such as hierarchical constraints, and achieve the effect of reducing expenses, saving experimental costs, and shortening time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0032]Since in the GO annotation scheme, the function is gradually refined from top to bottom, for some genes, it may not have the function represented by the bottom node, which makes for these nodes, the number of samples with this function is very small , the number of samples that do not have this function is large, and this situation is known as the dataset imbalance problem. The existence of this kind of problem will reduce the accuracy of classification. Therefore, when constructing positive and negative sample sets for nodes, certain strategies need to be adopted to solve this problem.
[0033] Since a gene sample is represented by a multi-dimensional vector, a sample has many attribute values, and processing these attribute values at the same time will introduce a large number of calculations. For different functional nodes, the attributes related to the function may be different, and some attributes may be irrelevant attributes, and processing irrelevant attributes ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0053] The specific process of constructing positive sample sets and negative sample sets according to the improved sibling principle described in step 2 of this embodiment is as follows:
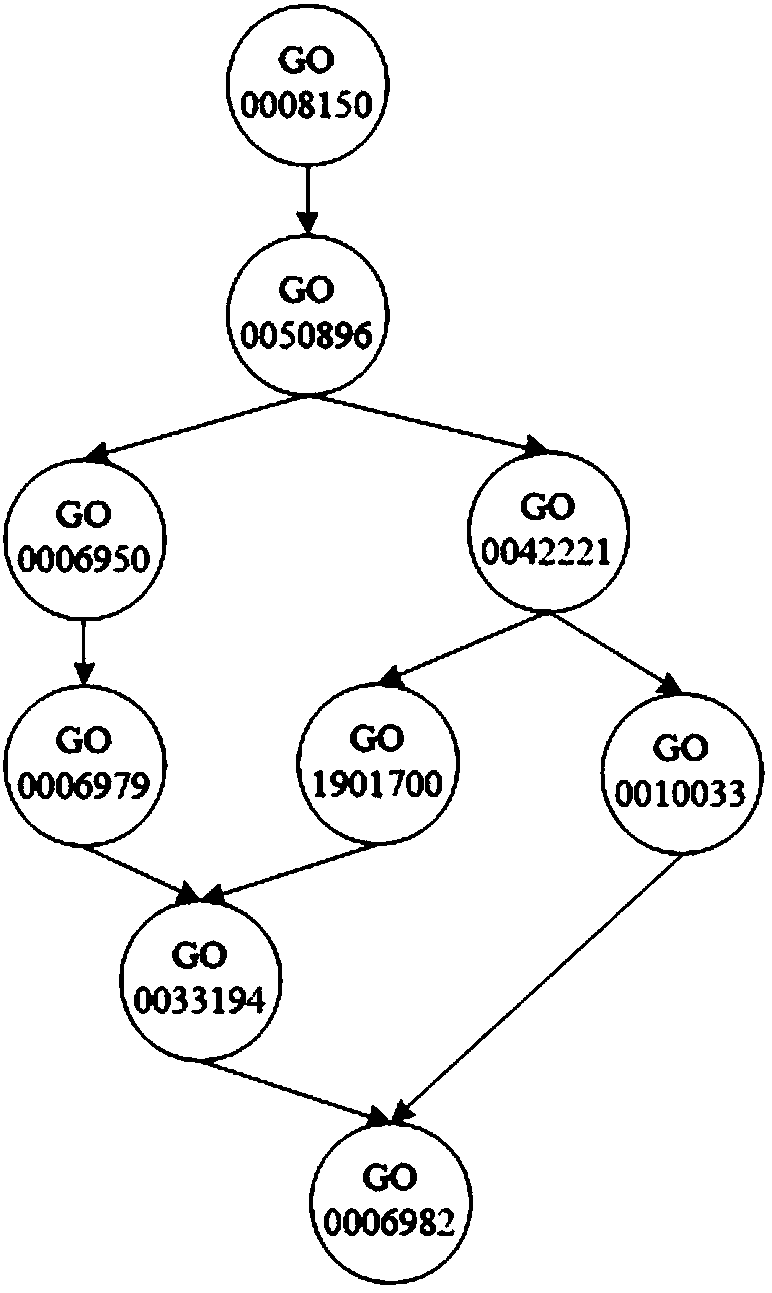
[0054] For each node in the GO annotation scheme, in the training set, the samples belonging to the node are used as positive samples, and the samples belonging to the sibling nodes of the node are used as initial negative samples, and at the same time, the negative samples that belong to the positive sample set are eliminated in the initial negative sample set. , and take it as the final negative sample set, that is, the negative sample set; among them, if a node has no sibling nodes, trace upwards and select samples belonging to the sibling nodes of its parent node as negative samples;
[0055] Specific symbols indicate:
[0056] Tr + (c j )=*(c j )
[0057]
[0058] Among them, Tr represents the training set containing all samples; node c j Represents the corresponding class labe...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0060] The specific implementation process of step 3 of this embodiment is as follows:
[0061] Step 3.1,
[0062] First, use the concept of information gain in the C4.5 decision tree algorithm to calculate the information gain of each attribute, and at the same time calculate the gain ratio of each attribute;
[0063] For a certain node, let D be the sample set, Gain(R) be the information gain, and Gainratio be the information gain ratio for attribute R, then its calculation formula is:
[0064]
[0065]
[0066] Gain(R)=Info(D)-Info R (D)
[0067]
[0068]
[0069] Among them, p i Indicates the proportion of samples belonging to category i in the sample set, m is the number of categories contained in the sample set, Info(·) indicates the entropy value of the sample set, that is, the amount of information required to separate different categories of the sample set; k indicates The attribute R has k different values, D j is a sample set composed of samples who...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com