Periodic gap constrained negative sequence pattern mining method
A pattern mining and negative sequence technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, knowledge expression, etc., can solve problems such as inability to take into account negative sequences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
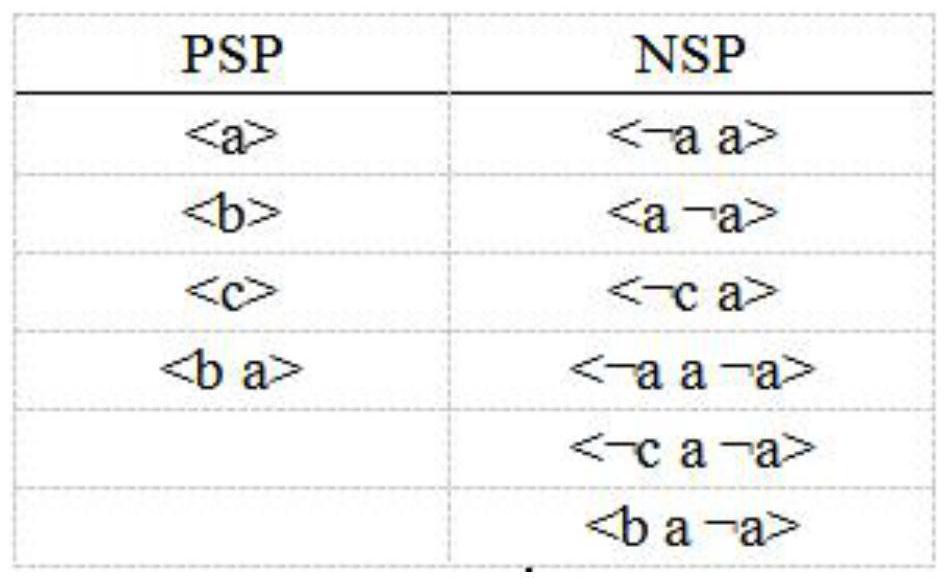
[0117] Given a sequence database D={s 1 = d 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 d 5 d 6 d 7 d 8 d 9 d 10 =ttcctccgcg,s 2 = d 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 d 5 =tggct}, given the density threshold ρ=0.1, the minimum gap constraint M=0, and the maximum gap constraint N=2.
[0118] The first step is to read the sequence database D given by the user, the threshold ρ and the period gap constraint [M,N]:
[0119] Read into the sequence database D, it can be seen that D has a total of g sequences, and each sequence is recorded as sequence s 1 , sequence s 2 , ..., sequence s g , where the sequence s i The elements contained in (1≤i≤g) are respectively denoted as element d 1 , element d 2 , ..., element d l , that is, the length is l, read in D to get h different elements, and get the element set E={e 1 、e 2 ...e h }. Read in the threshold ρ, and read in the periodic gap constraint [M,N].
[0120] The specific processing method is as follows:
[0121] Read int...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com