Coarse mesh-based rapid turbulence wall surface function aerodynamic force prediction method
A prediction method and coarse grid technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, CAD numerical modeling, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of excessive computer internal resources and slow calculation convergence speed, so as to improve calculation efficiency, Reduced workload and high calculation accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
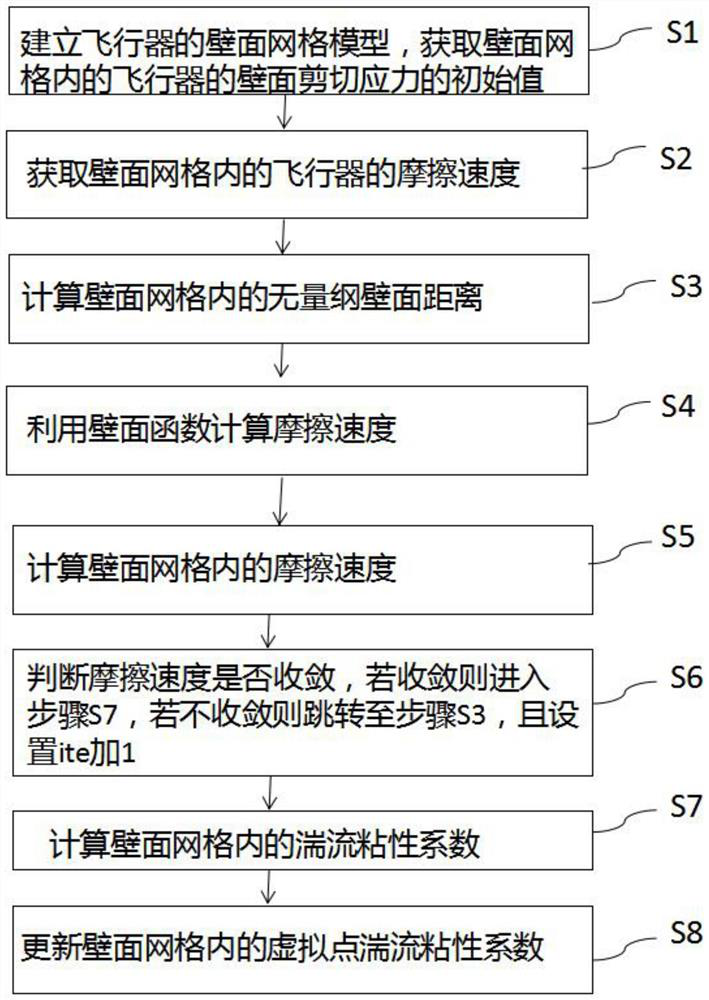
[0063] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 8 As shown, a method for predicting the aerodynamic forces of fast turbulent wall functions based on coarse grids includes the following steps:
[0064] S1, establish the wall mesh model of the aircraft, and obtain the initial value of the wall shear stress of the aircraft in the wall mesh, the formula is:
[0065]
[0066] Among them, τ is the shear stress, τ w is the wall shear stress, μ w is the wall molecular viscosity coefficient, μt is the turbulent flow viscosity coefficient, U is the inner wall parallel velocity of the wall grid, y is the wall distance, is the sign of the partial derivative, is the partial derivative of the wall parallel velocity in the wall normal direction in the wall grid, U P is the velocity of grid points on the wall;
[0067] S2, get the friction velocity U of the aircraft in the wall grid τ , whose formula is:
[0068]
[0069] Among them, ρ w is the wall density;
[0070] S3, calculate the dim...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 8 As shown, this embodiment is based on Embodiment 1, reflecting the technical effect of adopting the present invention.
[0110] This technology uses the wall function based on the analytical velocity distribution in the wall coarse grid, and obtains the friction velocity through constructor iteration, which can effectively improve the prediction accuracy of the wall coarse grid, and with the increase of the wall grid distance, the grid volume The overall reduction can significantly save computing time and computing memory.
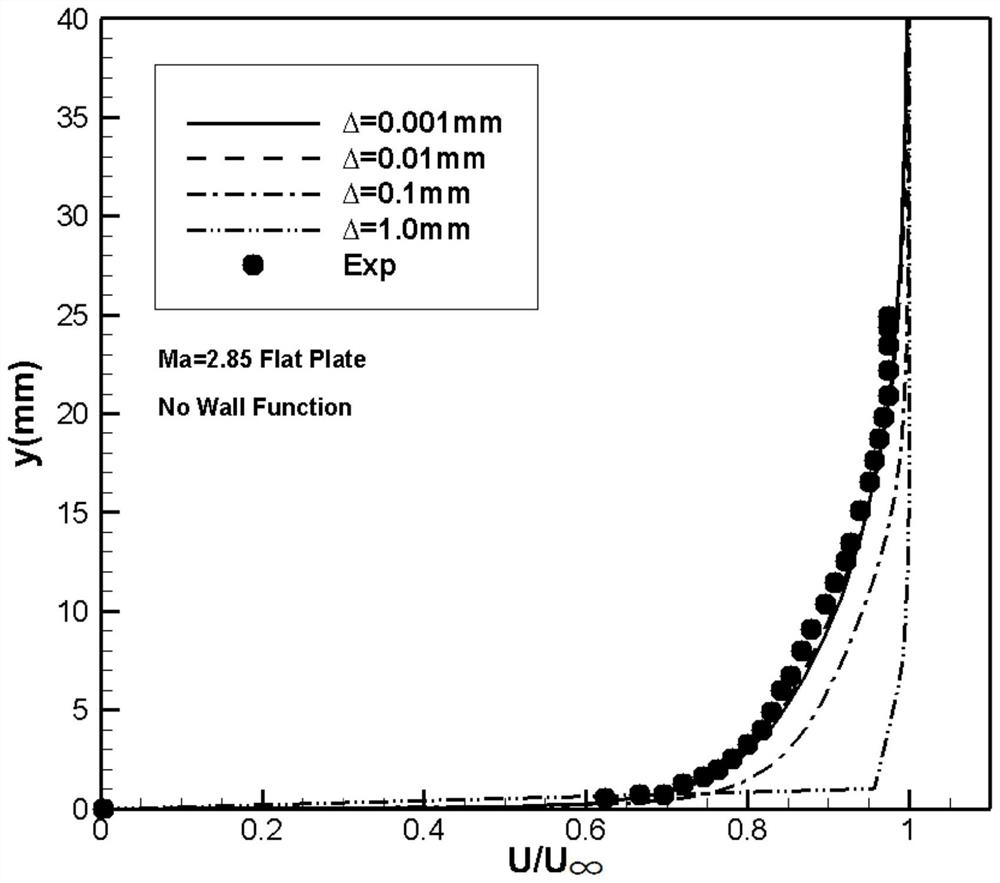
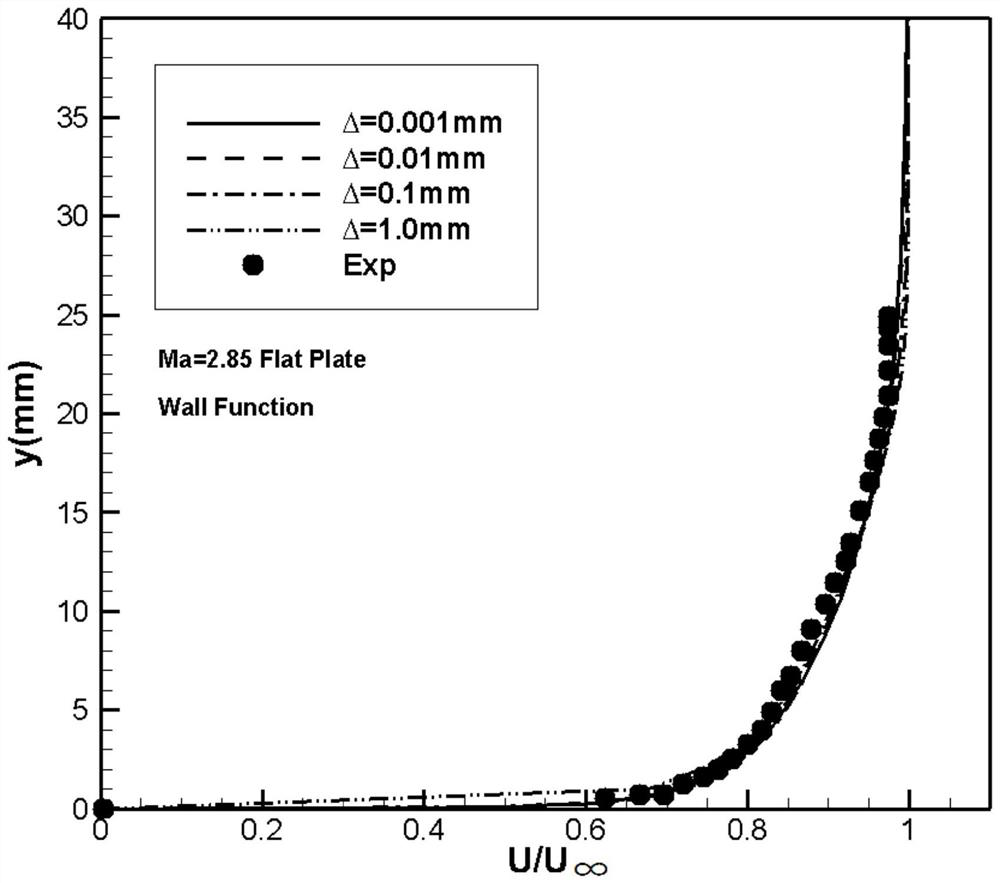
[0111] figure 2 , image 3 is the boundary layer velocity distribution of the hyper-slab turbulent flow with incoming flow Ma=2.85, when the wall function is not used ( figure 2 ), the numerical results of the coarse grid, the results of the dense grid, and the experimental results have large deviations, and the accuracy becomes worse with the increase of the grid wall distance, while image 3 After using the wall...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com