Application of a scoring system based on immune gene pairs in predicting the effect of immunotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
A non-small cell lung cancer and gene pairing technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of low clinical application value, small sample overfitting, lack of validation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
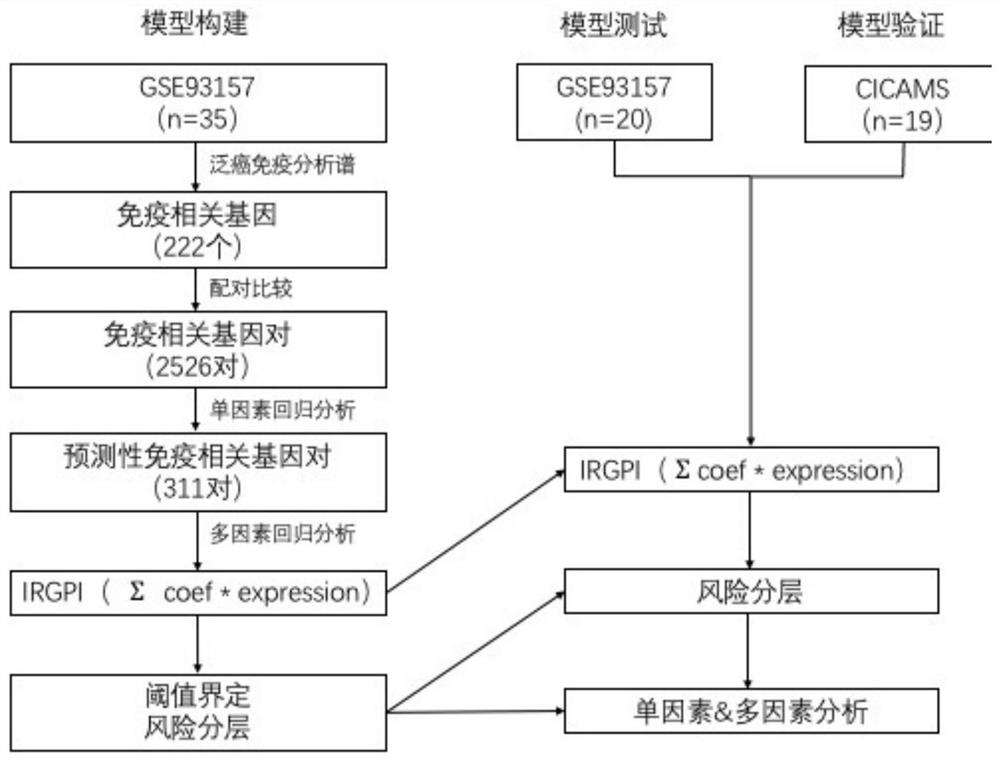
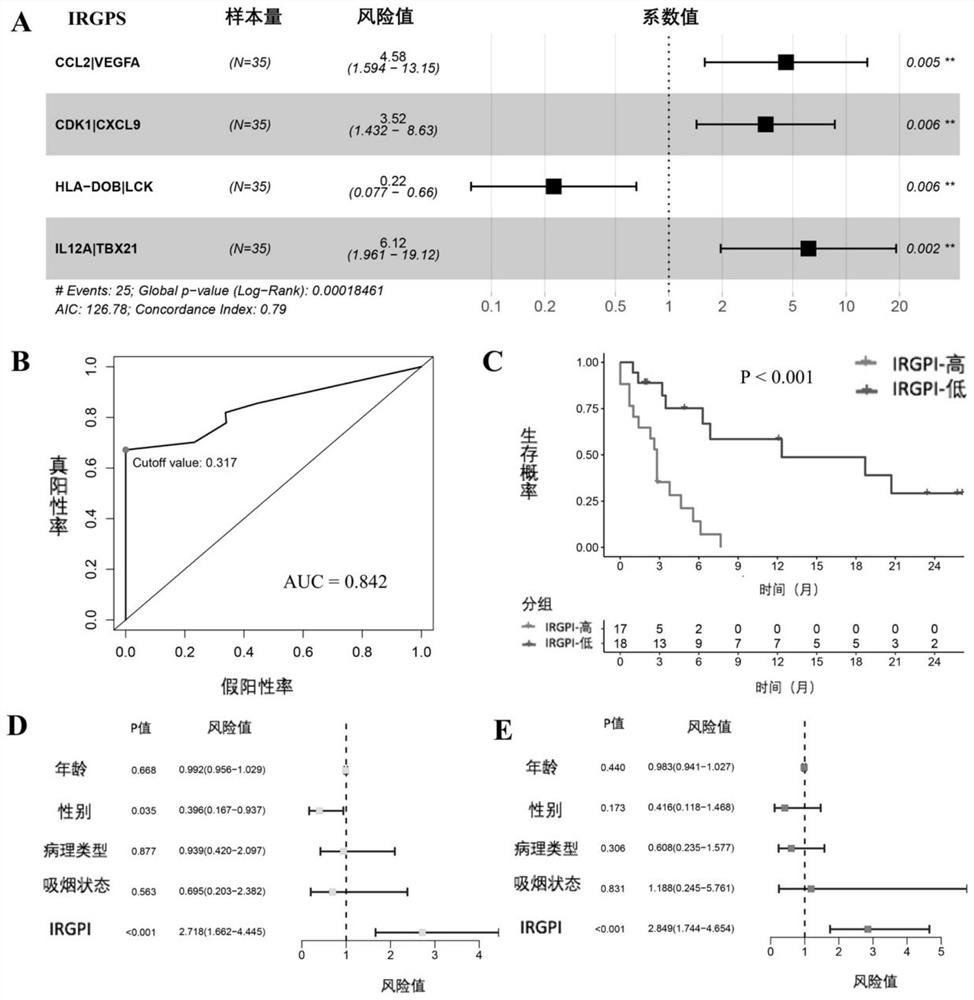
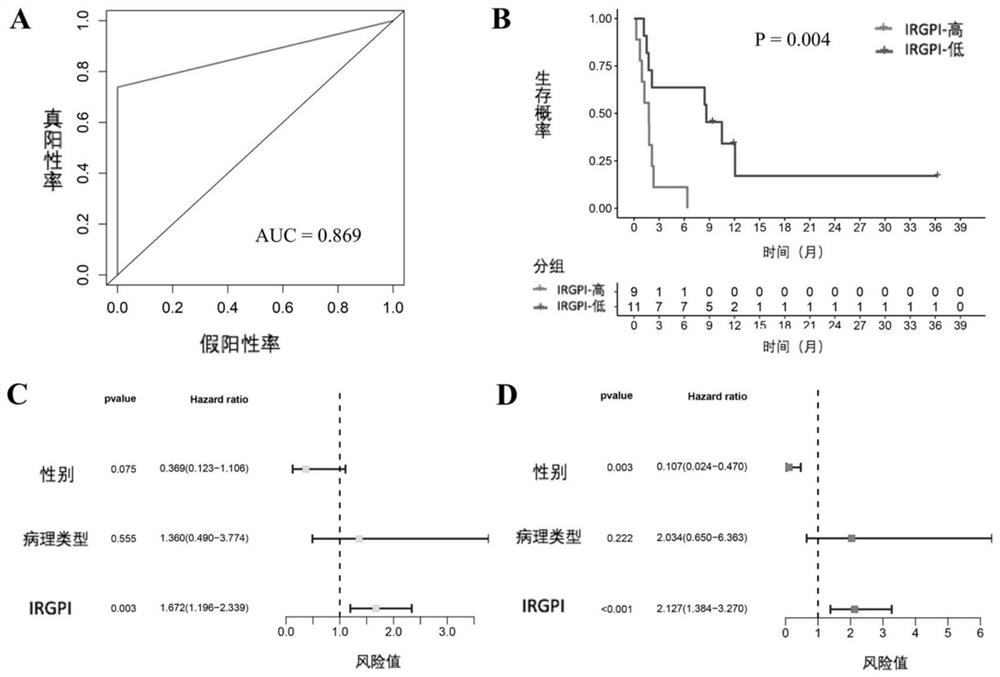
[0046] Example 1. Application of IRGPI in predicting the efficacy and prognosis of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer 1. Research subjects
[0047] The information of the research subjects is shown in Table 1, which are divided into three cohorts, namely the GSE93157 cohort, the GSE136961 cohort and the CICAMS cohort.
[0048] Table 1. Information on research objects
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] Among them, the GSE93157 cohort mainly included patients with advanced thoracic malignancies who were treated with anti-PD-1 antibodies at Hebron Valley Hospital and Barcelona University Hospital in Spain. Inclusion criteria were: 1) patients with clinically diagnosed locally advanced or locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer; 2) received immunotherapy for the first time, with no limit on the number of lines of treatment; 3) both in Hebron Valley Hospital and Barcelona in Spain before immunotherapy Lung cancer surgery is performed at the University Hospita...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com