Greedy K-mean self-organizing neural network multi-robot path planning method
A K-means, neural network technology, applied in instruments, adaptive control, control/regulation systems, etc., can solve problems such as inability to solve multi-robot path planning, low operating efficiency of multi-robot systems, and unbalanced multi-robot load, etc. To achieve the effect of improving load imbalance, good scalability, and meeting the needs of engineering applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
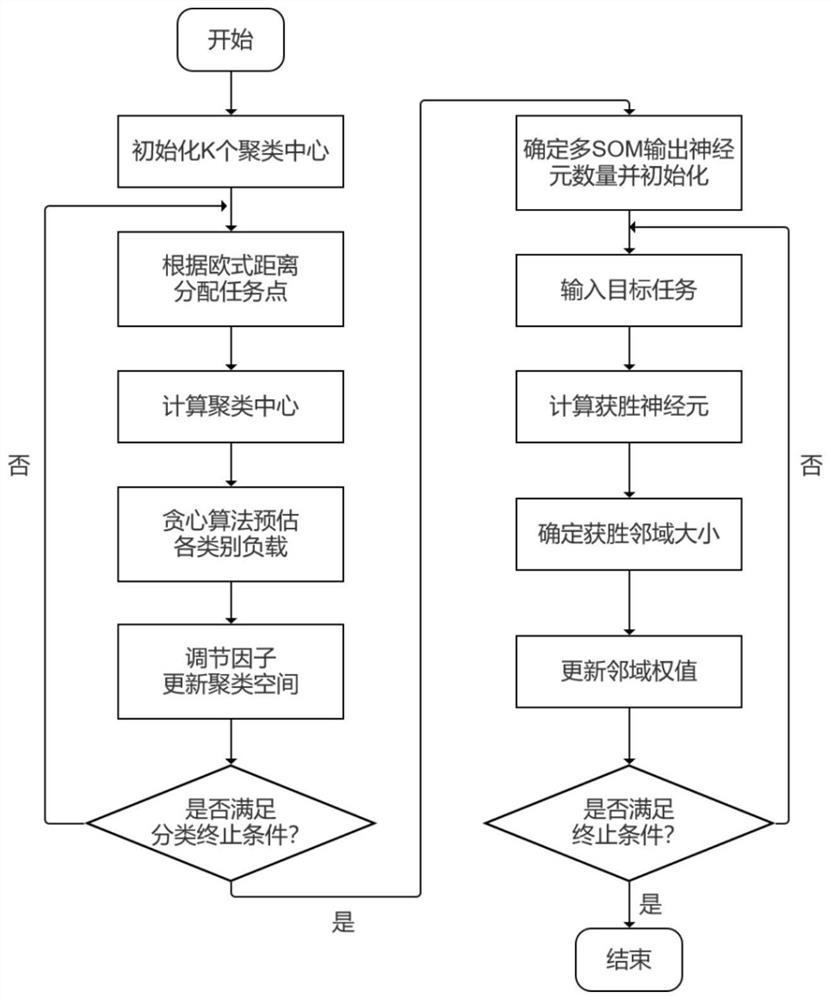
[0076] like figure 1 As shown, a greedy K-mean self-organized neural network multi-robot path planning method.
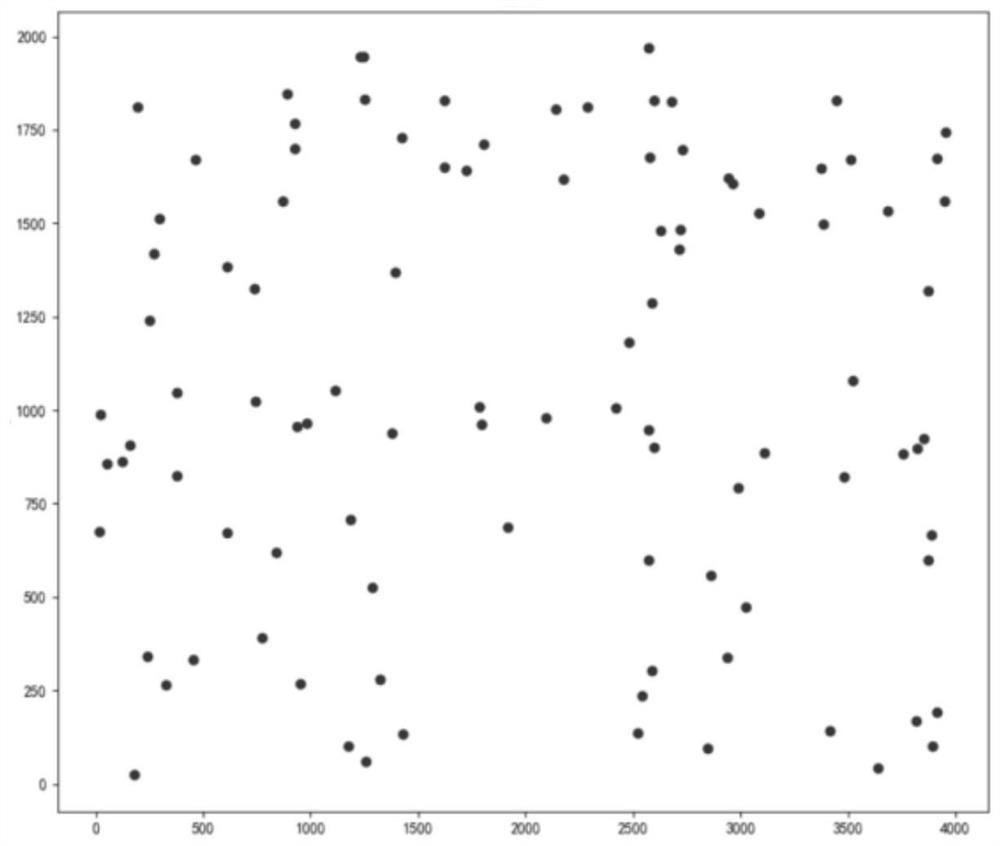
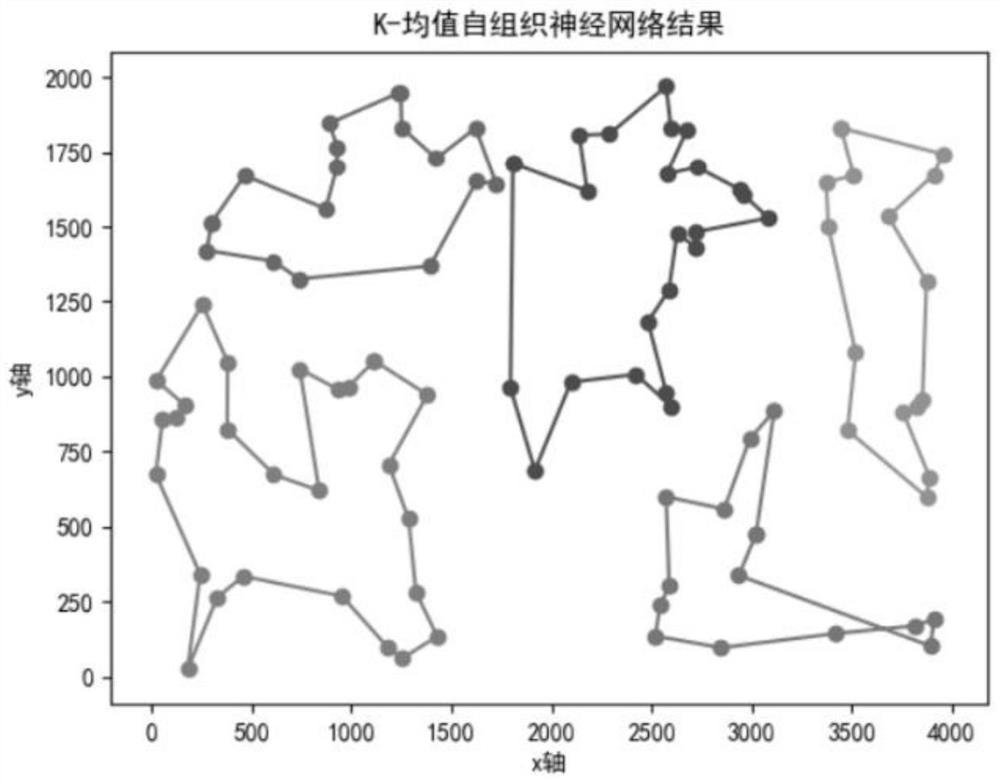
[0077] Take the standard travel provider TSPLIB dataset KRA100 as an example, figure 2 It is the original task data of Kroa100 data set, and the number of robots is 5 sets, using a greed of K-mean self-organizing neural network algorithm for multi-robot path planning.
[0078] Step 1: Use the greed K-mean algorithm to obtain the tasks required to each robot
[0079] Step 1.1: Start iteration, determine the number of clusters K, the maximum number of iterations greedykmeans_max_iter, the bias multiples δ, initialization K poly class c = {c = {C 1 , C 2 , ..., c k }.
[0080] Step 1.2: Calculate all task points g = {g 1 , g 2 , ..., g n } The European distance from the K polylass center, respectively.
[0081]
[0082] Where D ij Indicates task point g i To the cluster center C j European distance, (x i Y i ) Represents task point g i Position coordinates. (x j Y j ) Re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com