Rock mass homogeneous region division method based on improved concatenated table method
A contingency table and rock mass technology, applied in image analysis, image data processing, 3D modeling, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the coupling relationship of different attributes, reducing the accuracy of homogeneous area division, etc., achieving easy application, high The effect of precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
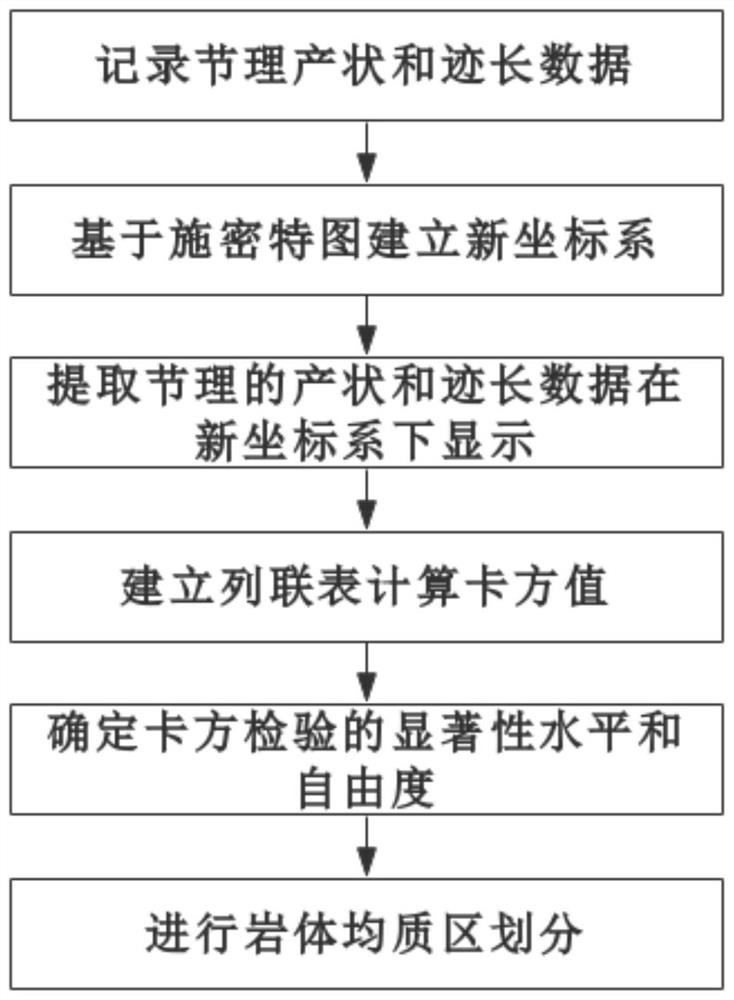
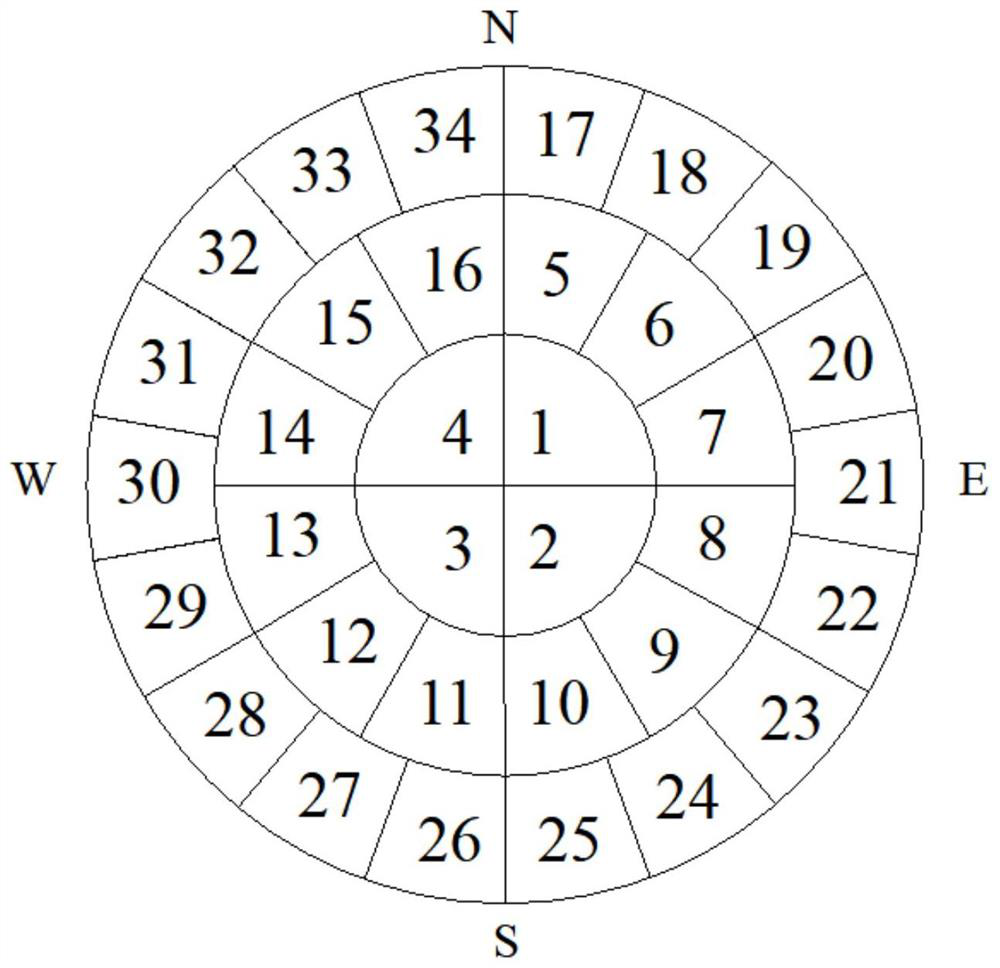
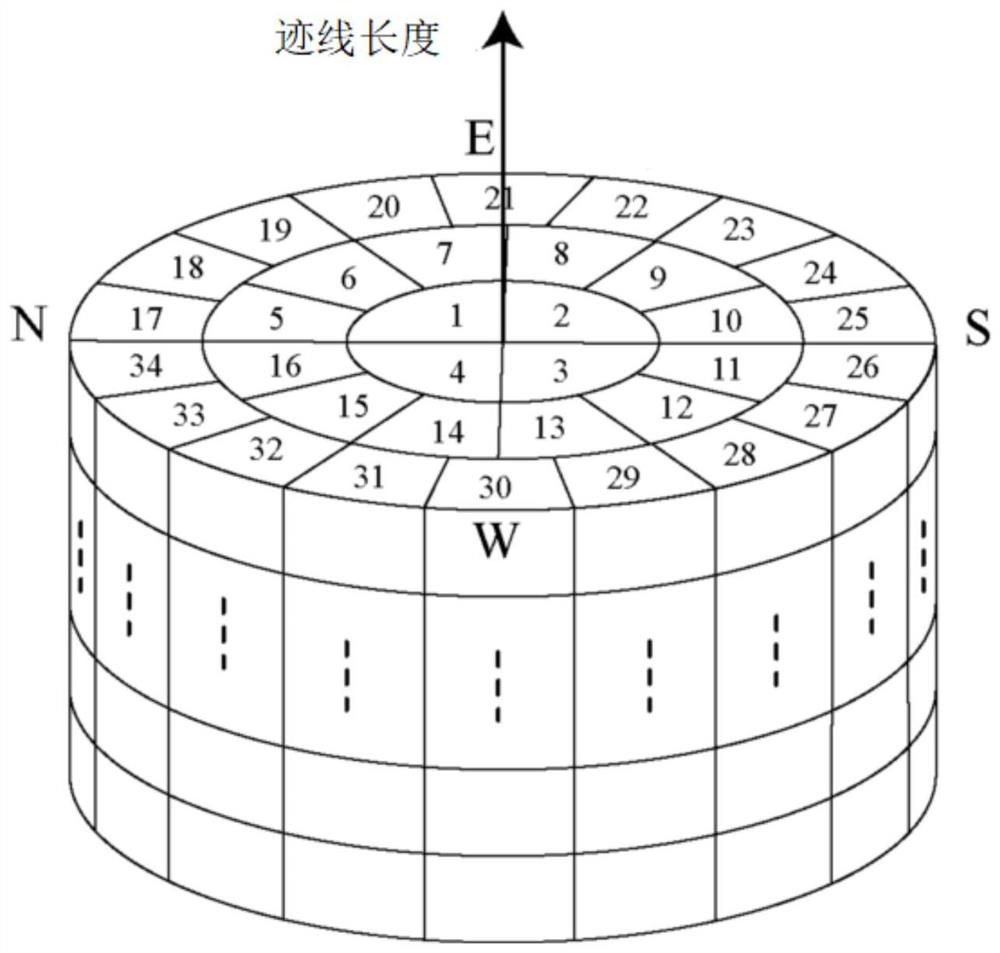
[0033] It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments of the present invention and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other. The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
[0034] In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments It is only some embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. The following description of at least one exemplary embodiment is merely illustrative in nature and in no way taken as limiting the invention, its application or uses. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordina...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com