Finite element analysis method for lattice material deformation mode
A technology of material deformation and analysis method, which is applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., and can solve problems such as cumbersome, inability to realize visualization and quantitative analysis, and inability to visualize analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
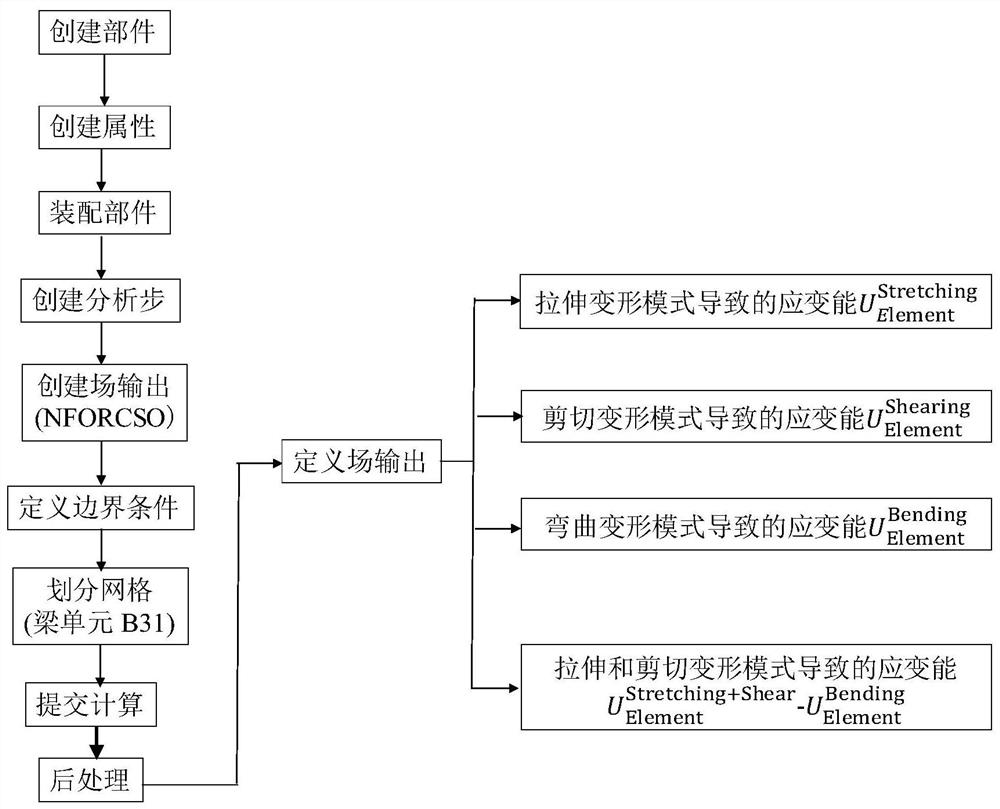
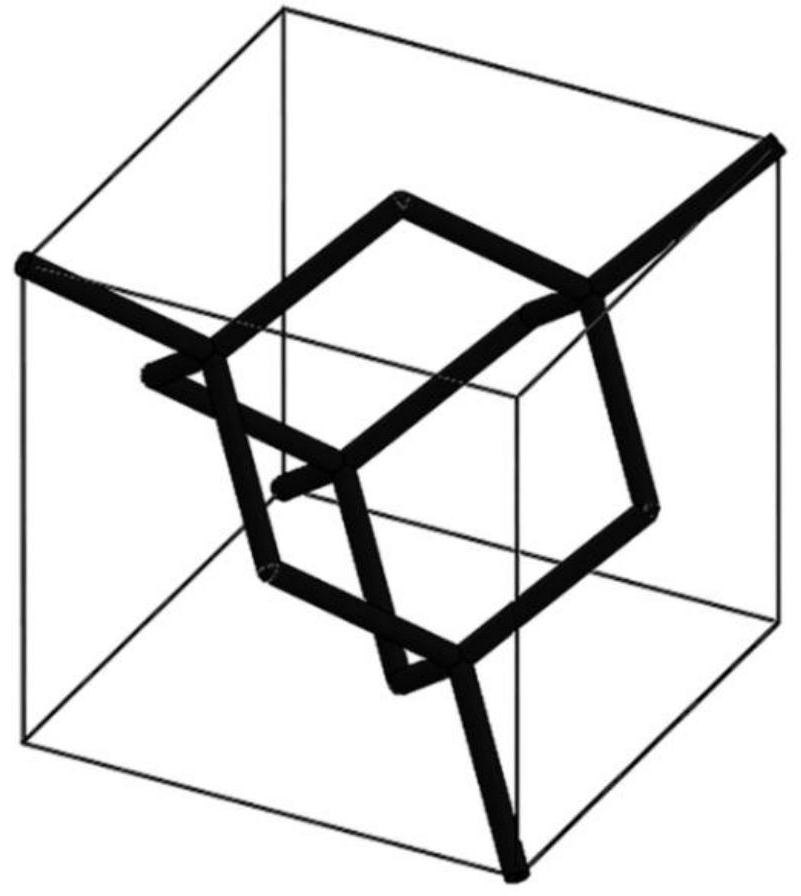
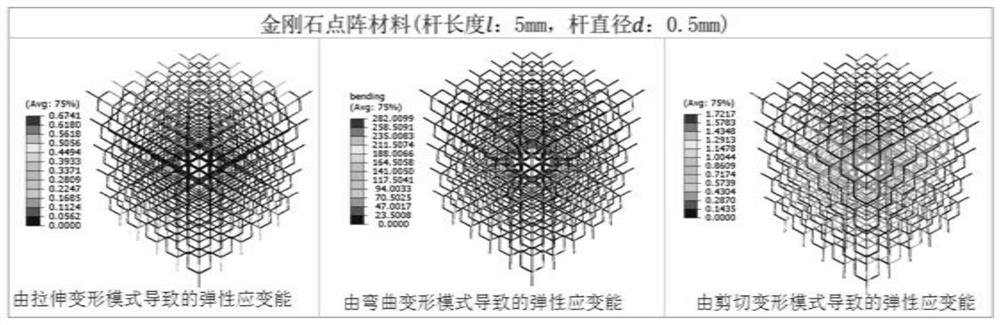
[0049] In this embodiment, the strain energy of the diamond model is quantitatively analyzed. In the diamond model ( figure 2 ) as an example, to obtain a lattice material whose slenderness is 10, adopt such as figure 1 The shown finite element analysis method obtains the strain energy distribution caused by the tensile deformation mode, bending deformation mode and shear deformation mode of the diamond lattice material as follows: image 3 As shown, the quantitative comparison of the strain energy caused by the above three deformation modes is shown in Table 1. It can be seen that the strain energy caused by the tensile deformation mode is much larger than that caused by the bending and shear deformation modes. When larger, diamond is a stretched lattice material.
[0050] Table 1: Strain energy due to different deformation modes in diamond as a function of slenderness
[0051]
[0052]
Embodiment 2
[0054]In this embodiment, a visual analysis of the strain energy of the diamond model as a function of the slenderness is performed. In the diamond model ( figure 2 ) as an example, analyze the strain energy caused by the tensile + shear deformation mode and the strain energy caused by only the bending deformation mode at different slenderness. When the slenderness is small, the strain energy caused by the tensile and shear deformation modes is greater than Strain energy due to bending deformation modes such as Figure 4 As shown, this visualization clearly rejects the Gibson-Ashby model's classification of diamond as a bend-dominated lattice material.
Embodiment 3
[0056] In this embodiment, the strain energy of the orthogonal dodecahedron model is quantitatively analyzed. In the orthogonal dodecahedron model ( Figure 5 ) as an example, to obtain a lattice material whose slenderness is 10, adopt such as figure 1 The shown finite element analysis method obtains the strain energy distribution caused by the tensile deformation mode, bending deformation mode and shear deformation mode of the orthogonal dodecahedral lattice material as follows: Figure 6 As shown, the quantitative comparison of the strain energy caused by the above three deformation modes is shown in Table 2. It can be seen that the strain energy caused by the tensile deformation mode is much larger than that caused by the bending and shear deformation modes. When larger, the orthogonal dodecahedron is a stretched lattice material.
[0057] Table 2: Variation of strain energy with slenderness due to different deformation modes in an orthorhombic dodecahedron
[0058]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com