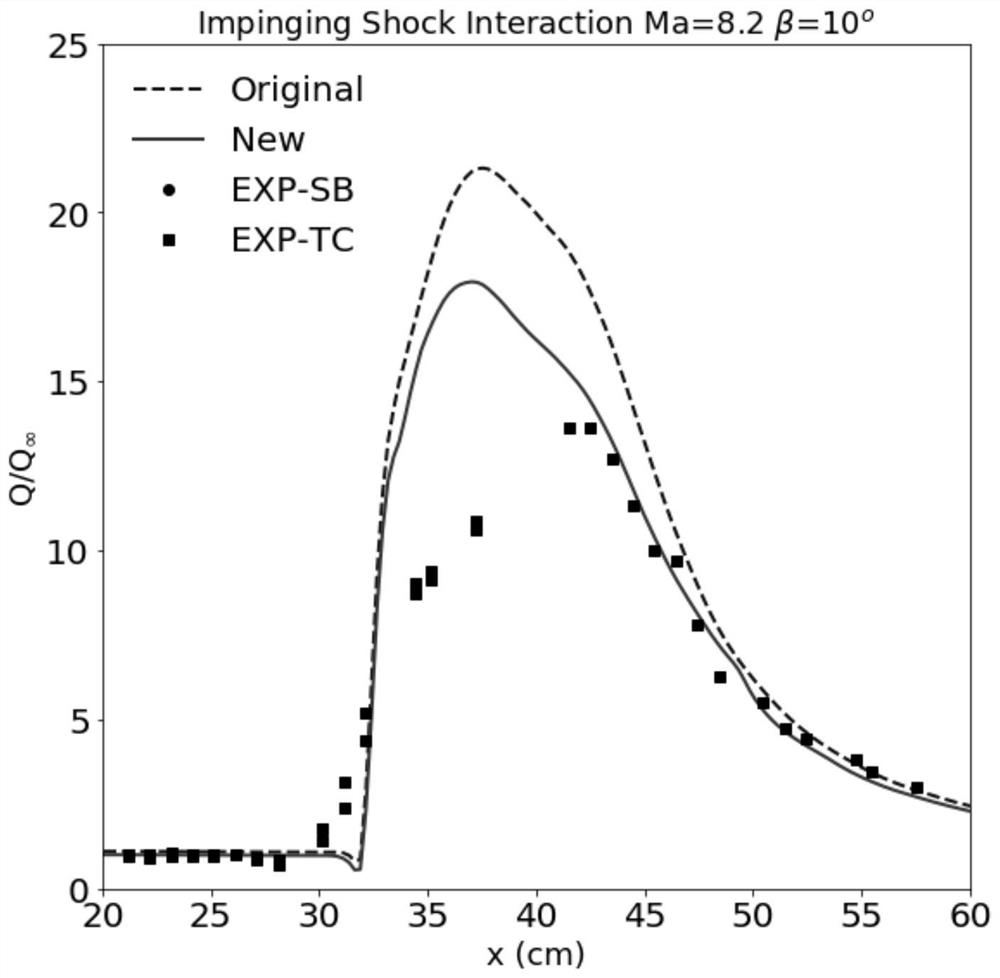
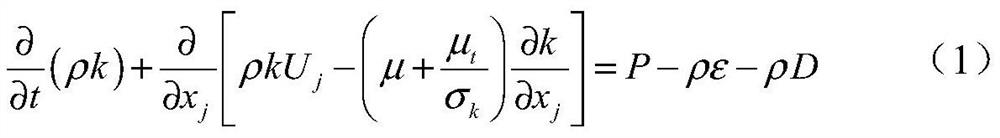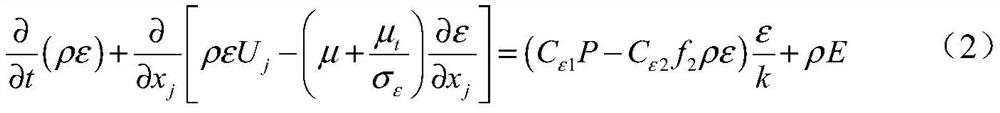A Compressible Correction Method Based on Launder-sharma k-epsilon Model
A model, turbulence model technology, applied in the field of computational fluid dynamics Reynolds-average turbulent numerical simulation, can solve the problem of high heat flow prediction in the separation zone, and achieve the effect of suppressing the turbulent viscosity coefficient, maintaining robustness, and reducing wall heat flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The invention discloses a compressible correction method based on the Launder-Sharma k-epsilon model. The Lauder-Sharma k-epsilon model:
[0036]
[0037]
[0038] where μ t =v t ρ, μ=νρ.
[0039] The viscosity coefficient in the prior art is:
[0040]
[0041] Among them, C ε1 ,C ε2 ,C μ ,σ ε , and σ k Represents a constant: C ε1 =1.44C ε2 =1.92C μ =0.09σ ε =1.3σ k =1;
[0042] Other,
[0043]
[0044]
[0045] where the turbulent Reynolds number R t =k 2 / (νε), the source term in the turbulence model equation is defined as:
[0046]
[0047]
[0048] A correction was added to the epsilon equation:
[0049]
[0050] where Y is the wall distance.
[0051] The method of the present invention constructs a compressible correction based on compressible flow characteristics, and defines the compressible correction as:
[0052]
[0053] Then, the viscosity coefficient formula is modified as:
[0054] Among them, the constant in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com