Unbalanced feature selection method based on global minimum redundancy
A feature selection method and minimum redundancy technology, applied in the direction of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer components, etc., can solve the problems of class imbalance and low classification accuracy, so as to ensure rich information and improve Classification effect, effect of reducing redundant relations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
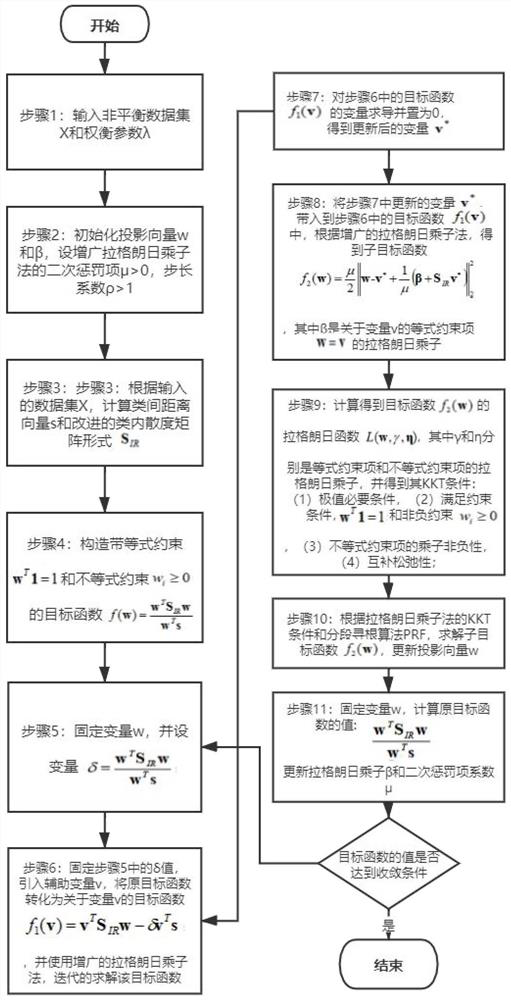
[0047] combined with figure 1 It can be seen that the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0048] Input: unbalanced dataset X, trade-off parameter λ∈[0,1]. where X={x 1 ,x 2 ,...x n},x i =[x 1 (i),x 2 (i),...,x d (i)], f i Represents the i-th feature, and the class label of the sample is represented as y i ∈{0,1}. For the convenience of expression, the samples belonging to the class c ∈ {0,1} are expressed as The number of samples of category c is n c , while the mean vector of class c is expressed as μ c ∈ R d×1 , μ ∈ R d×1 is the overall mean vector.
[0049] Step 1: Initialize the projection vector w ∈ R d×1 and β∈R d×1 , assuming that the penalty coefficient of the quadratic term of the augmented Lagrange multiplier method μ>0, and the step coefficient ρ>1 of the augmented Lagrange method;
[0050] Step 2: According to the input data set X, calculate the inter-class distance vector s∈R d×1 and the improved within-class scatter matrix form S ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com