Point cloud registration strategy in flatness measurement of laser contourgraph
A laser profiler and point cloud registration technology, which is applied to measurement devices, instruments, optical devices, etc., can solve the problems of long calculation time and insufficiency, difficulty in obtaining effective local features, and low rough registration accuracy. The effect of ideal flatness measurement results and improved registration accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
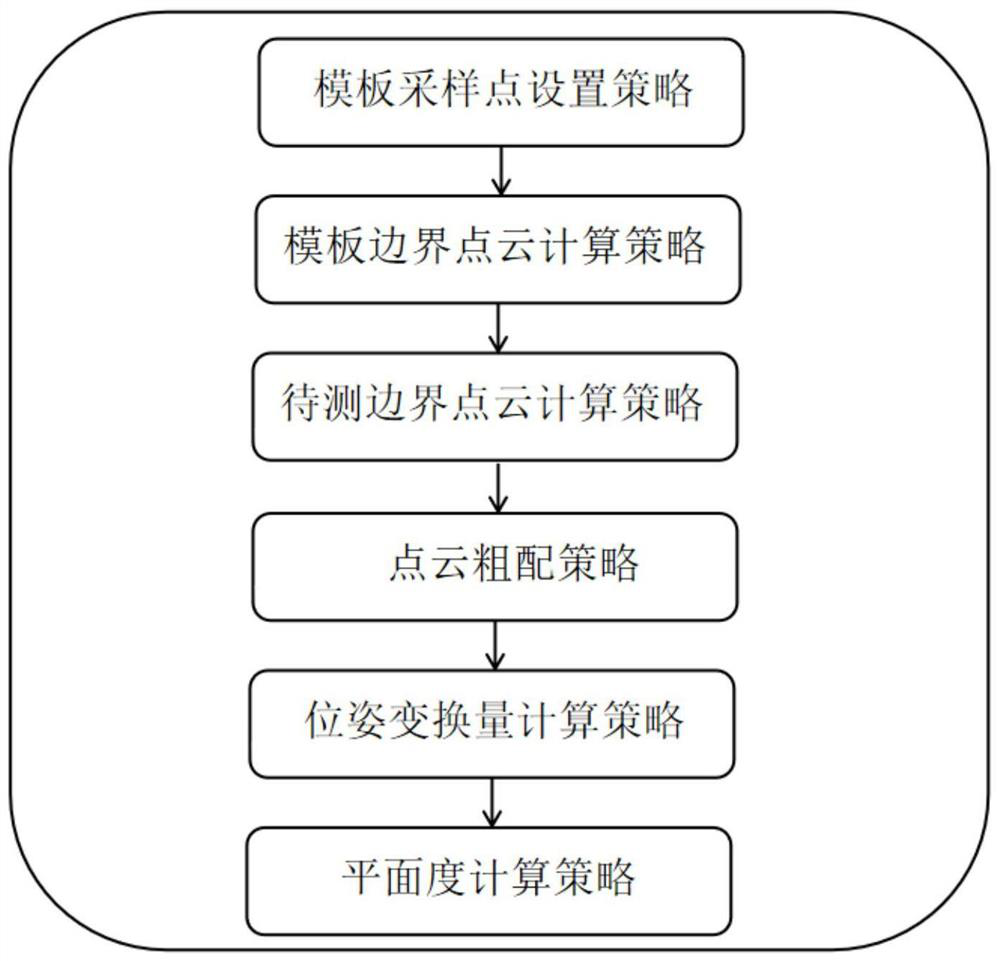
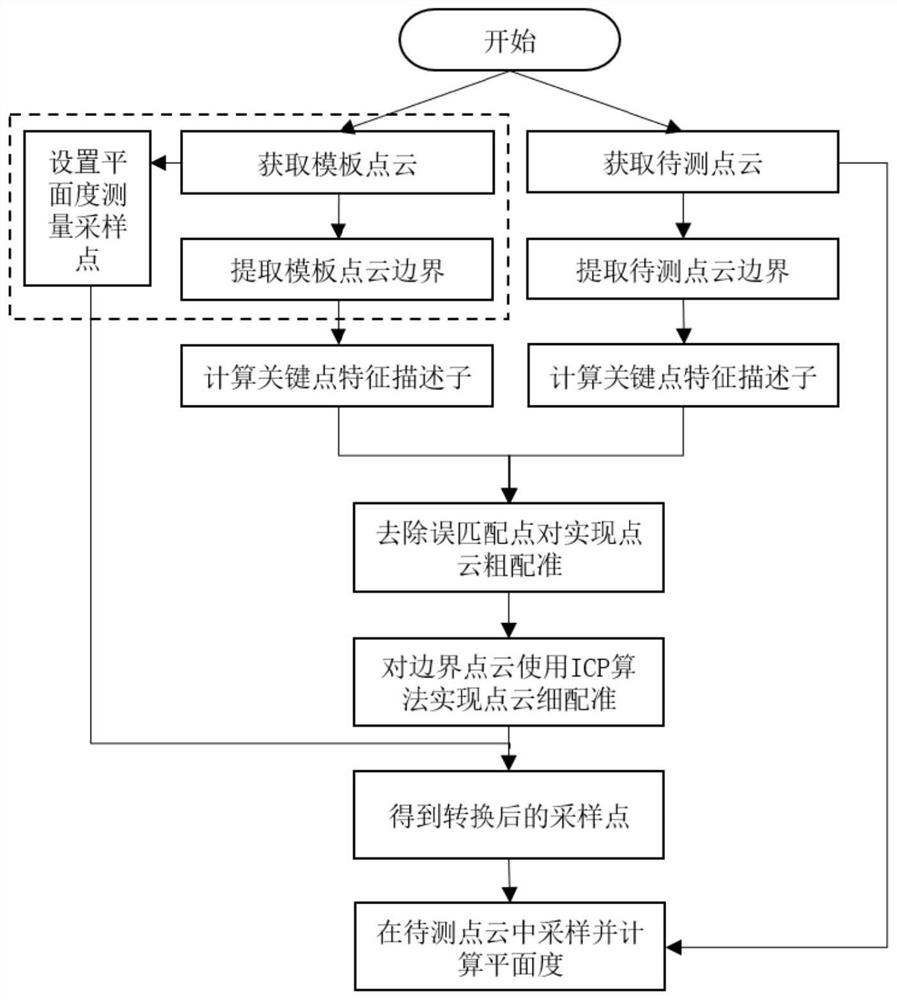
[0071] Such as figure 1 As shown, the point cloud registration strategy in laser profiler flatness measurement includes template sampling point setting steps, template boundary point cloud calculation steps, boundary point cloud calculation steps to be measured, point cloud rough matching steps, and pose transformation calculation steps steps and flatness calculation steps;
[0072] Such as figure 2 As shown, the template sampling point setting step obtains a point cloud of an object to be measured as a template point cloud, and sets sampling points in the template point cloud;
[0073] In the template boundary point cloud calculation step, the template point cloud is used as the original point cloud input point cloud boundary extraction algorithm, and the output boundary point cloud is used as the template boundary point cloud;
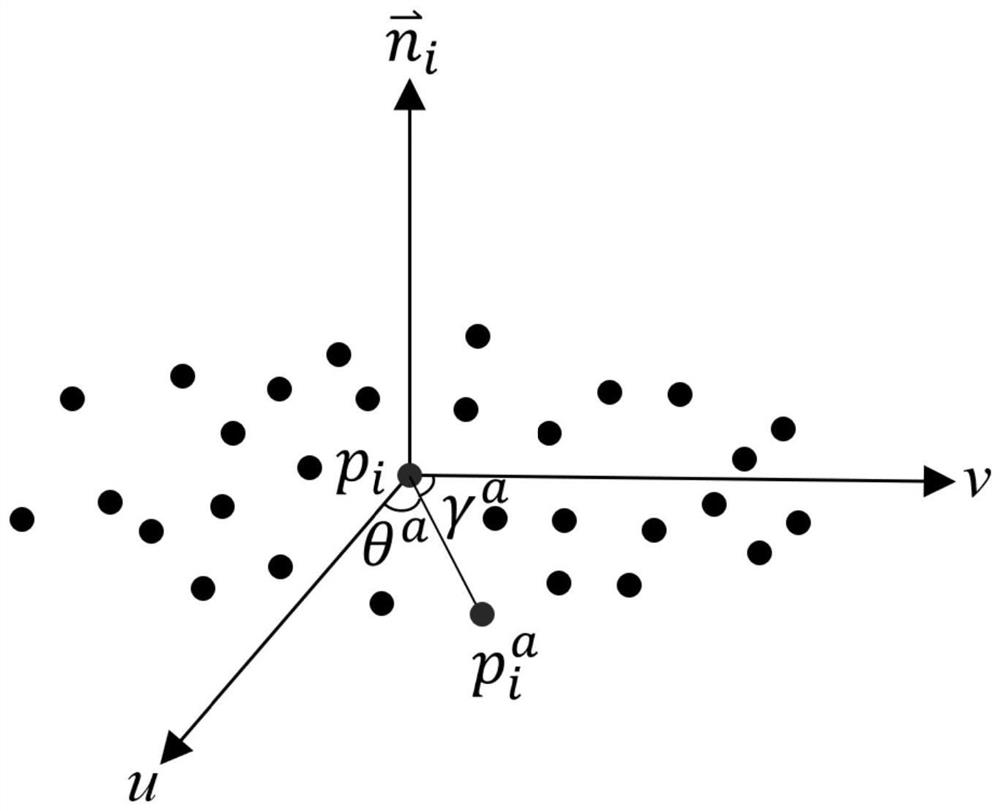
[0074] The step of calculating the boundary point cloud to be measured is to obtain the point cloud information of the object to be measured as t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com