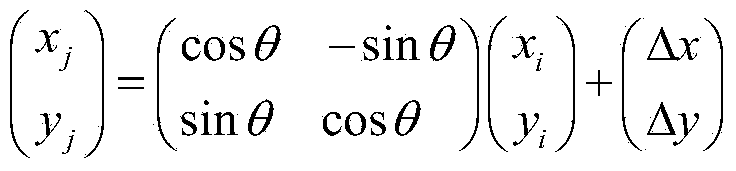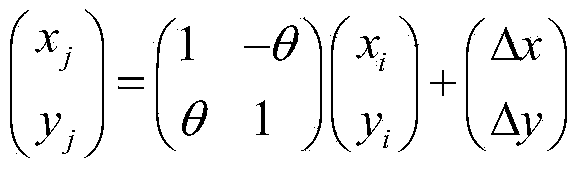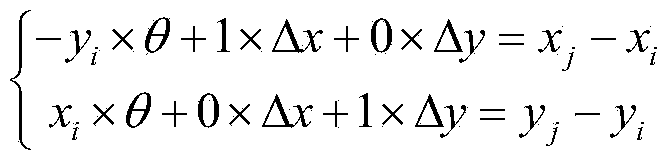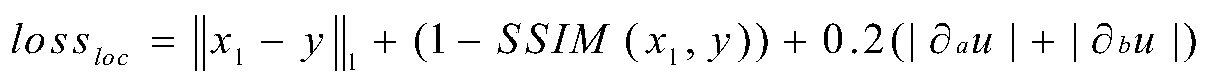Patents
Literature
97results about How to "Improve registration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
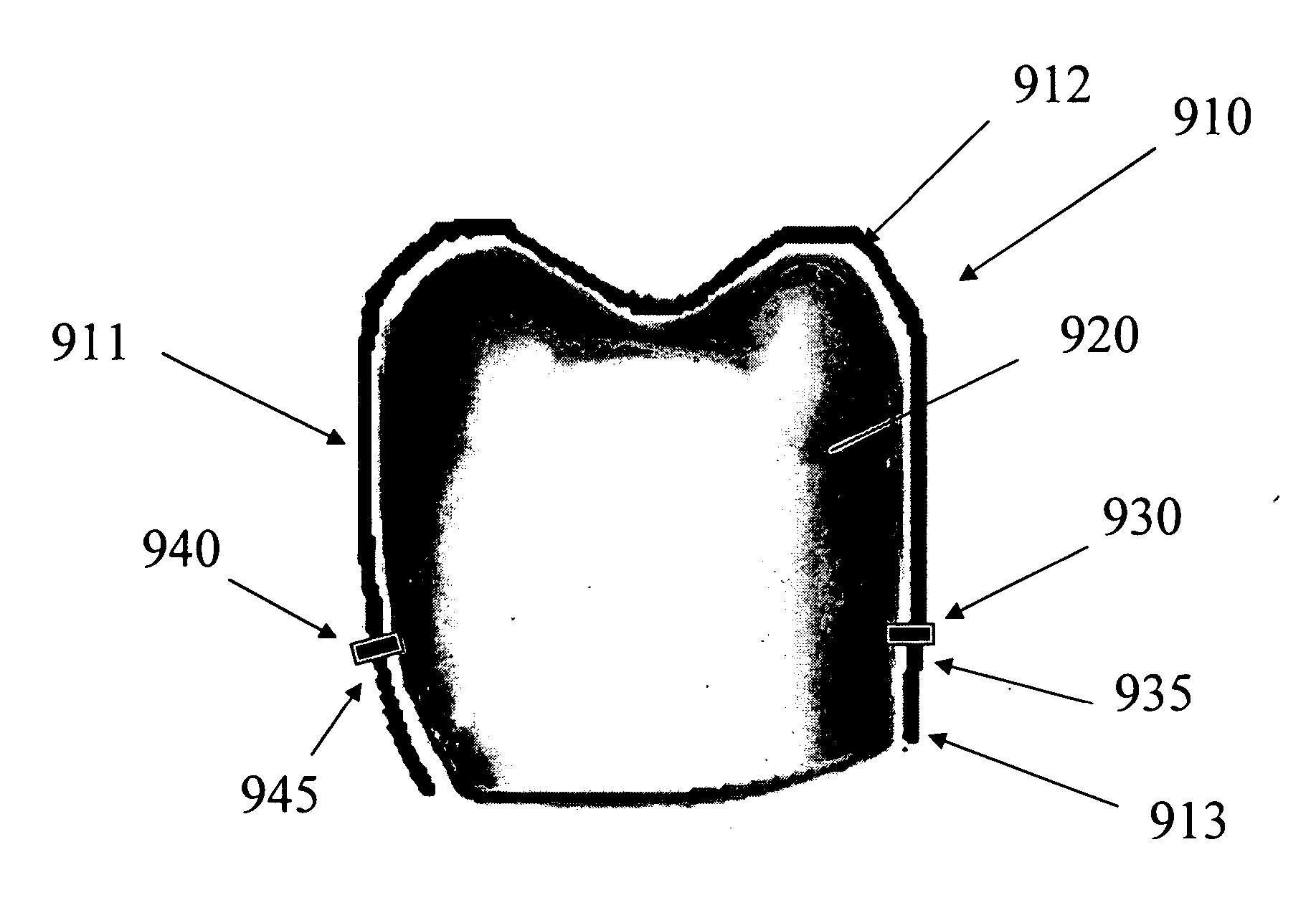
Dental aligner devices having snap-on connectors
InactiveUS20060234179A1Improve accuracy and effectivenessReduce numberOthrodonticsDental toolsOrthodontic BraceEngineering
A system for producing corrective movement in a subject's teeth includes a dental aligner device having one or more through-holes and one or more connectors fixed to the subject's teeth. The connectors can snap into the through-holes when the dental aligner is worn on the subject's teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
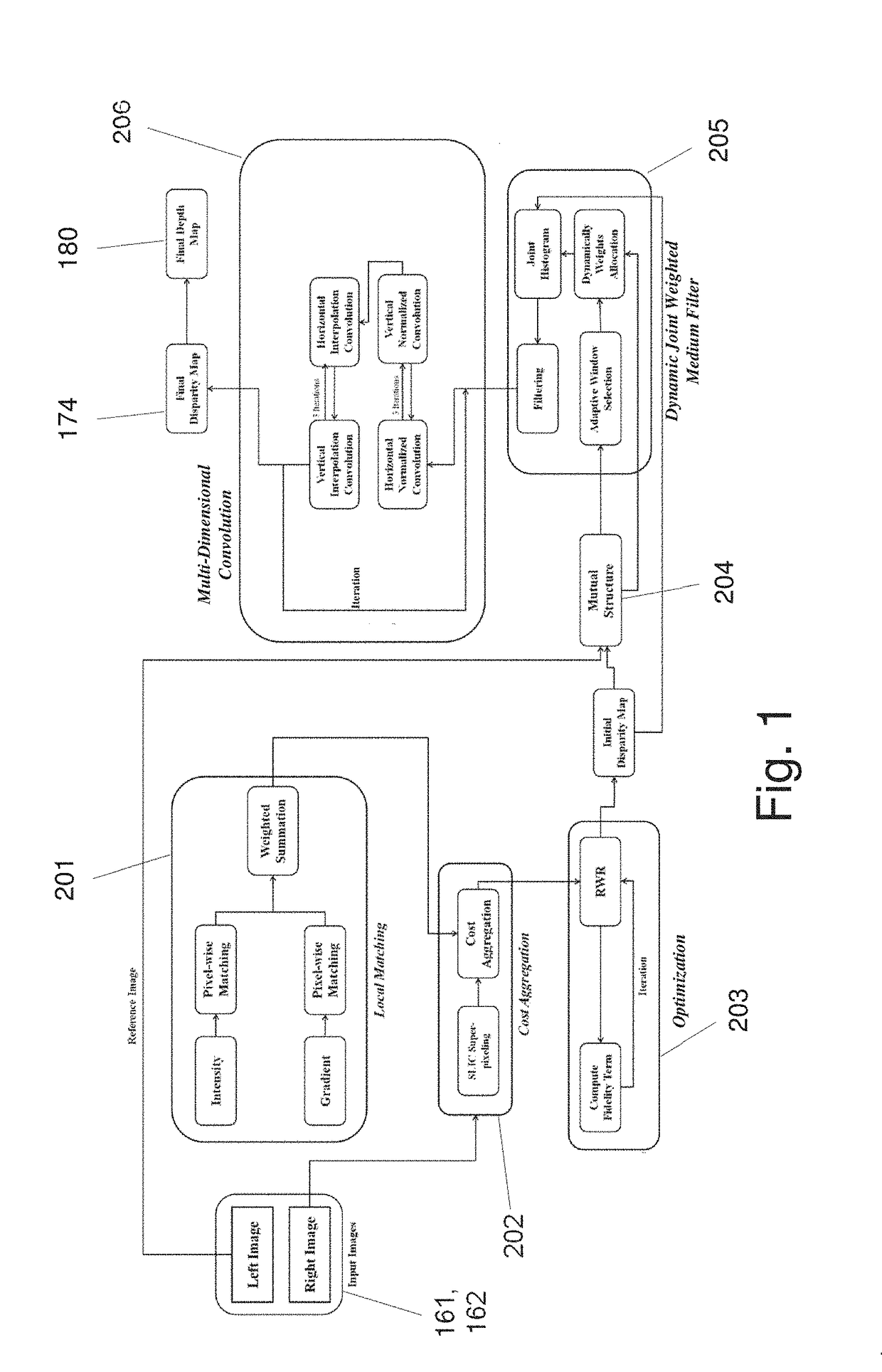
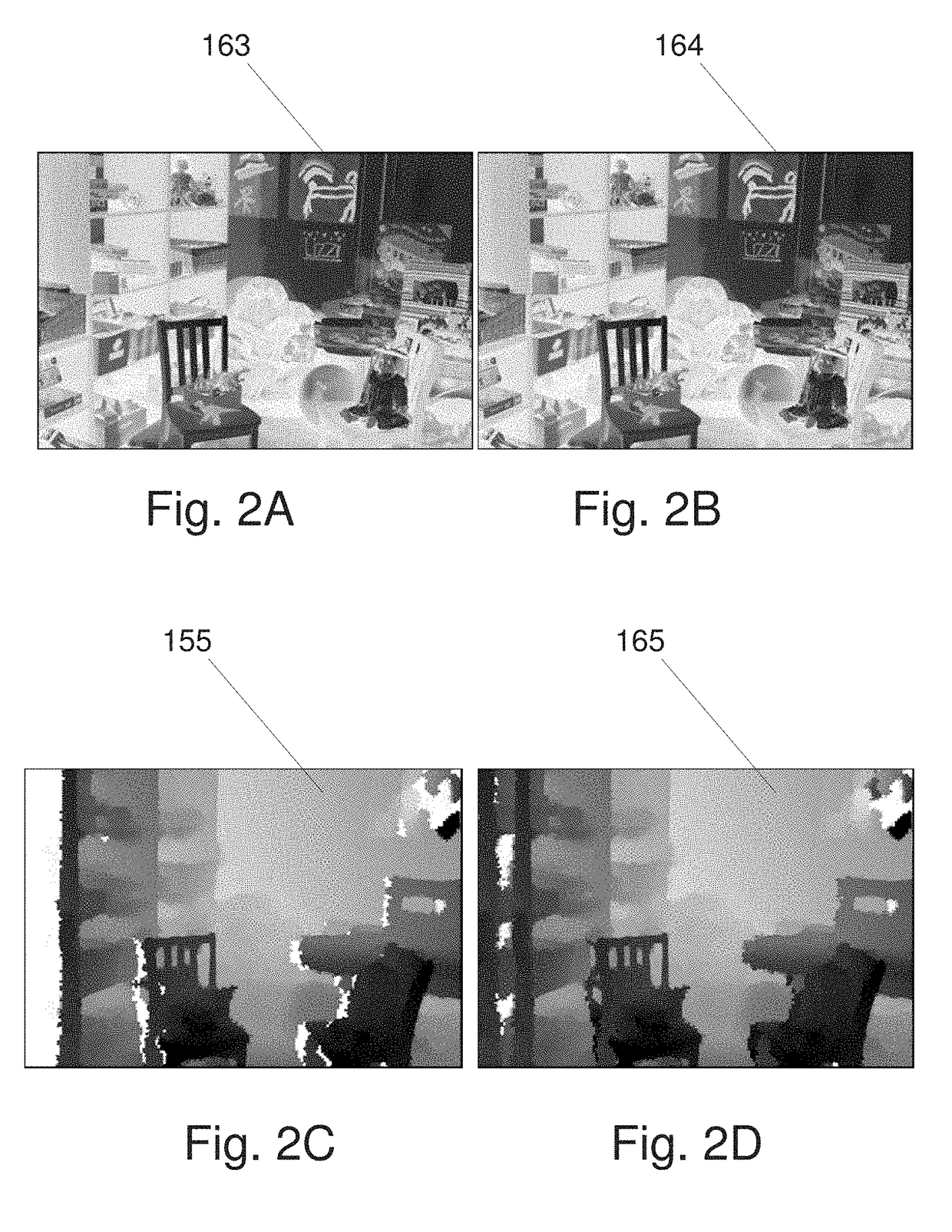
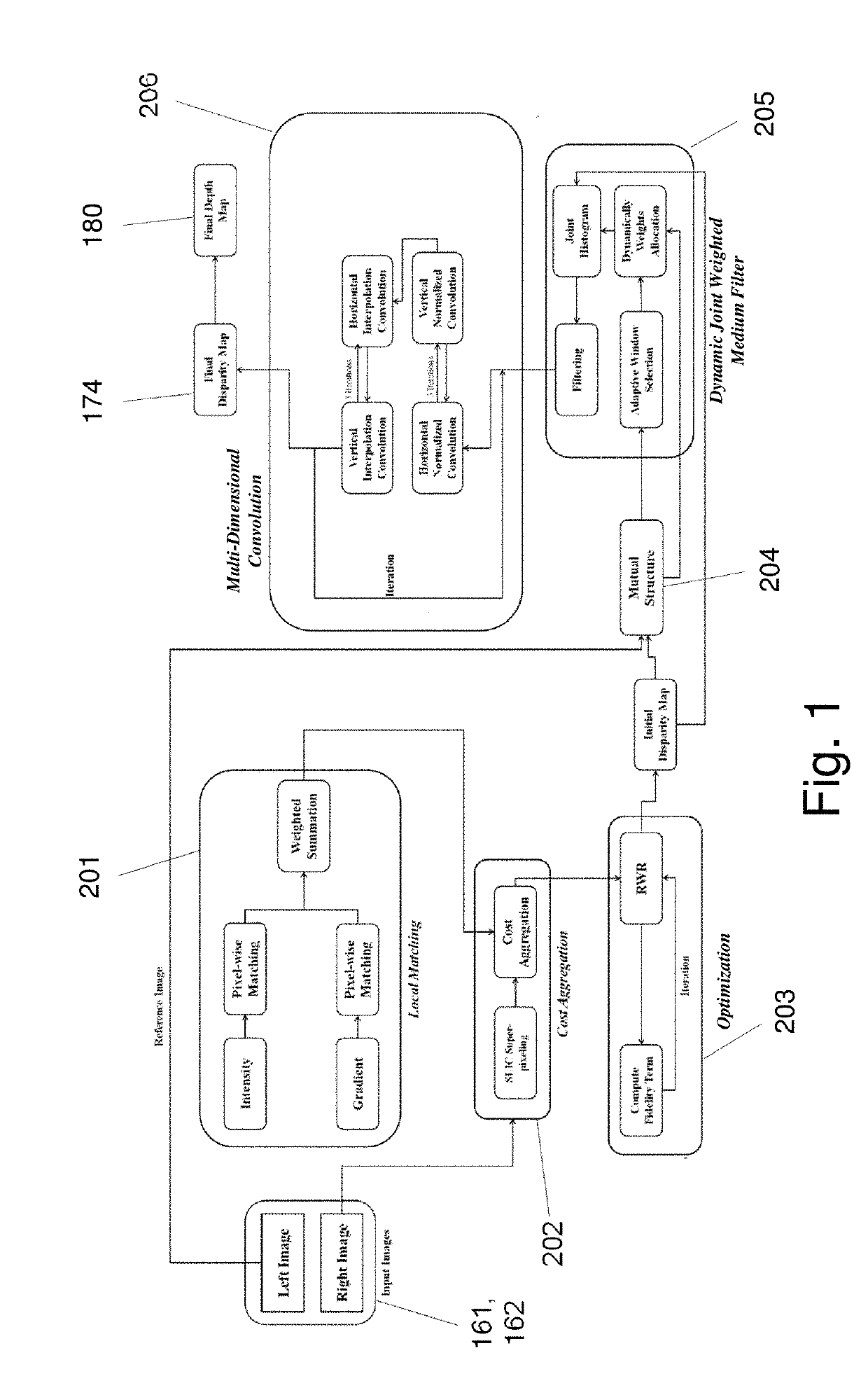
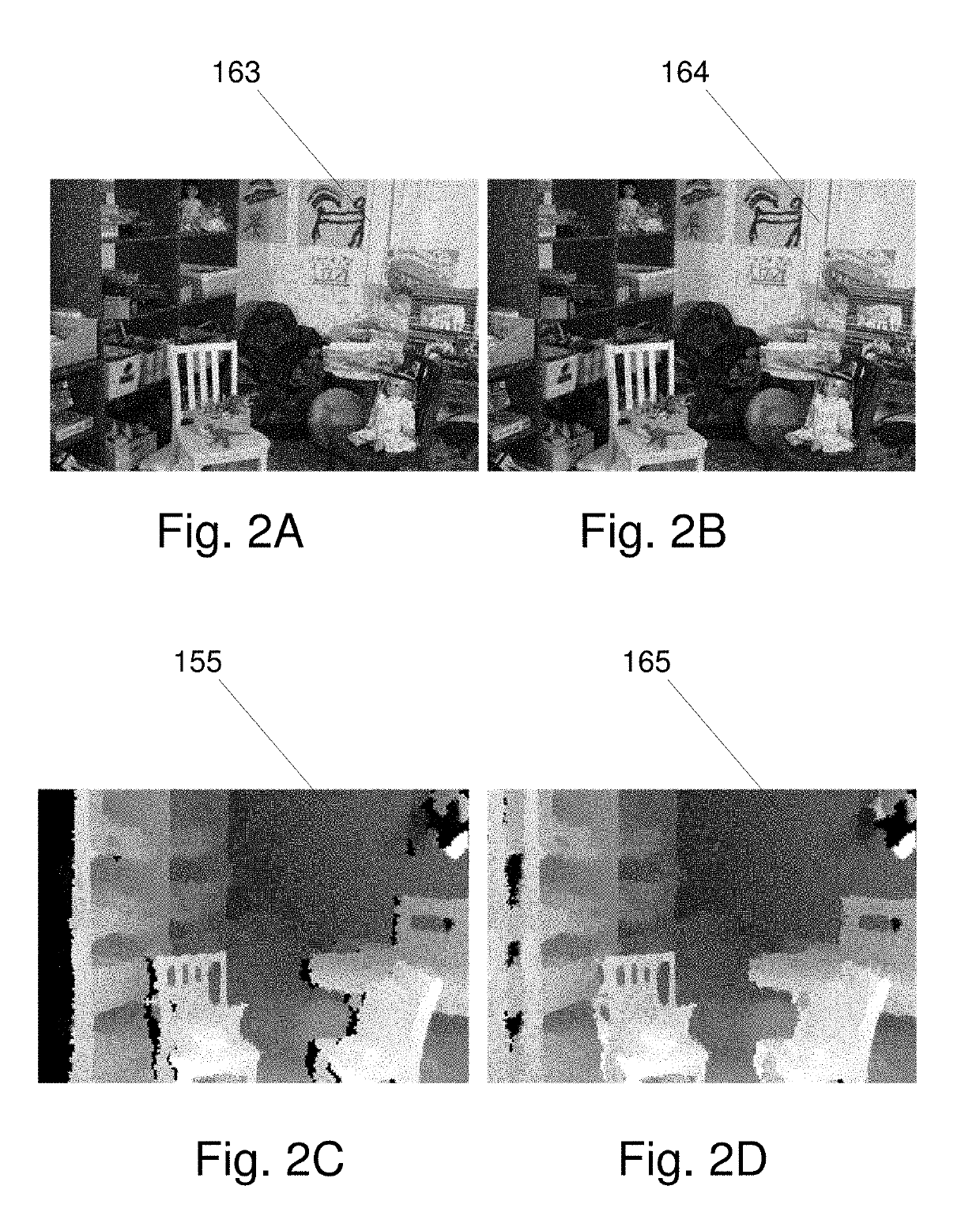
Systems and Methods for Estimating and Refining Depth Maps
ActiveUS20180027224A1Improved image registrationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxData value
A method for improving accuracy of depth map information derived from image data descriptive of a scene. In one embodiment Mutual Feature Map data are created based on initial disparity map data values and the image data descriptive of the scene. The Mutual Feature Map data are applied to create a series of weighting functions representing structural details that can be transferred to the first disparity values to restore degraded features or replace some of the first disparity values with values more representative of structural features present in the image data descriptive of the scene.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
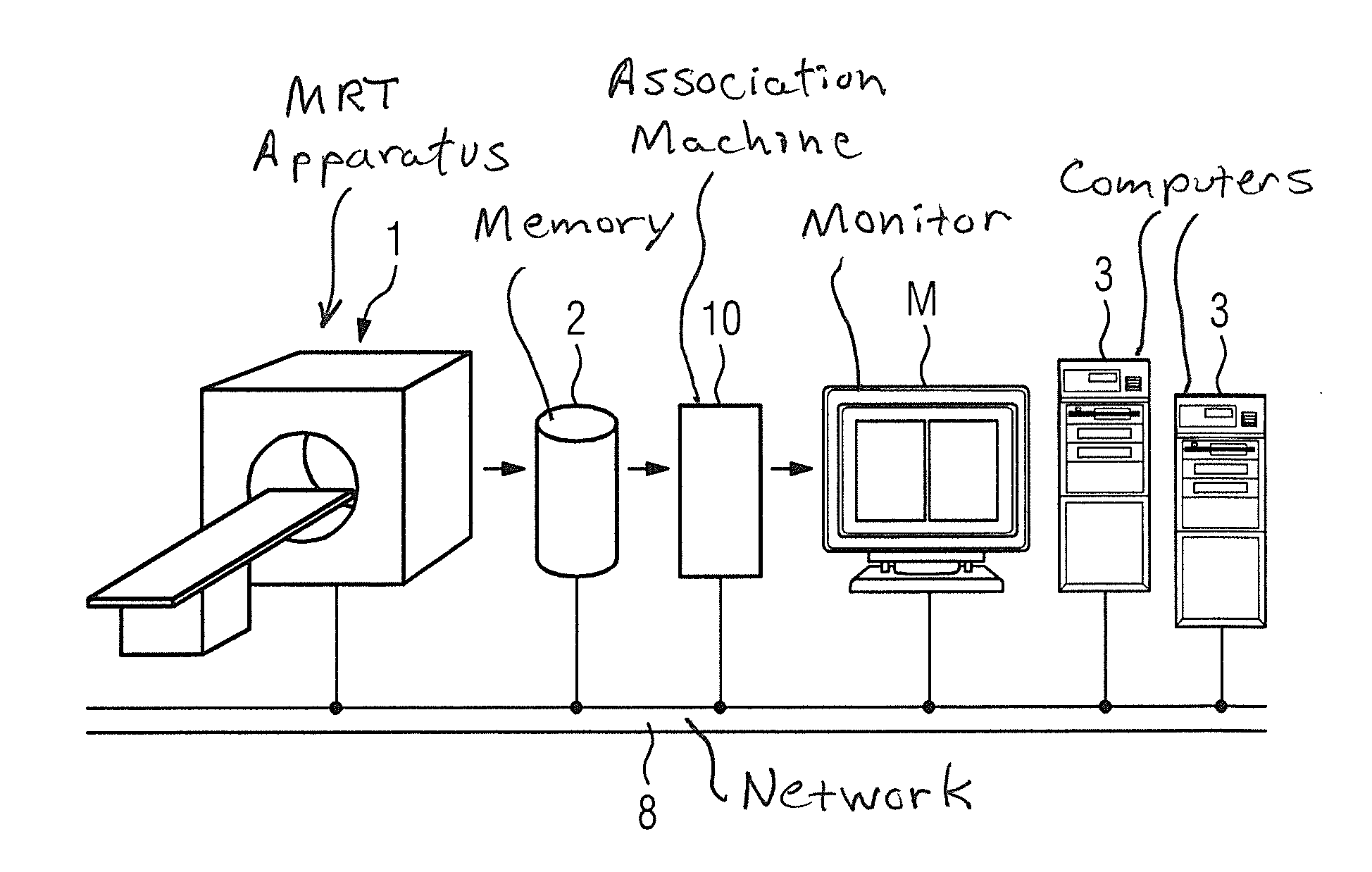
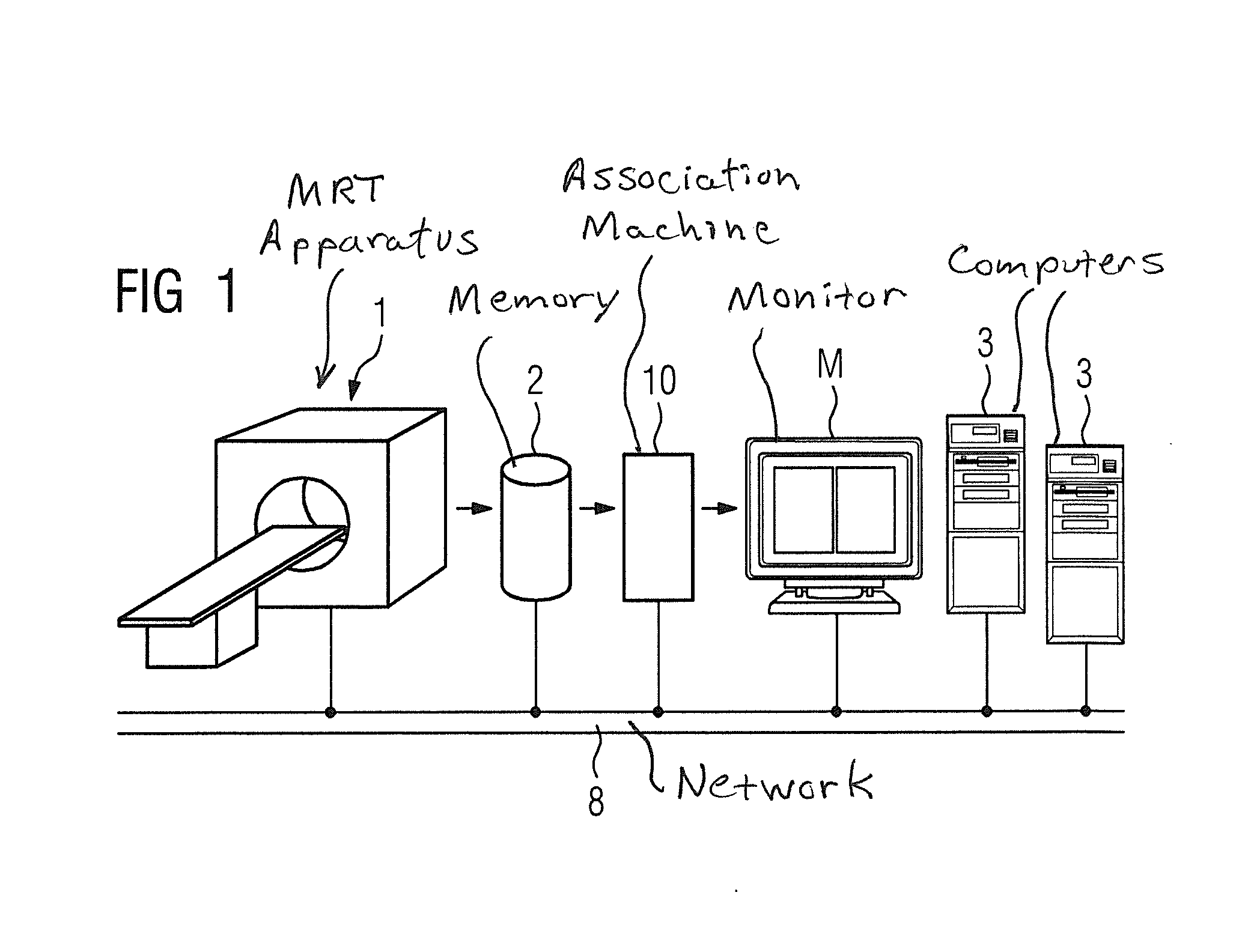
Automatic registration of image pairs of medical image data sets
InactiveUS20130195329A1Efficient use ofGood for conservationImage enhancementImage analysisDICOMData set
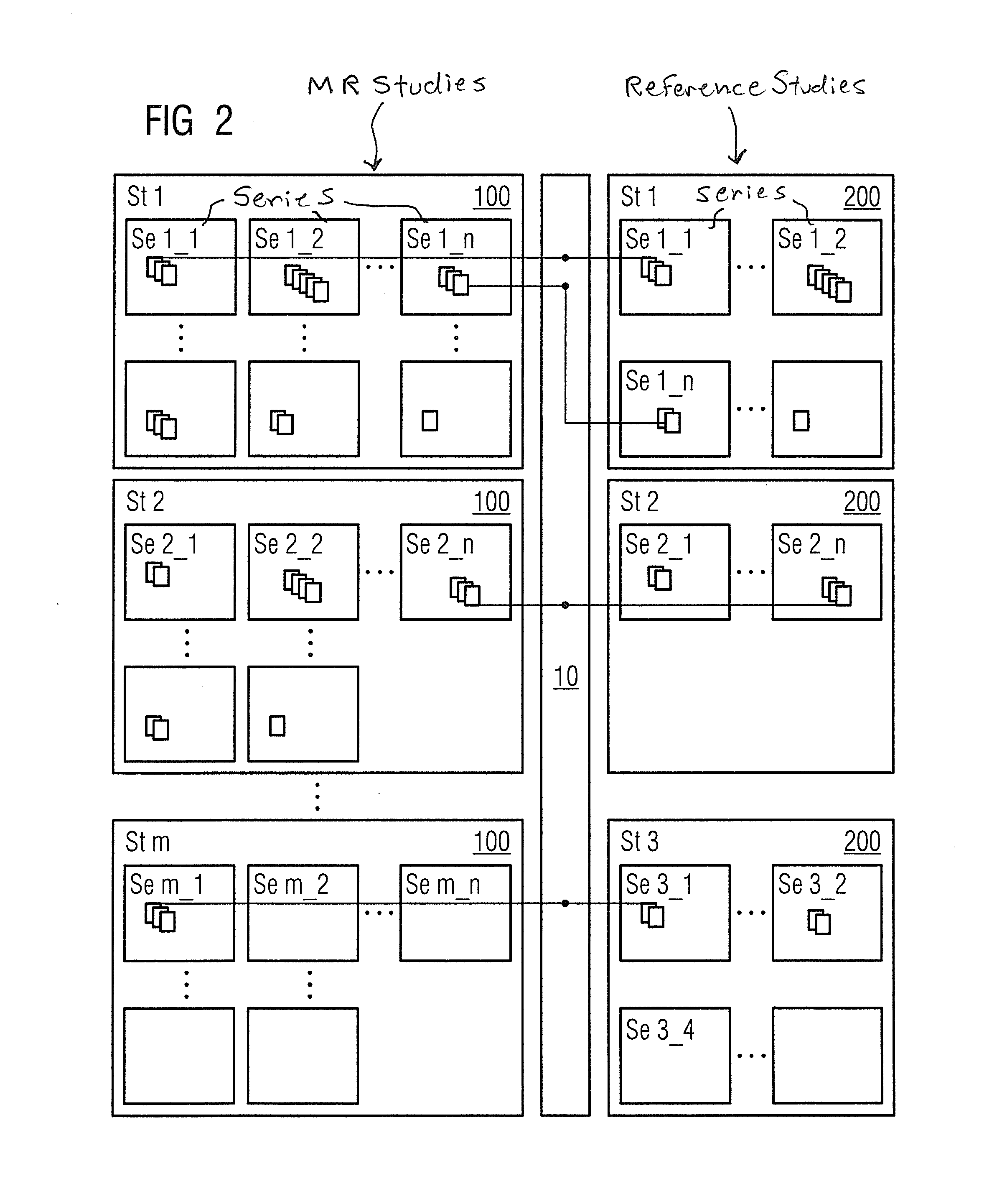
In a method, device and storage medium encoded with programming instructions for automatic image registration of image data of a current medical image MR study and at least one reference study, corresponding image pairs of the current study and the reference study are formed automatically with an association machine without needing the analyze the respective image data or pixel data. The pair determination takes place exclusively on the basis of the DICOM header data. A synchronized image processing and / or presentation of the generated image pairs takes place at a monitor.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
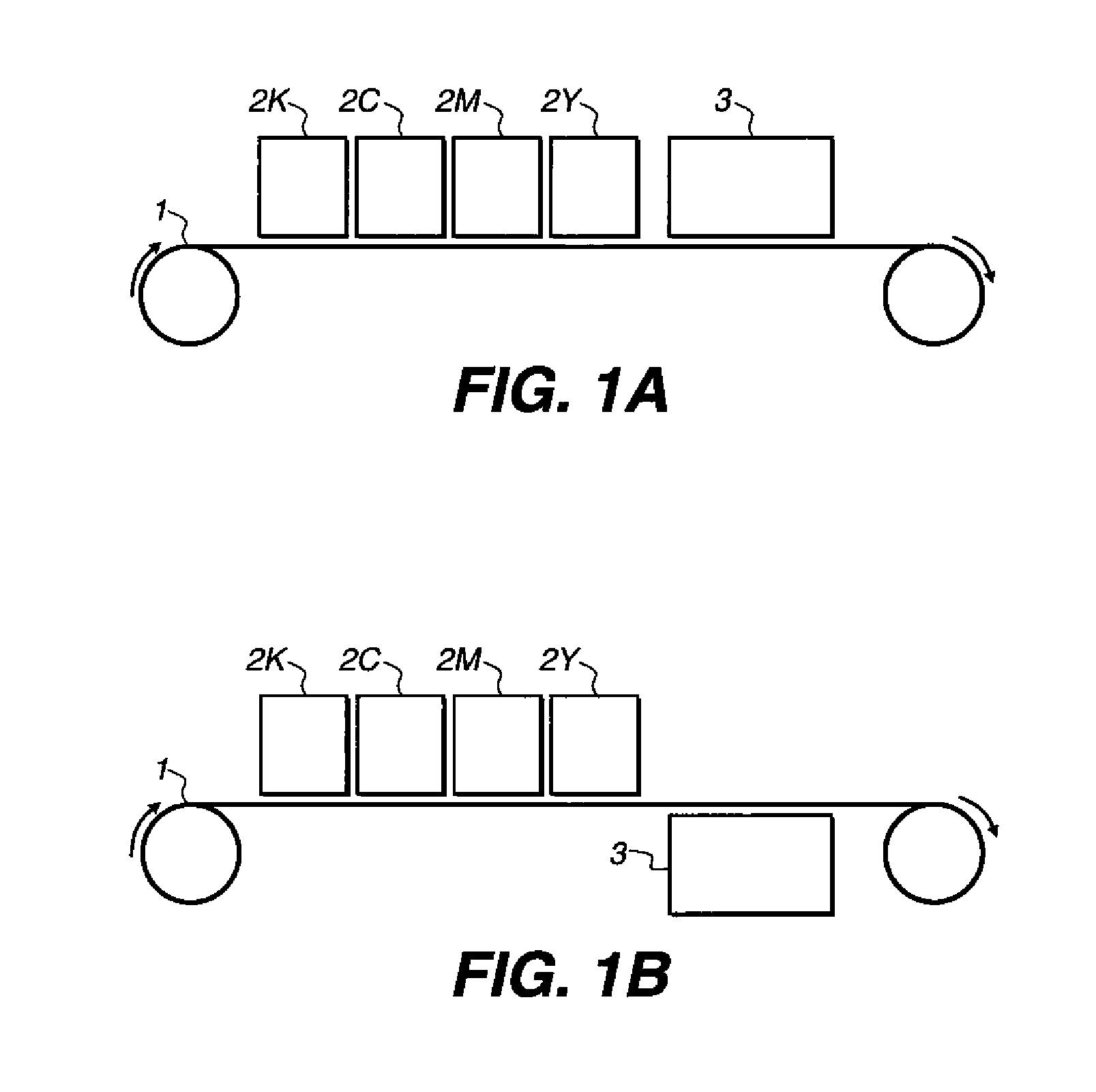
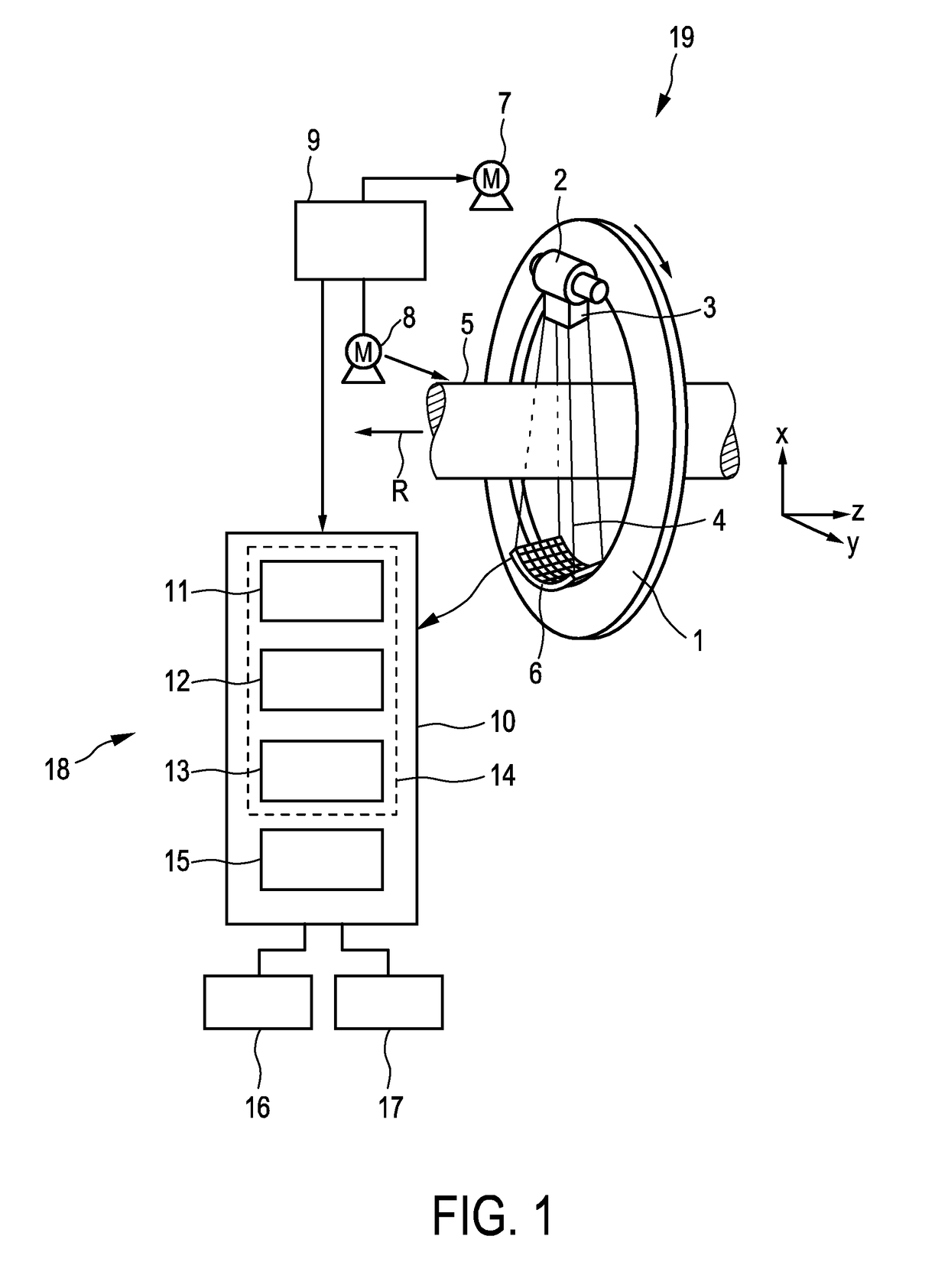
Image registration device
ActiveUS20060062488A1Improve registrationWithout affecting productivityCharacter and pattern recognitionElectrographic process apparatusComputer scienceImage registration
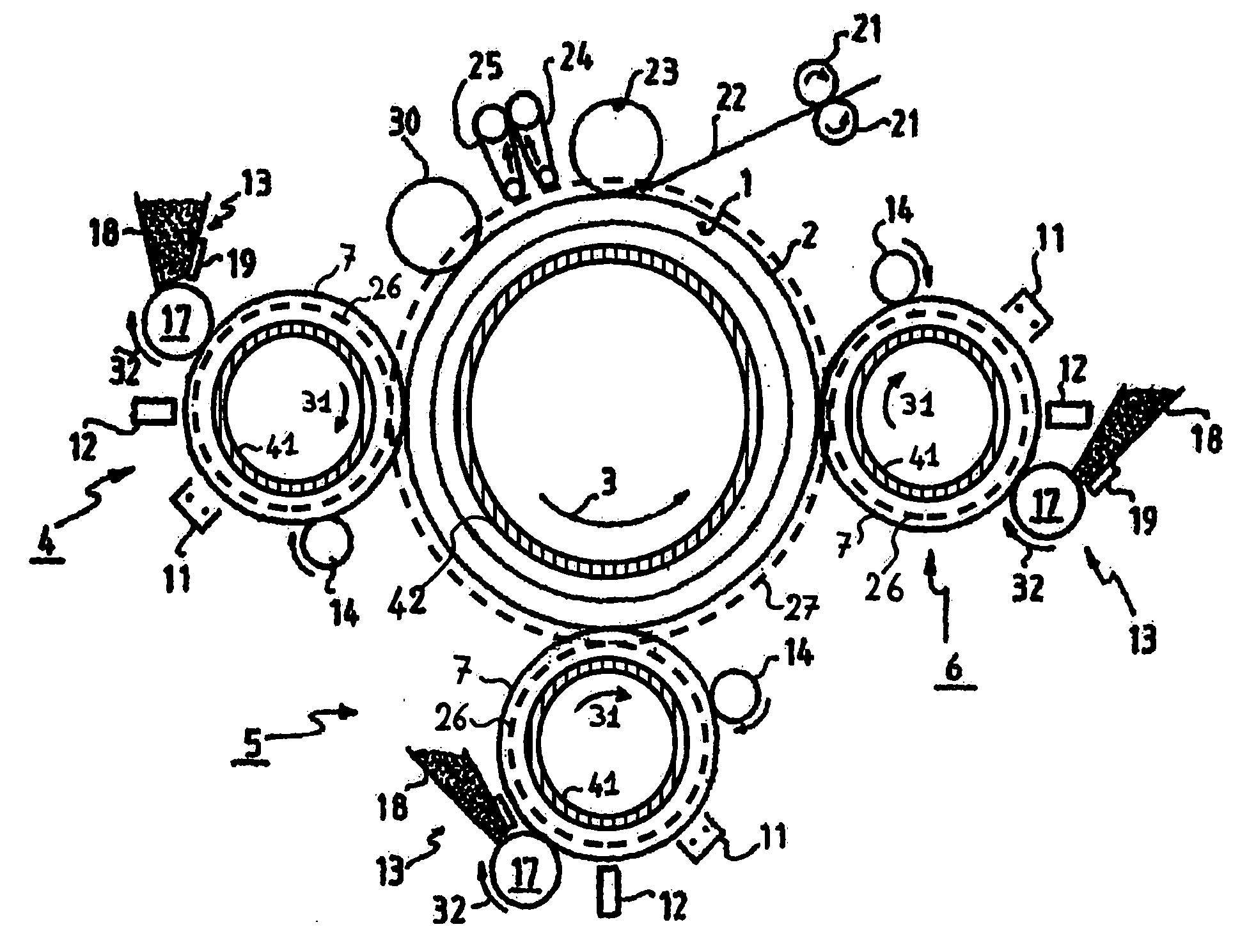
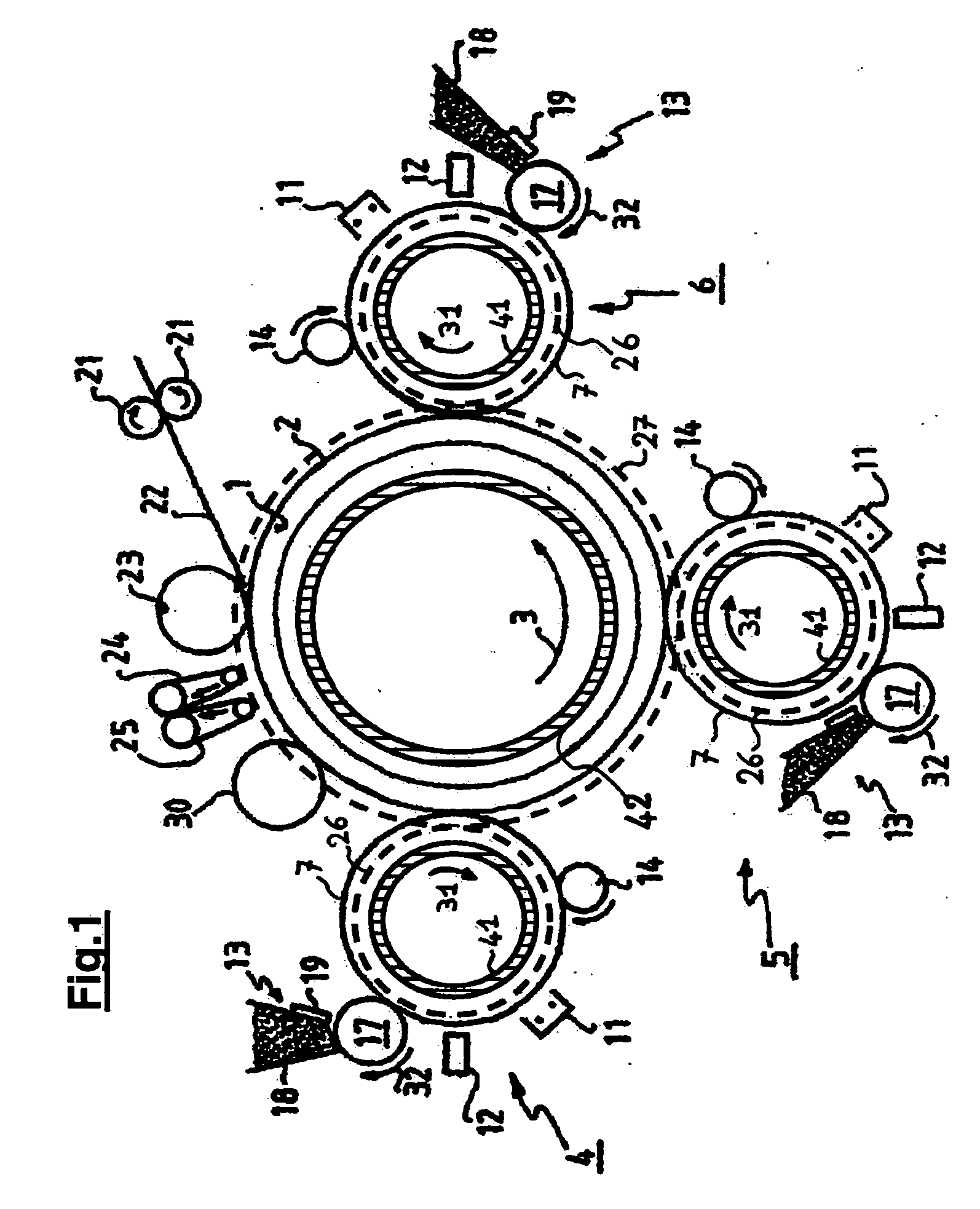
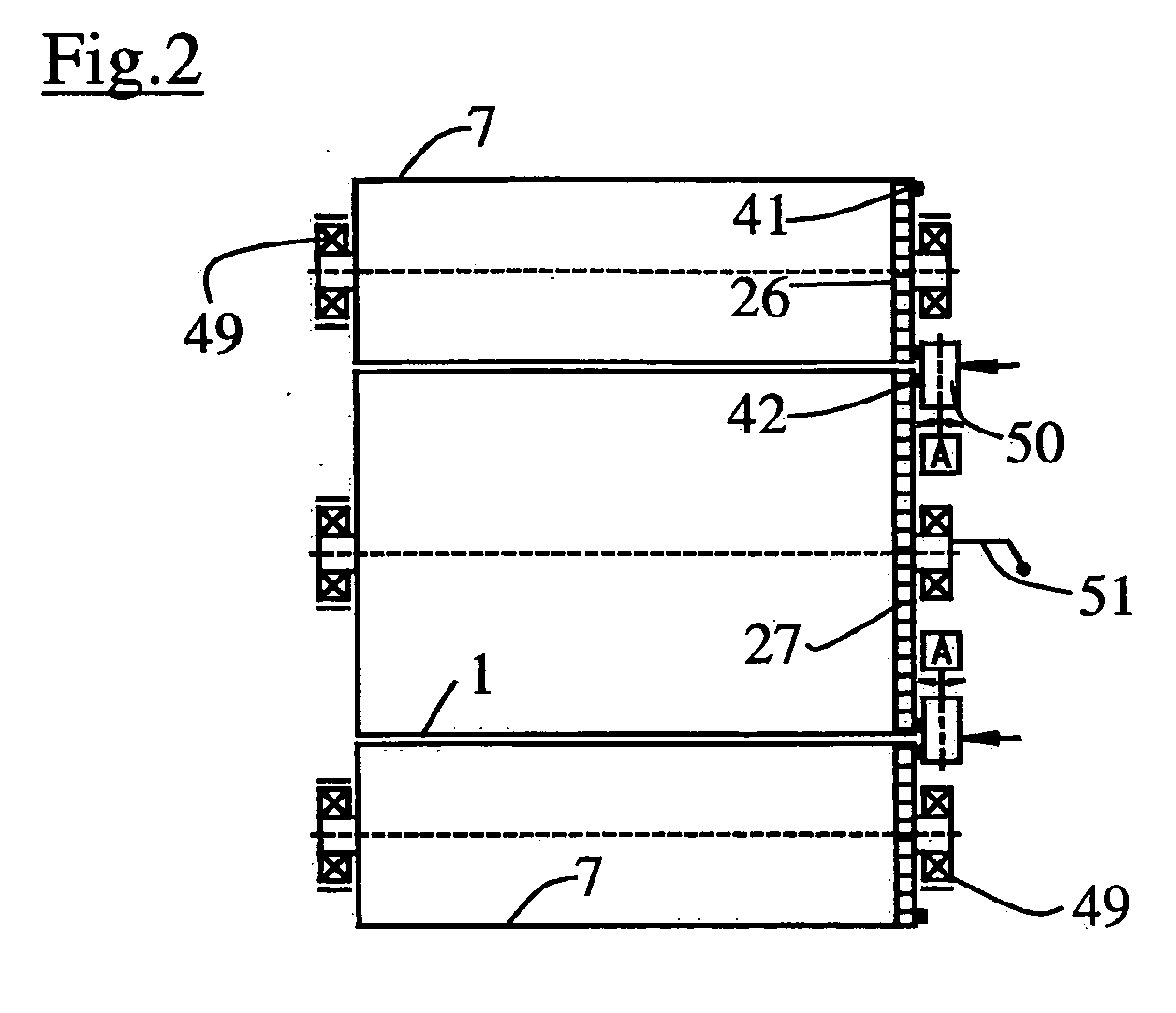
An image registration device for an image production system is disclosed which adjusts any axial image misregistration in situ and quasi instantaneously. This image registration device contains, in operation, a rotating image carrying element and a rotating image receiving element in rolling contact with each other and each having a flange co-axially mounted on their respective shafts. The image registration device includes a further rotating element in rolling contact with the flanges of the rotating elements to ensure that the image carrying element axially follows the image receiving element or vice versa to establish axial image registration.
Owner:OCE TECH
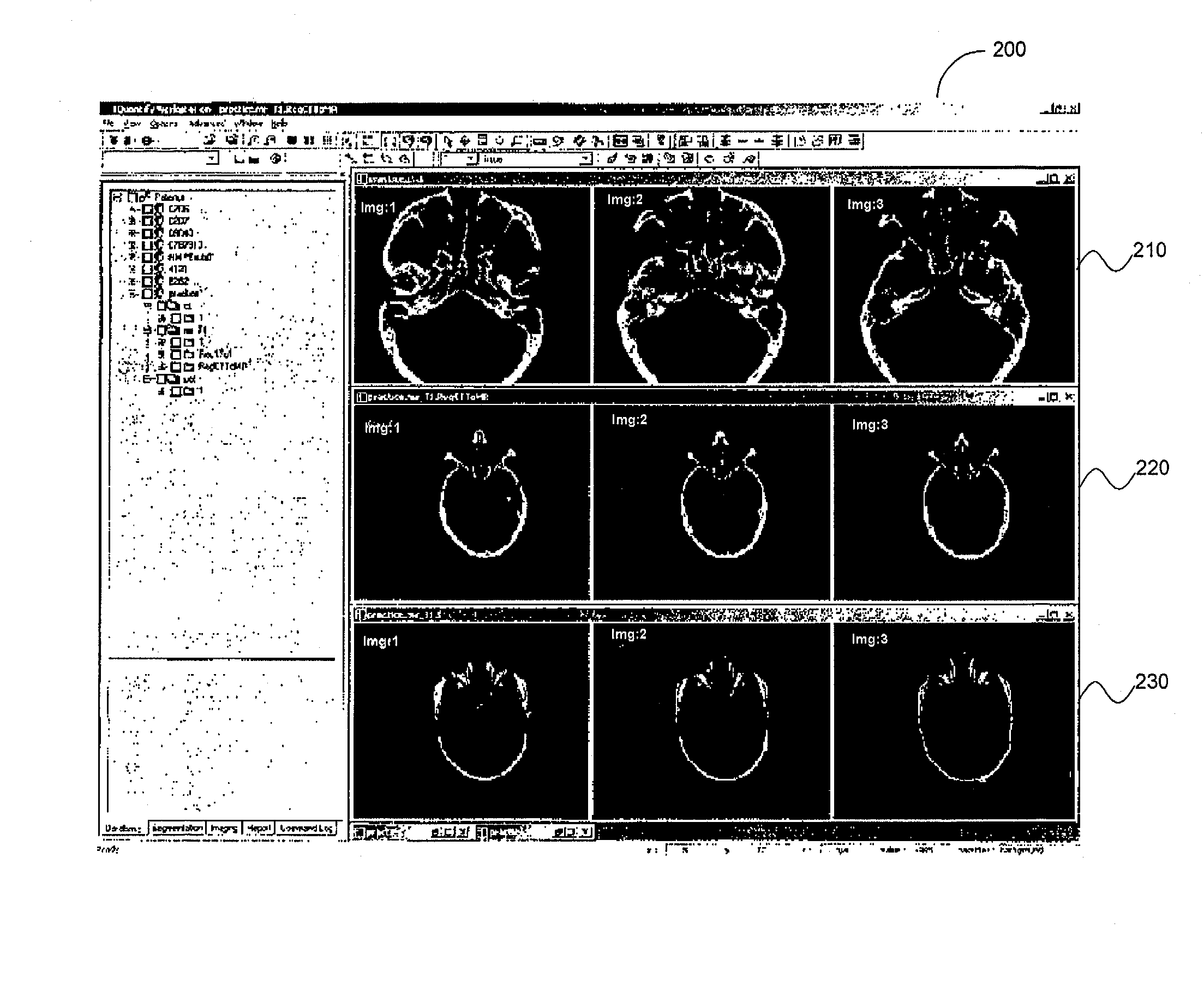
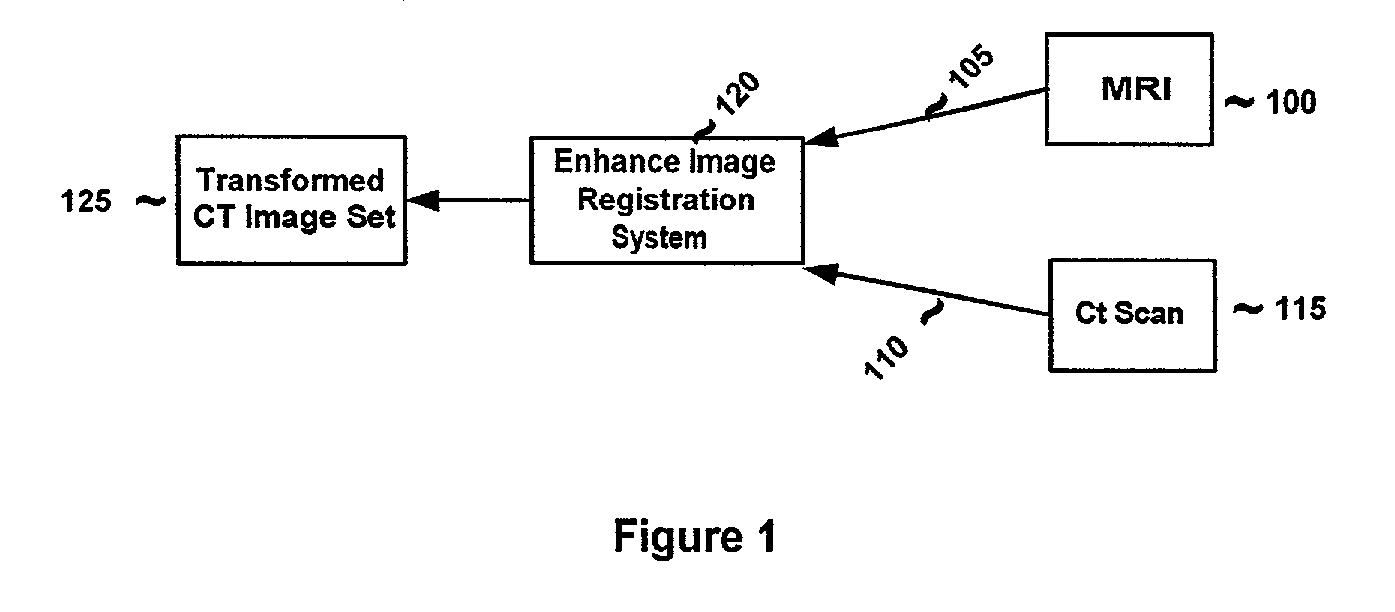
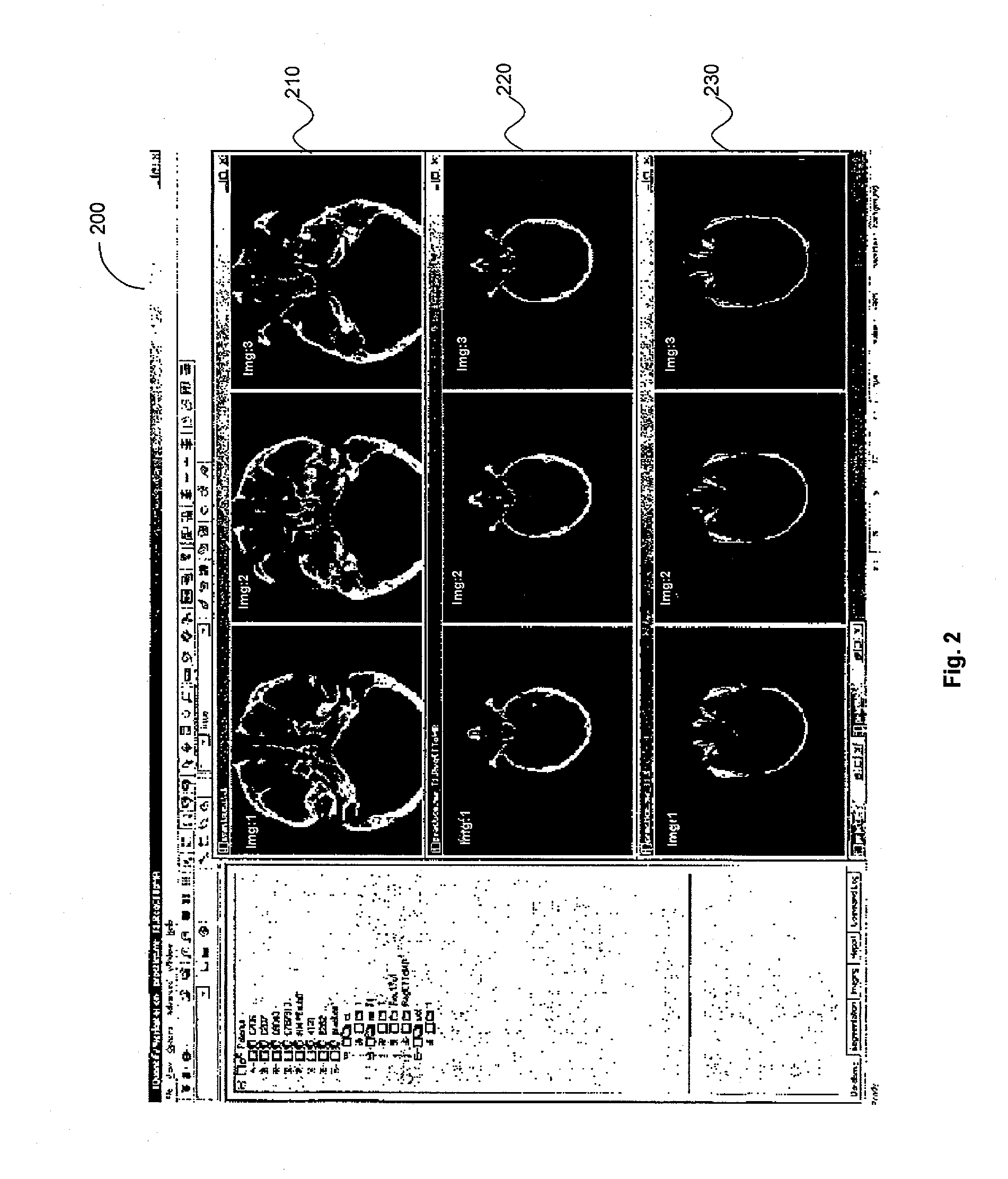
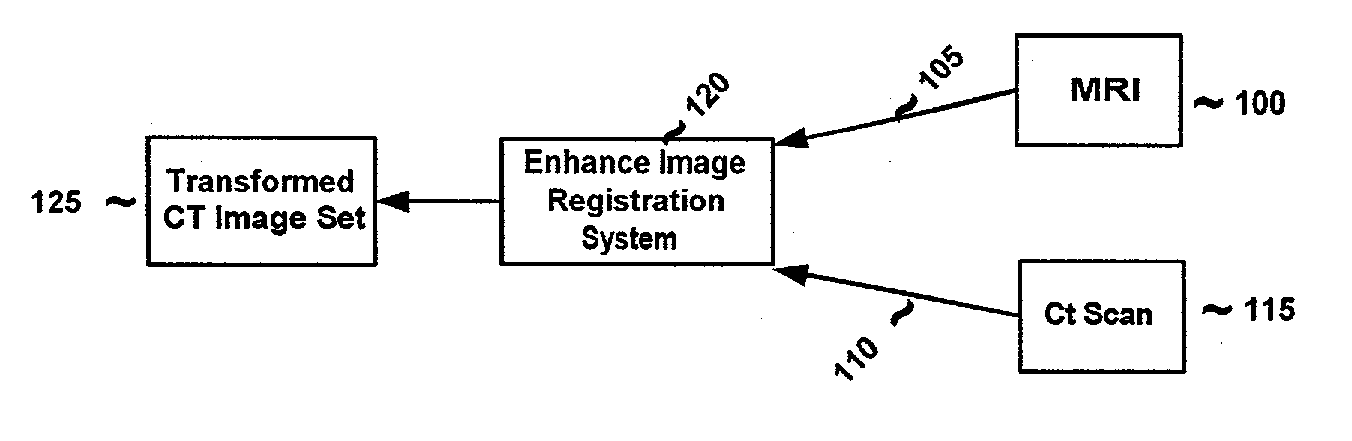
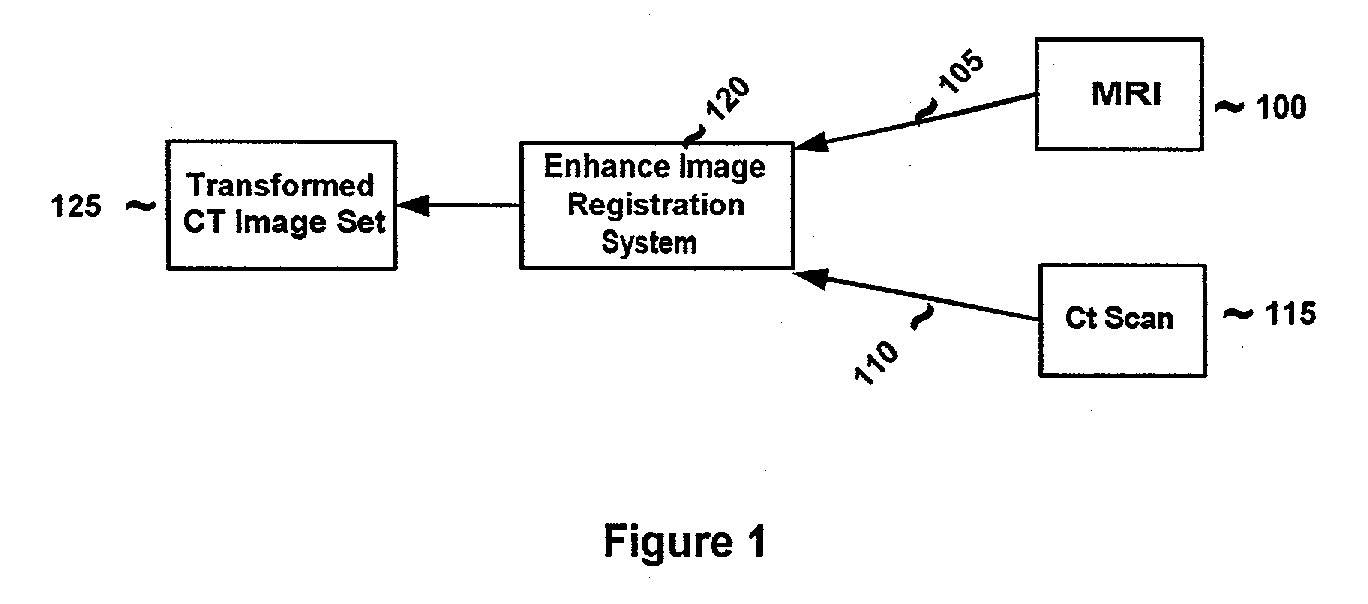
System and method for determining convergence of image set registration
ActiveUS7106891B2Efficiently determinedImprove registrationImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageComputer science
Computer-based methods and systems for automatically determining convergence when registering image sets are provided. Example embodiments provide an Enhanced Image Registration System (EIRS), which includes an Image Comparison Module, a Transformation Optimizer, and a Convergence Calculator. When the EIRS receives two image sets to align, the Image Comparison Module compares two image sets to determine or measure how closely the image sets are aligned. The Transformation Optimizer determines an appropriate transformation to apply to one of the image sets to align it with the reference image set. The Transformation Optimizer then applies the determined transformation. The Convergence Calculator examines one or more points within the transformed image set to determine when convergence is attained.
Owner:CLOUD SOFTWARE GRP INC
System and method for determining convergence of image set registration
ActiveUS20060165267A1Efficiently determinedImproved image registrationImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageImage registration
Computer-based methods and systems for automatically determining convergence when registering image sets are provided. Example embodiments provide an Enhanced Image Registration System (EIRS), which includes an Image Comparison Module, a Transformation Optimizer, and a Convergence Calculator. When the EIRS receives two image sets to align, the Image Comparison Module compares two image sets to determine or measure how closely the image sets are aligned. The Transformation Optimizer determines an appropriate transformation to apply to one of the image sets to align it with the reference image set. The Transformation Optimizer then applies the determined transformation. The Convergence Calculator examines one or more points within the transformed image set to determine when convergence is attained.
Owner:CLOUD SOFTWARE GRP INC
Systems and methods for providing depth map information
ActiveUS20190333237A1Improved image registrationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxImaging data
A method for providing depth map information based on image data descriptive of a scene. In one embodiment, after generating an initial sequence of disparity map data, performing a smoothing operation or an interpolation to remove artifact introduced in the disparity map data as a result of segmenting the image data into superpixels.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
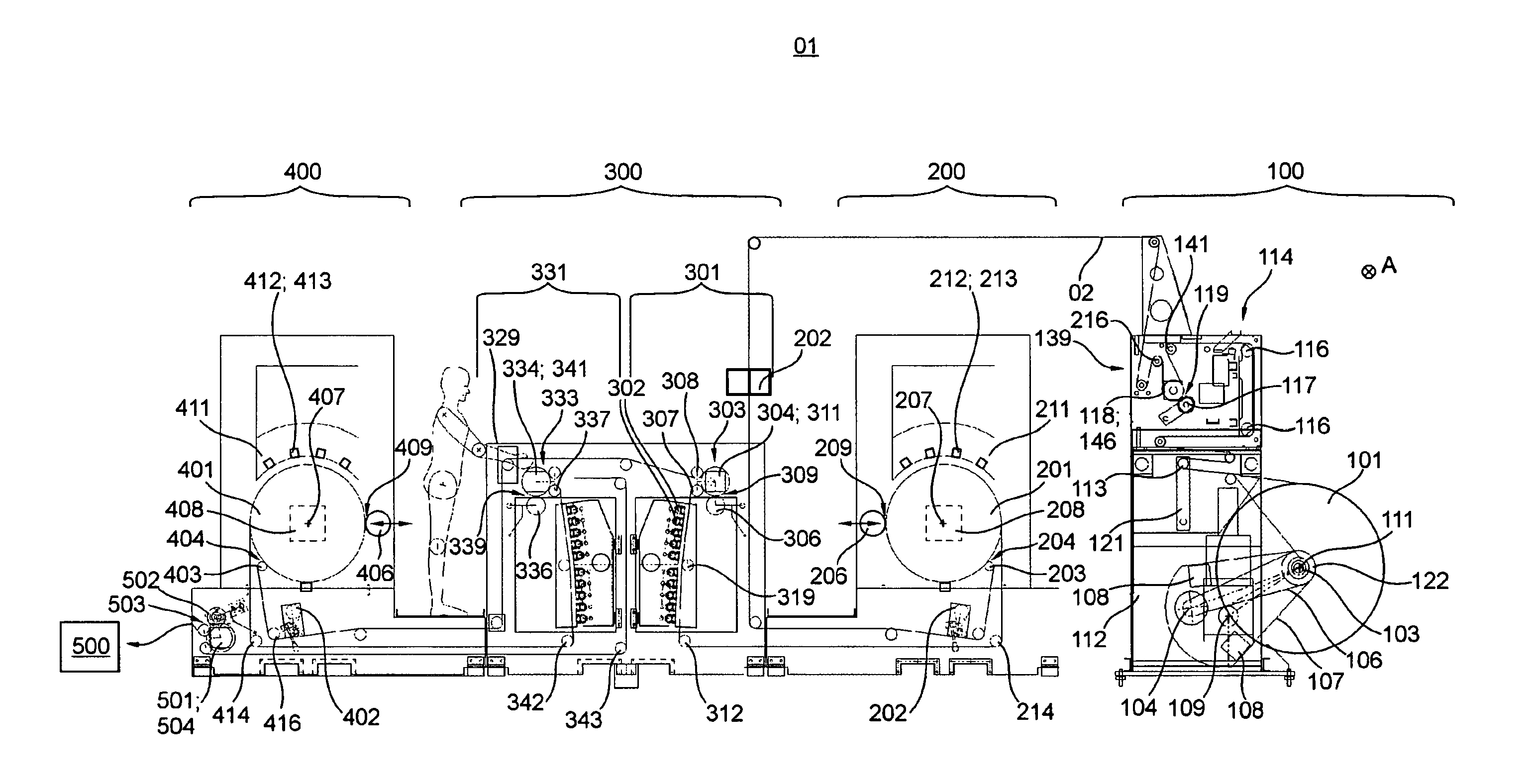
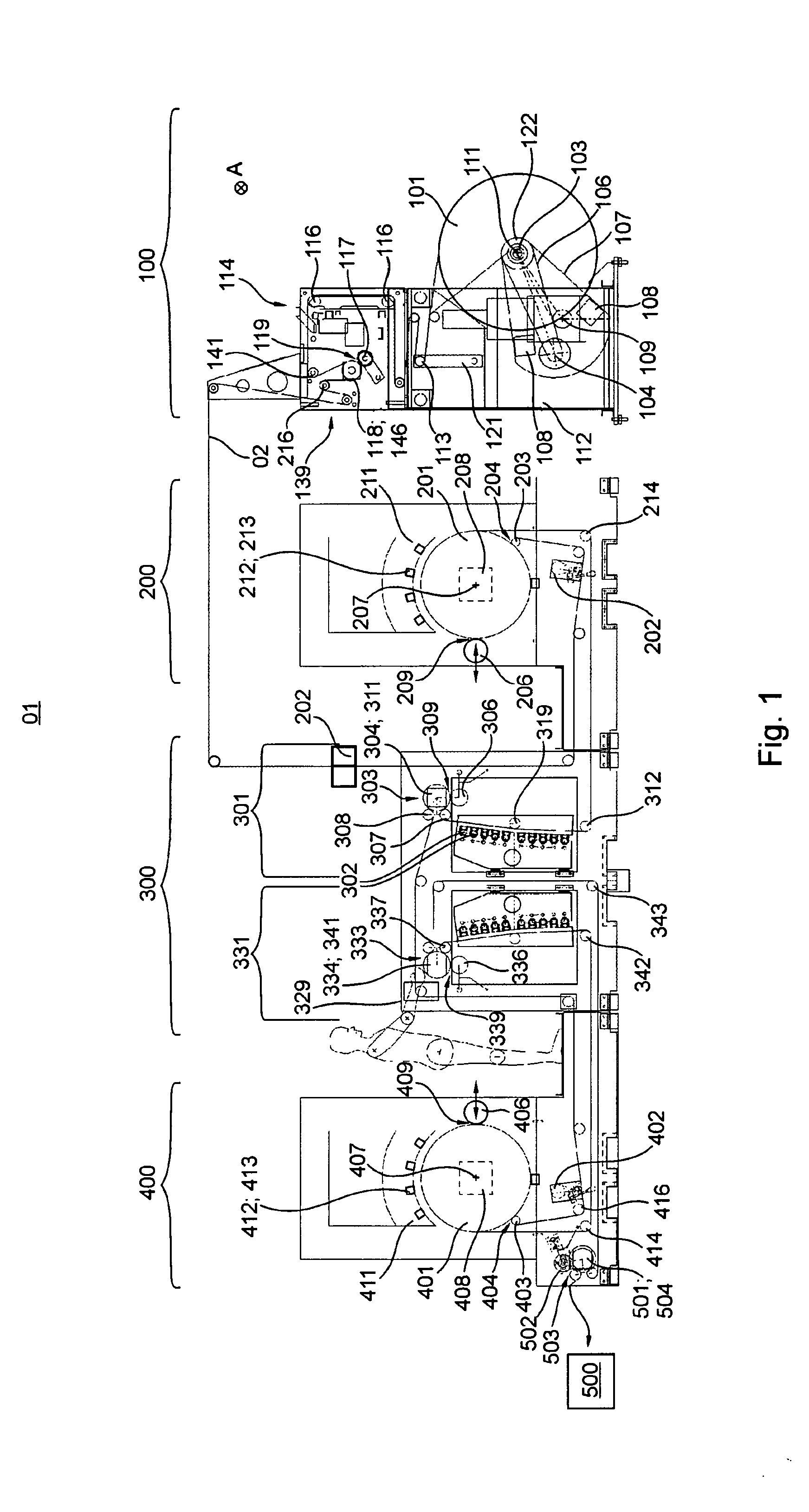
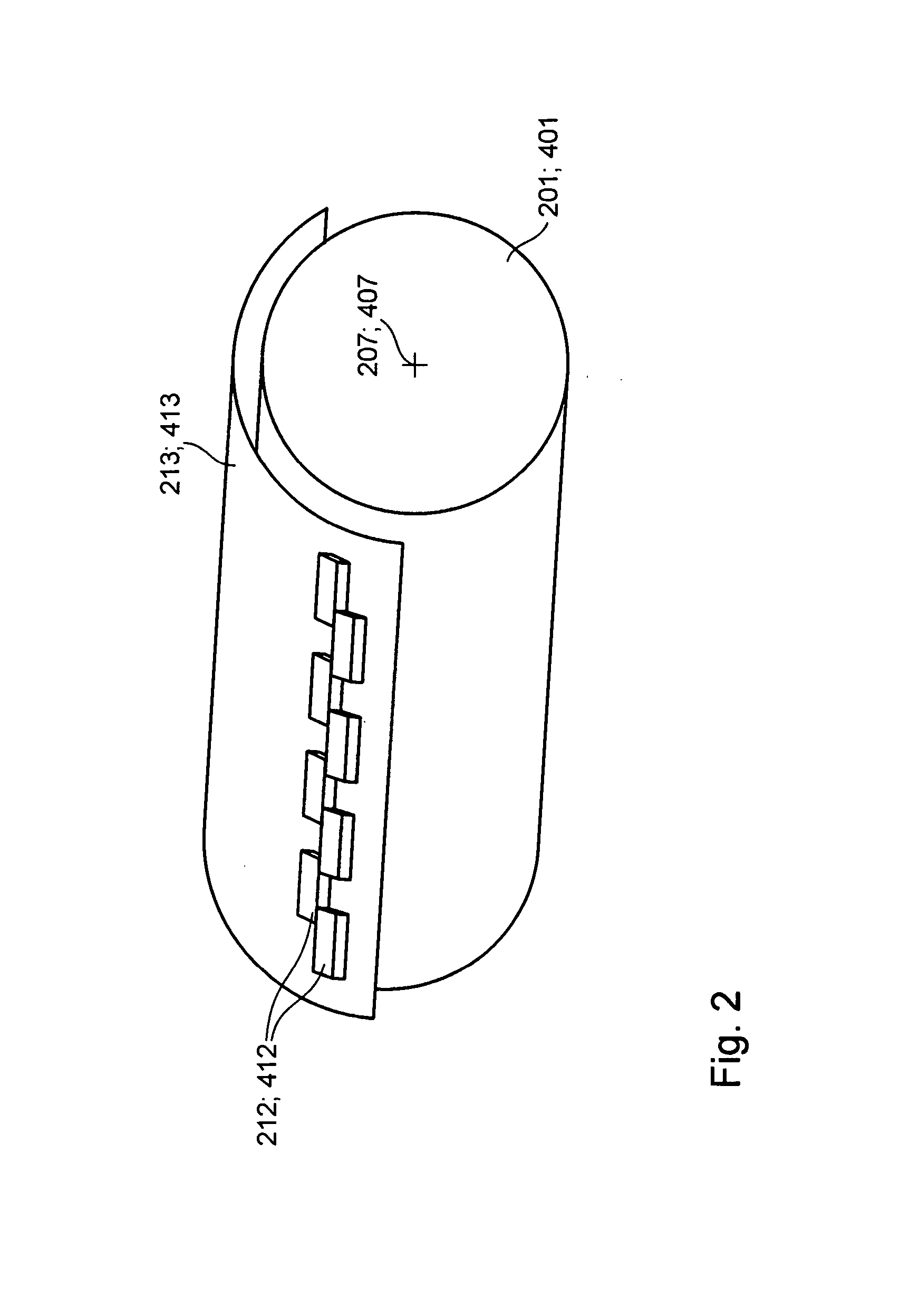
Printing machine and method for adjusting a web tension
ActiveUS20140104360A1Improve color registration and registerSave time and materialTypewritersOther printing apparatusDrive motorInkjet printing
The invention relates to a printing machine having at least one printer unit comprising at least one inkjet printhead, a central printing cylinder, and a drive motor of its own dedicated to the central printing cylinder. A conveying path of a printing material web through the printing machine has at least one first section and one second section, each defined by contact points of the printing material, which have motor-powered rotation bodies. At least the first section has a dedicated first measuring device for measuring a web tension of the printing material web in the first section. At least the second section has a dedicated second measuring device for measuring the web tension of the printing material web in the second section. A machine controller is arranged, by means of which the web tension in at least the first section and / or in the second section of the conveying path of the printing material web can be adjusted and / or is adjusted, taking into consideration at least both a measuring result from the first measuring device and a measuring result from the second measuring device. The invention further relates to a method for adjusting a web tension of a printing material web.
Owner:KOENIG & BAUER AG
Image processing method in microscopy
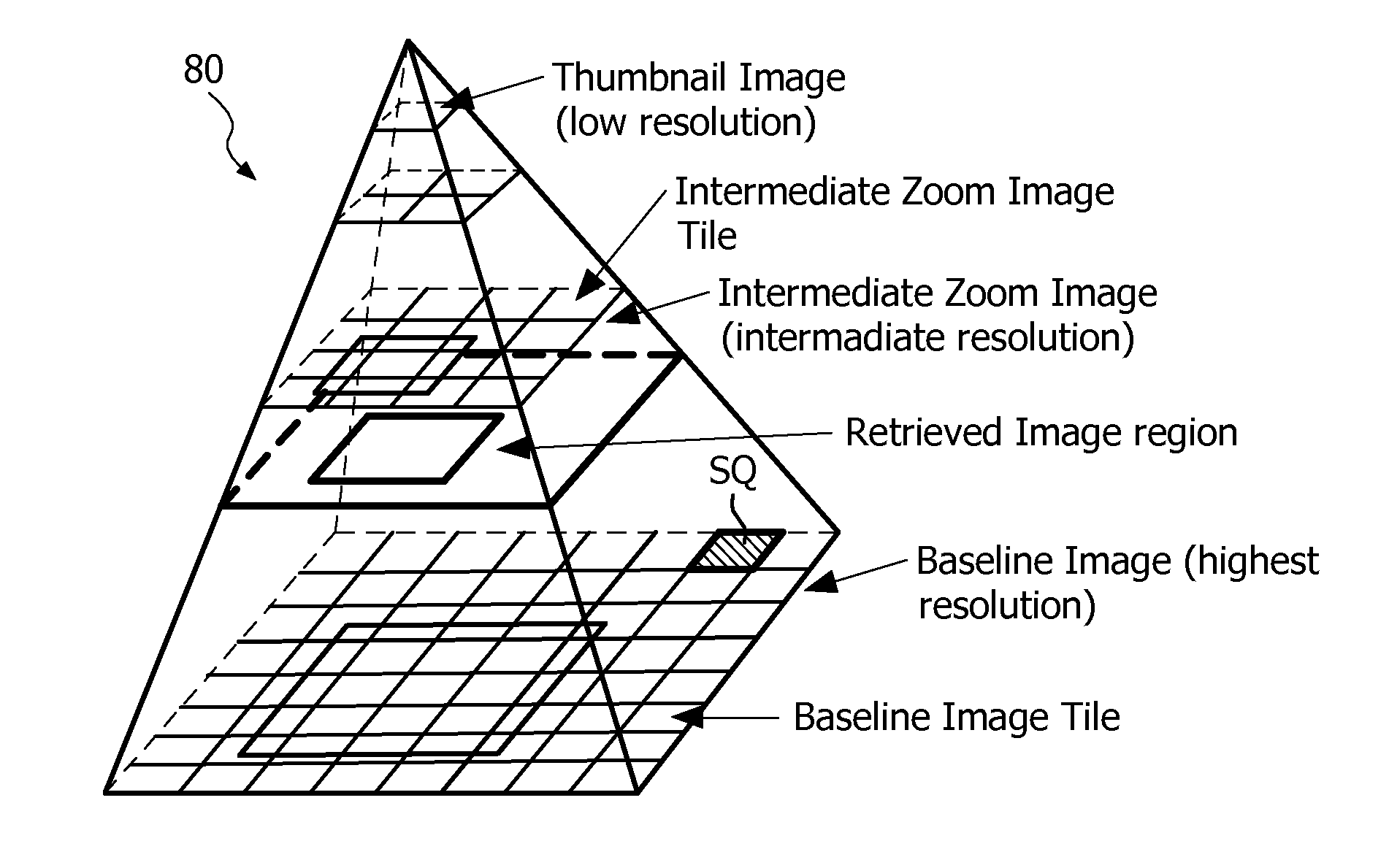
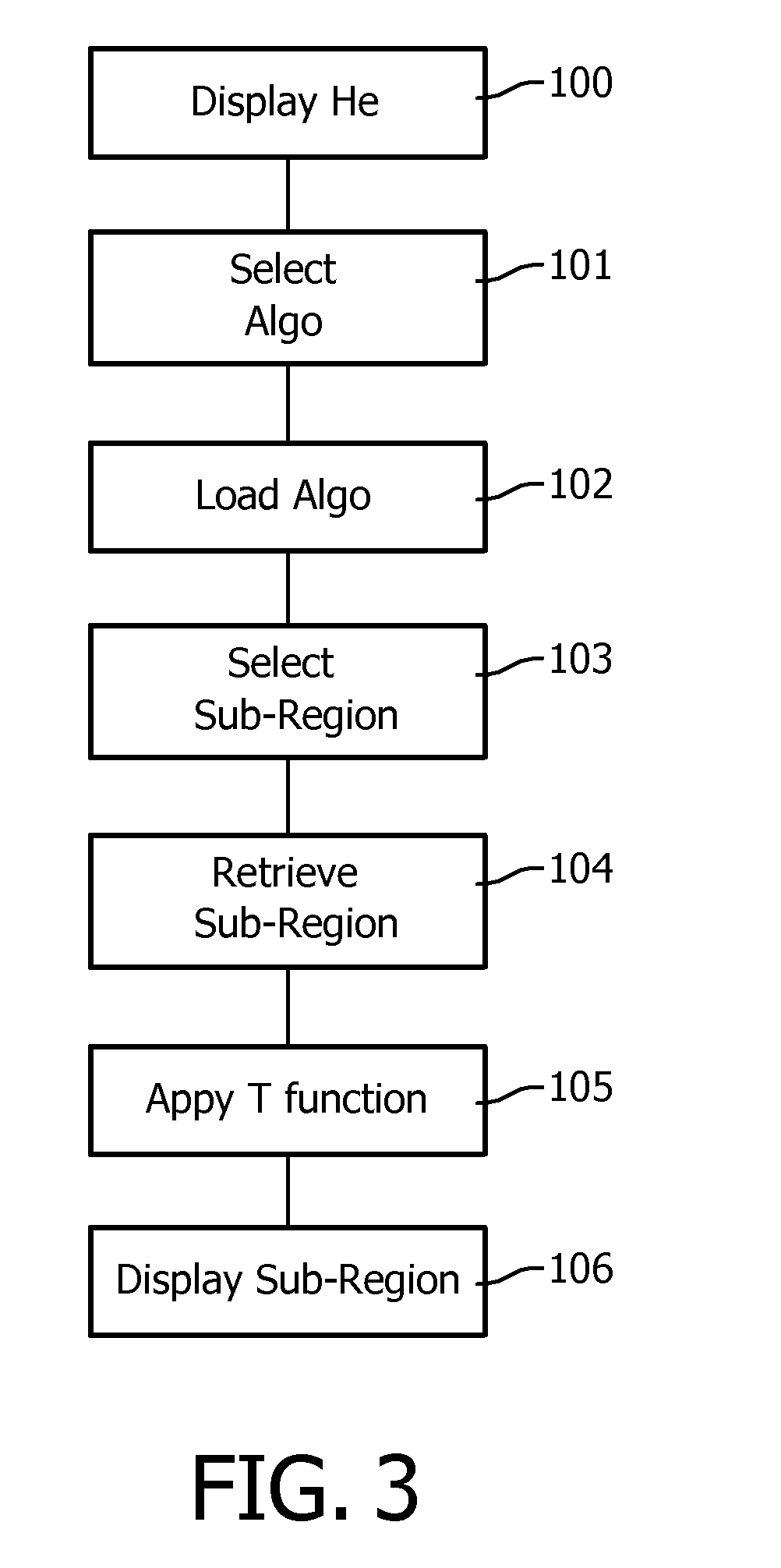
ActiveUS20130089249A1Improvement of image registration efficiencySmall dimensionImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageImaging processing
The invention pertains to the field of image processing in digital pathology. It notably proposes a method for processing a first digital image, representing a sample in a region, and which image has been acquired from the sample by means of a microscopic imaging system (1) and is stored in a multi-resolution image data structure (80), comprising the steps of:—retrieving (104) a sub-region of the first digital image at a first resolution, —executing (105) a transform function on the retrieved sub-region, the transform function modifying a content of the sub-region according to at least one metric derived from a second resolution representation of the first digital image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
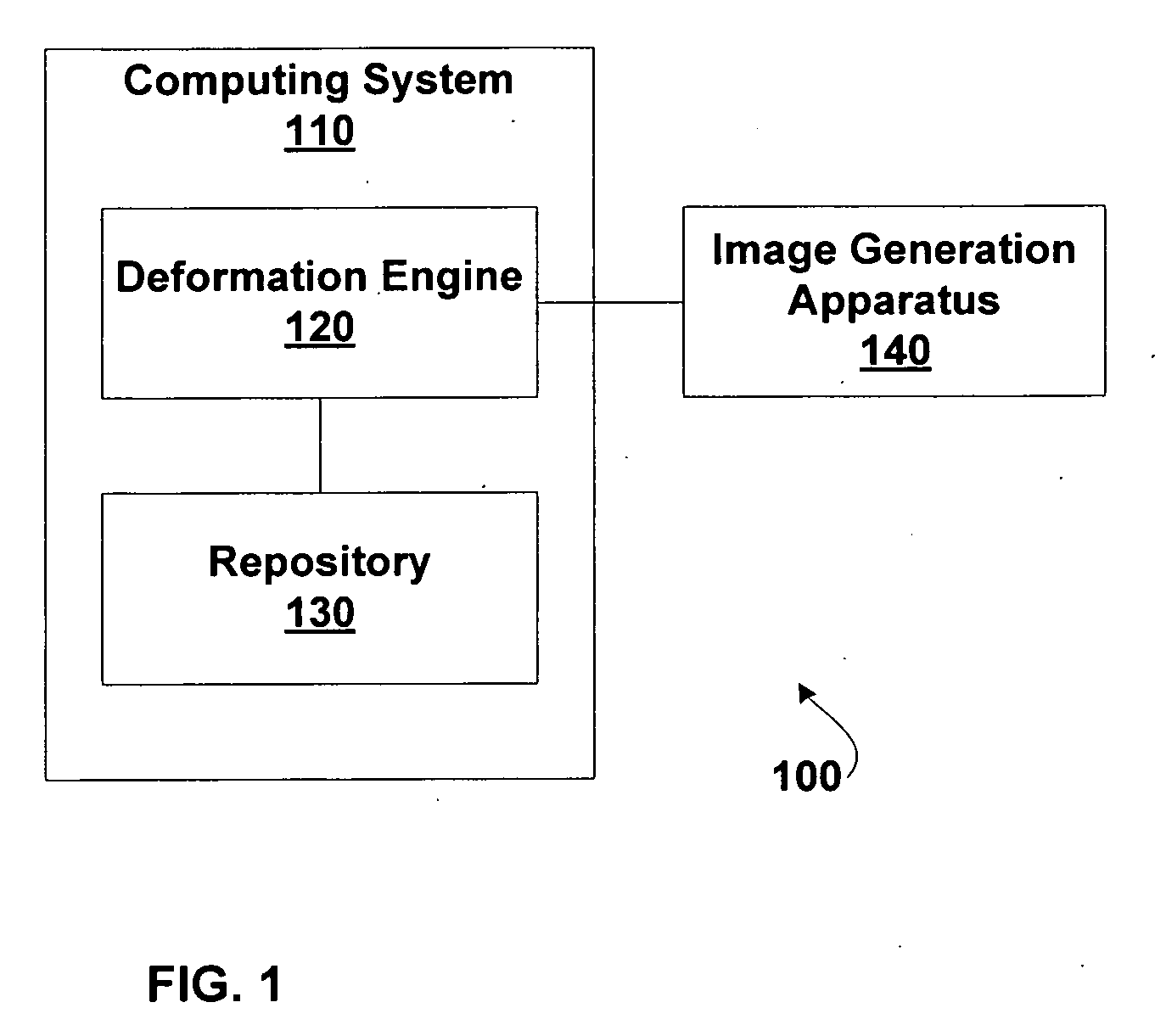
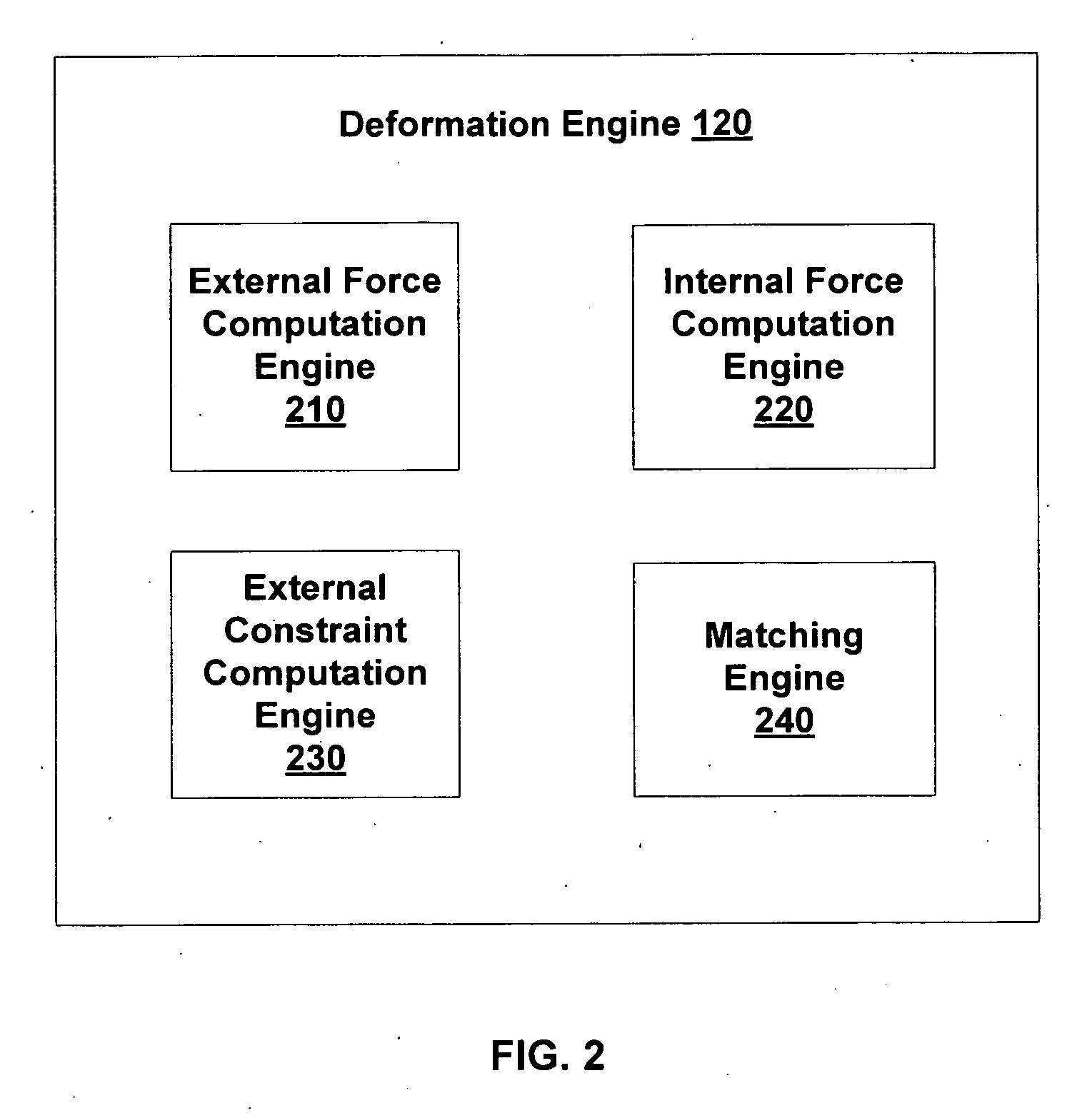
Spatially variant image deformation
ActiveUS20080080788A1Improved image registrationFaster and accurate resultImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageSpatial change
Disclosed are systems for and methods of registering (i.e., aligning) a deformable image with a reference image subject to a spatially variant flexibility model and / or a non-Gaussian smoothing model. These systems and methods allow for the consideration of differences between the ways in which structures of interest may move within a patient. The registration includes modifying the deformable image to match similar features in the reference image. The systems include a deformation engine configured for performing a deformation algorithm subject to the spatially variant flexibility and / or smoothing models.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
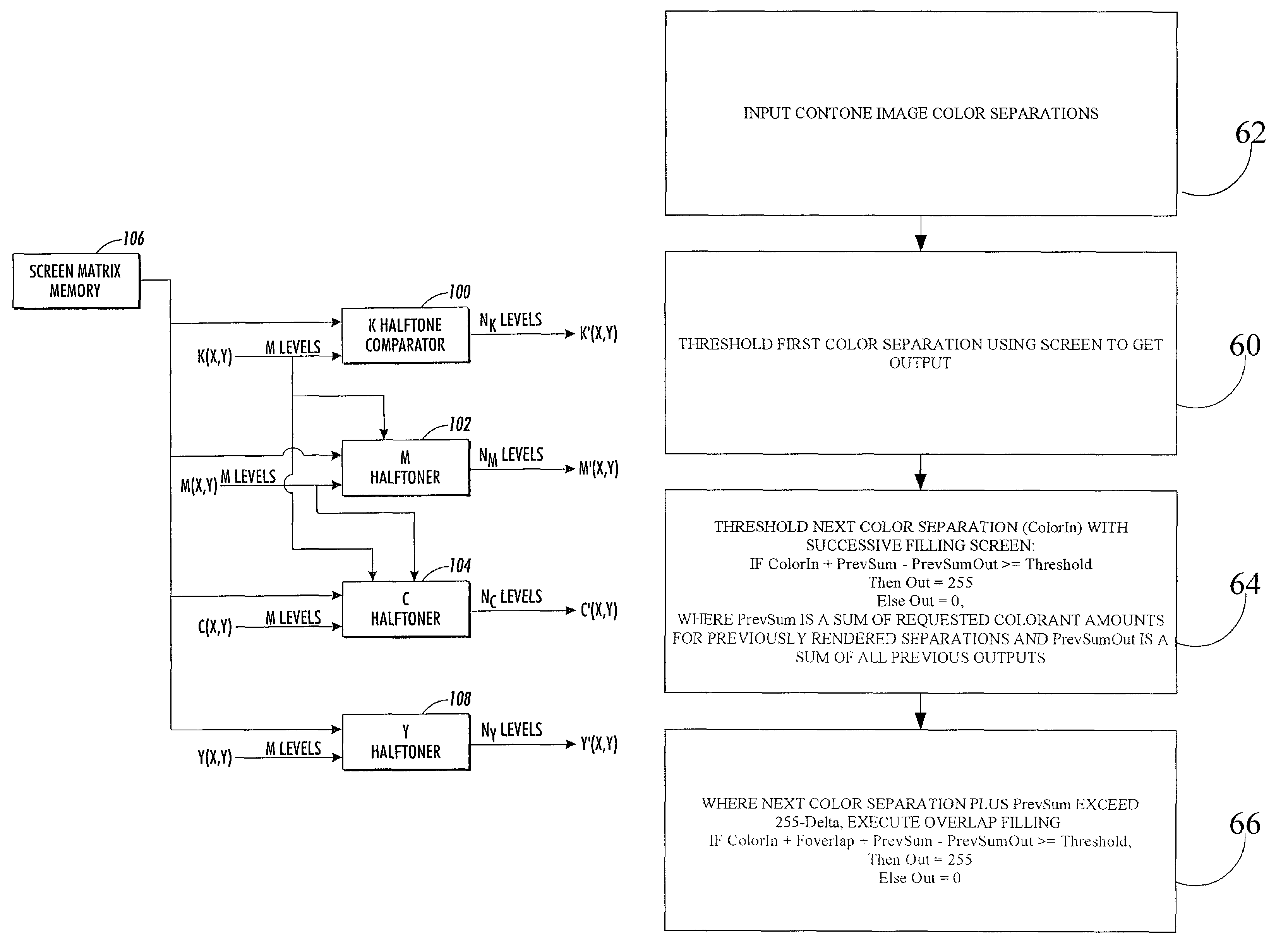
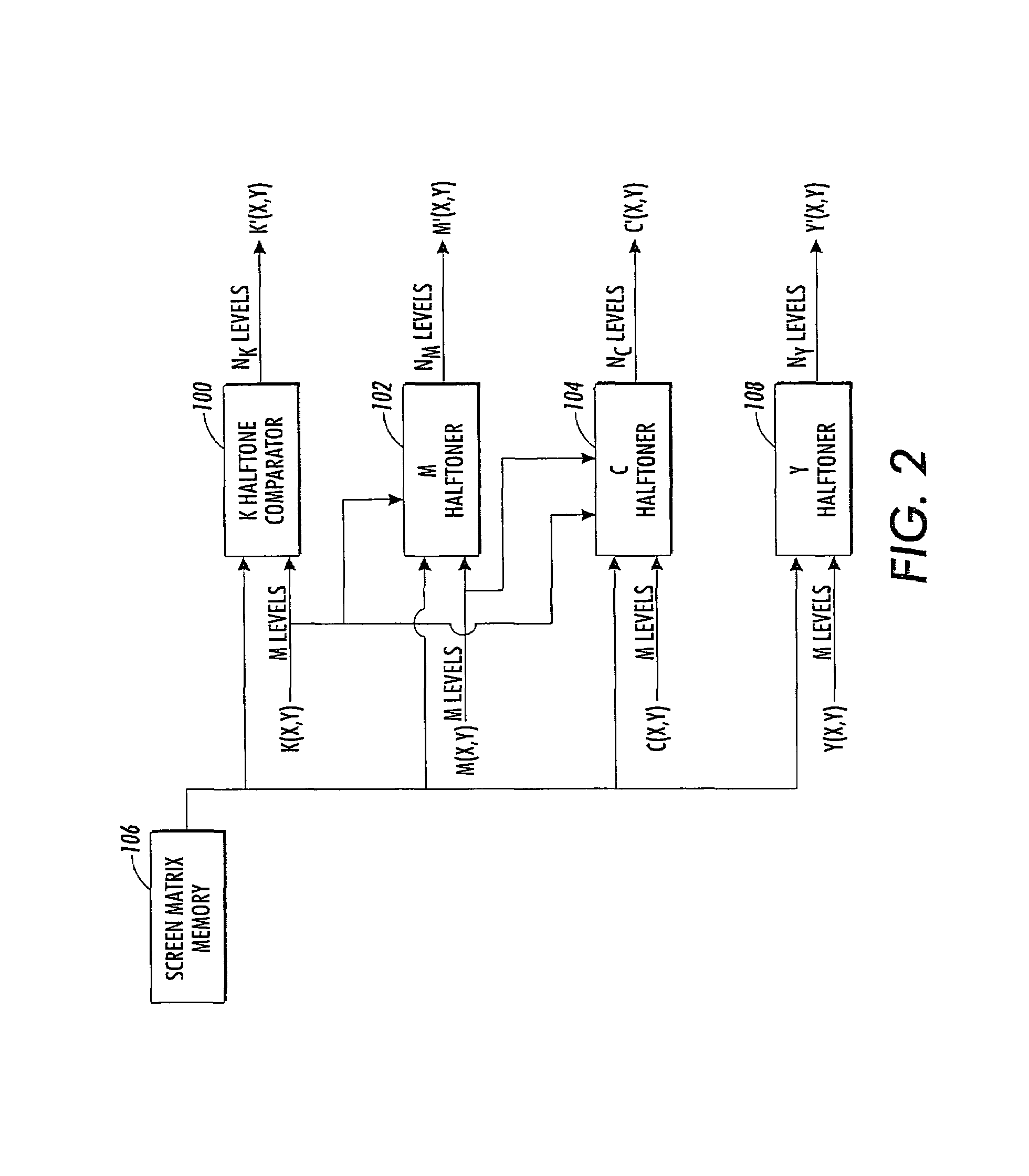
Color vector halftoning using a successive filling with improved color registration latitude
InactiveUS7095530B2Enhances color registration latitudeImprove system robustnessDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersColor imageColor vector
A method is provided for rendering a color image with a plurality of separations with a halftone process using a single screen. The screen is comprised of a plurality of pixel locations with associated threshold values and the image is comprised of a plurality of separation values. The method includes the steps of rendering a first one of the plurality of separations in accordance with the screen, wherein the plurality of pixel locations are turned on or off at a given pixel location based on a comparison of the image separation value at that pixel with the screen threshold value. The rendering of the next color separation is made in accordance with the rendering of the first separation and the screen, wherein for constant image separation values, pixel locations are turned on for the separation at pixel locations disposed in a highest available luminance region having a lowest available threshold value. When successive filling approaches the end portion of available threshold values, overlap filling with earlier rendered color separations occurs before the screen is completely filled.
Owner:XEROX CORP
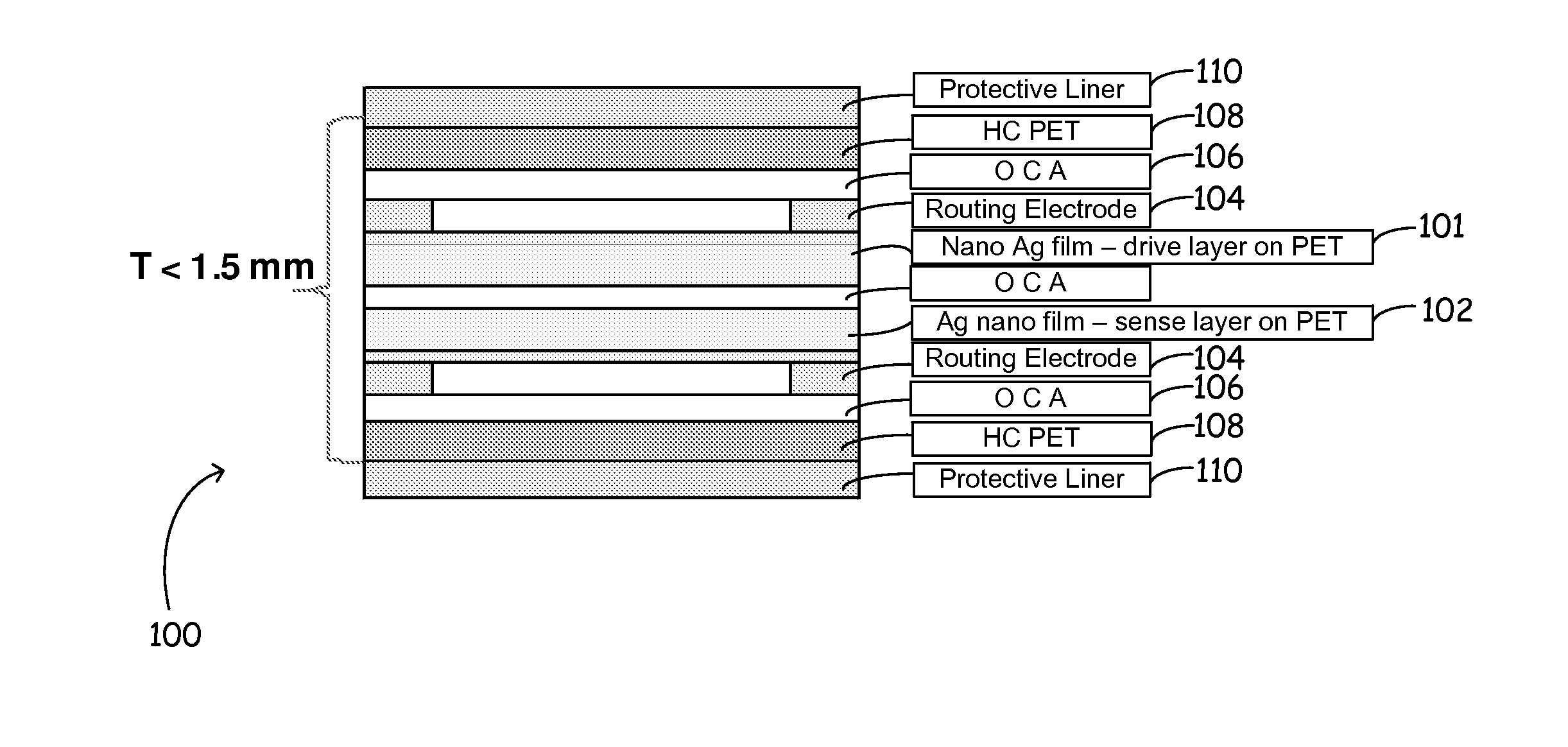
Methods and apparatus for the fabrication of pattern arrays in making touch sensor panels
InactiveUS20160001496A1Improve registrationEasy alignmentLamination ancillary operationsLaminationConductive coatingLaser patterning
An electrically conductive touch sensor panel construction and method and laser system for fabricating the same. The transparent touch sensor panel comprises at least two conductive coatings to provide a drive layer and a sense layer. The drive and sense layers are laminated together or otherwise assembled in a touch panel construction and in selected alignment. The layers are then subsequently laser patterned to form the conductive pathways for the touch panel sensor. The drive and sense layers may be concurrently or sequentially laser processed to form a selected pattern in each layer such that the drive and sense layers are substantially aligned forming a far more precise pattern array for the panel.
Owner:PRECO
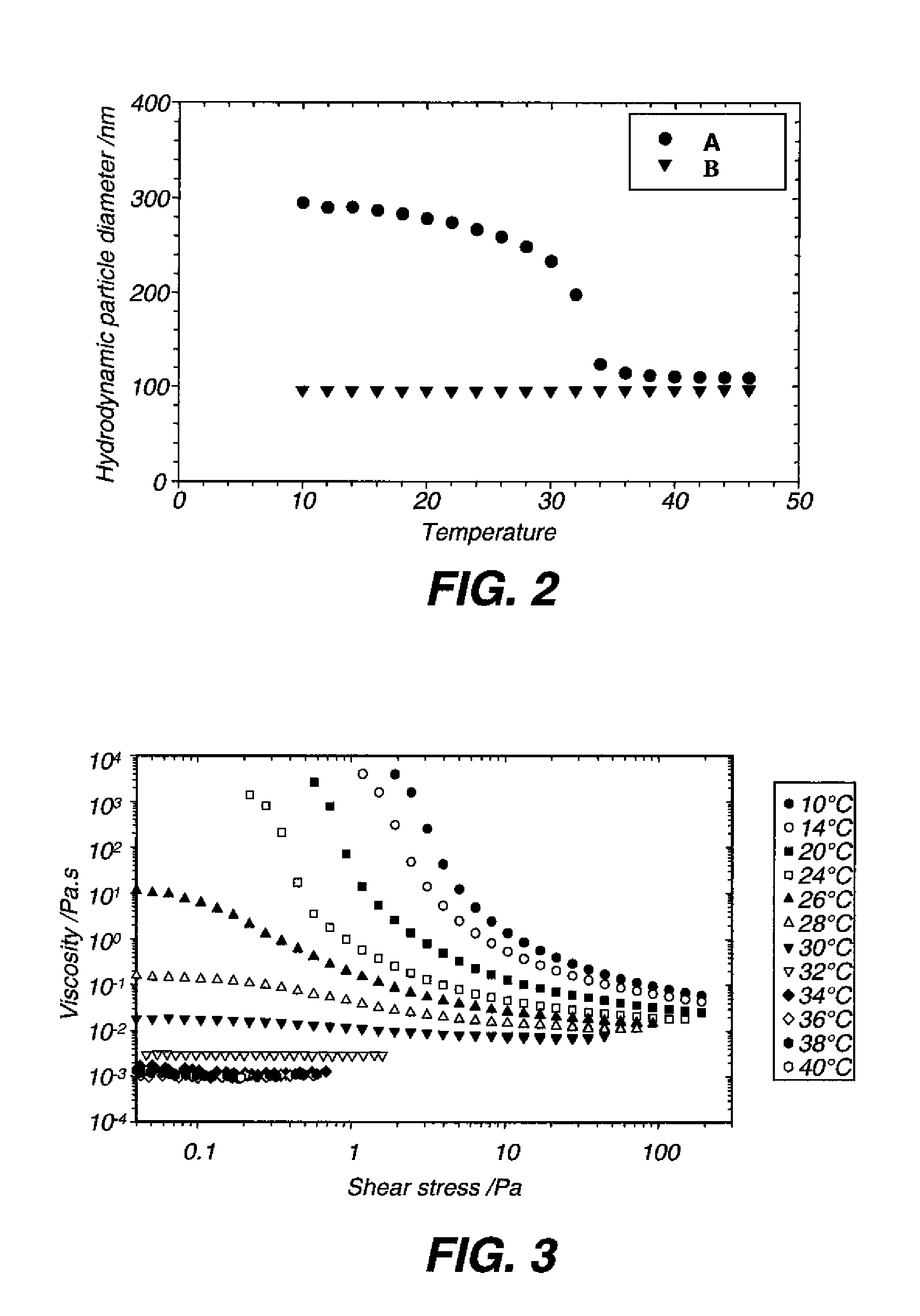
Inkjet printing system
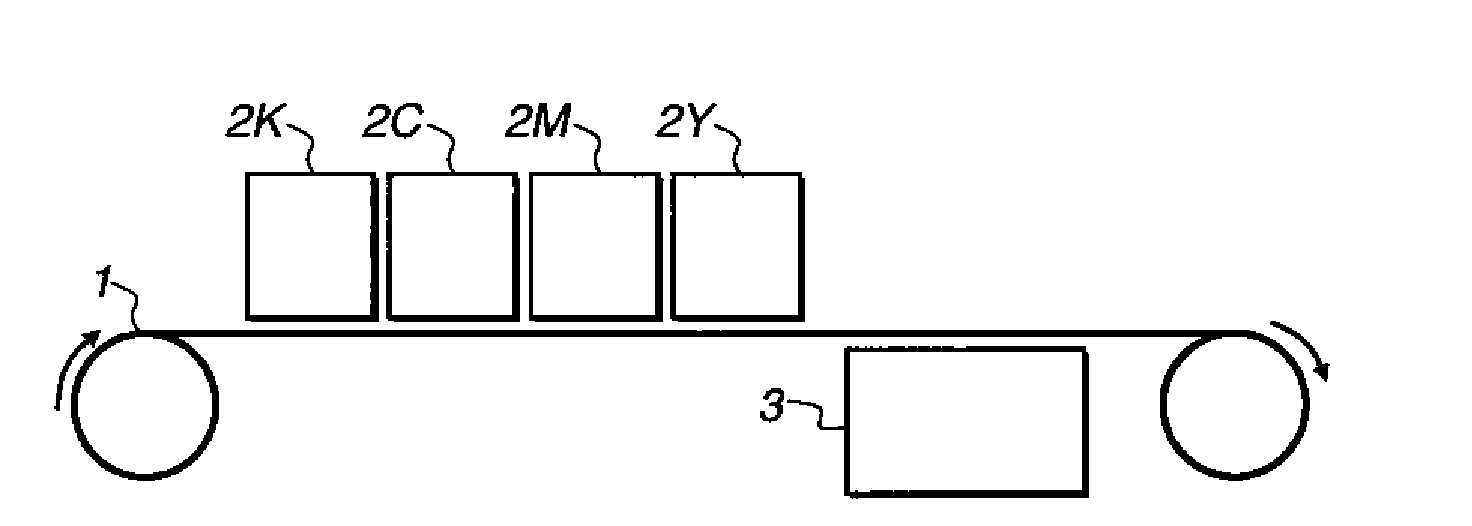
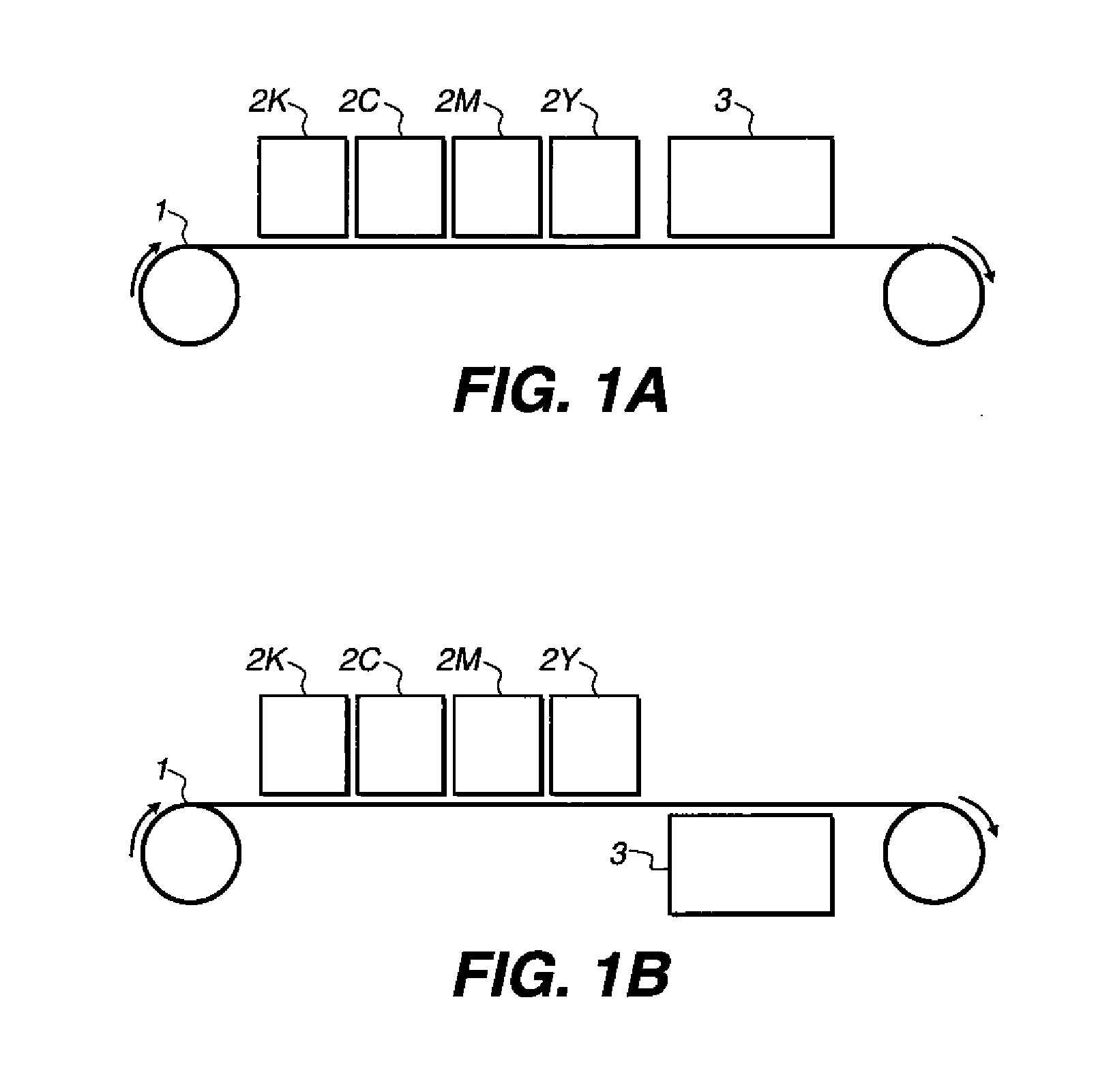
InactiveUS20090322811A1Reducing cost and complexity and energy consumption and footprintGood flexibilityMeasurement apparatus componentsInksEngineeringViscosity
An inkjet printing system comprising a plurality of static inkjet printing units each comprising at least one inkjet printing head; an ink-receiving element comprising a poorly-absorbing or impermeable substrate; an aqueous inkjet composition which comprises a polymeric compound comprising discrete particles responsive to an external stimulus, and a functional material, which may be incorporated as part of the polymeric particles, the composition having a first rheological state and a different second rheological state in response to a stimulated change in conditions, the first state being associated with a first lower viscosity of the composition, wherein the particles have a first lower volume, and the second state being associated with a second higher viscosity of the composition, wherein the particles have a second higher volume, and of drying the aqueous ink composition only positioned downstream of the plurality of the printing units.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
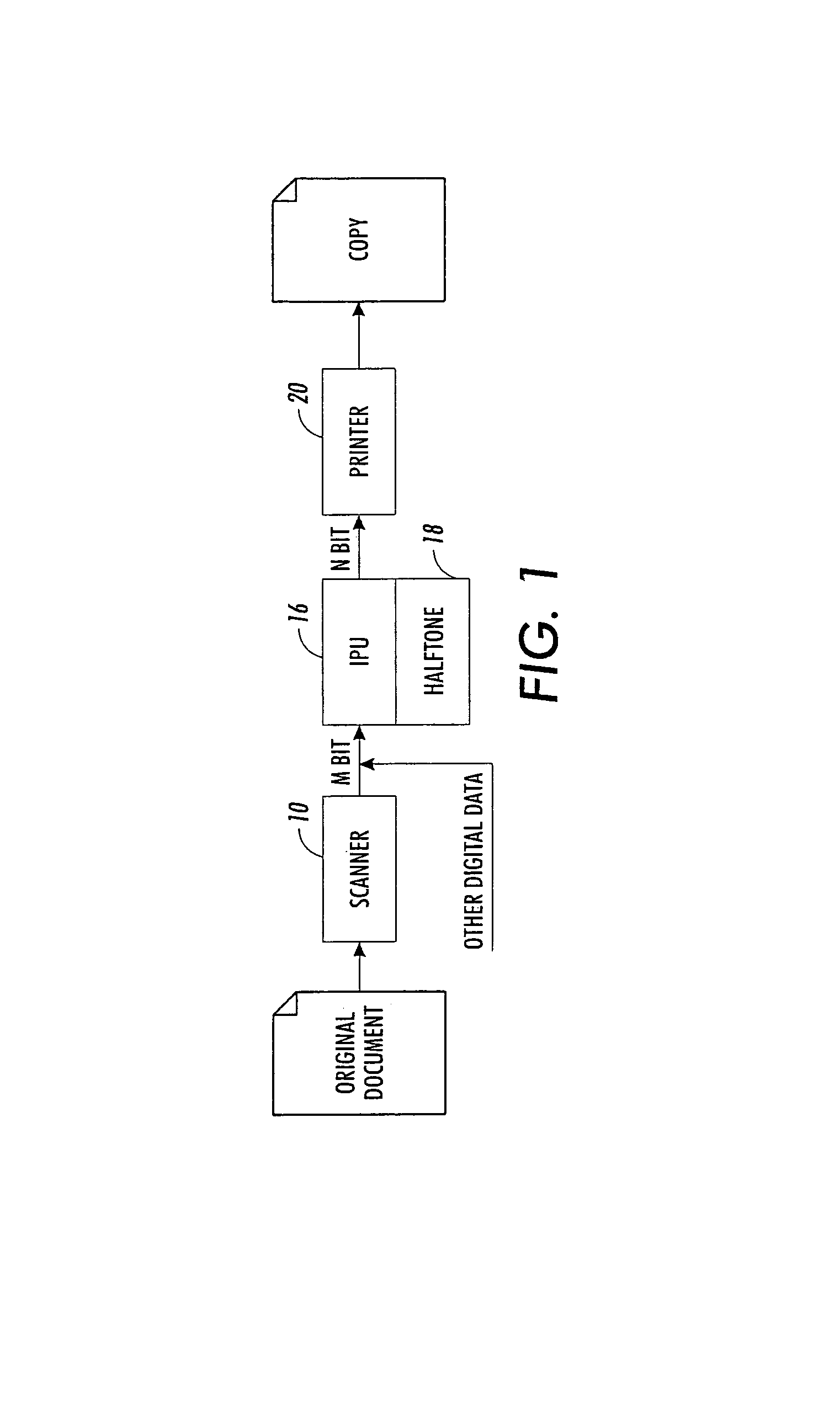
Method and apparatus for continuous motion film scanning
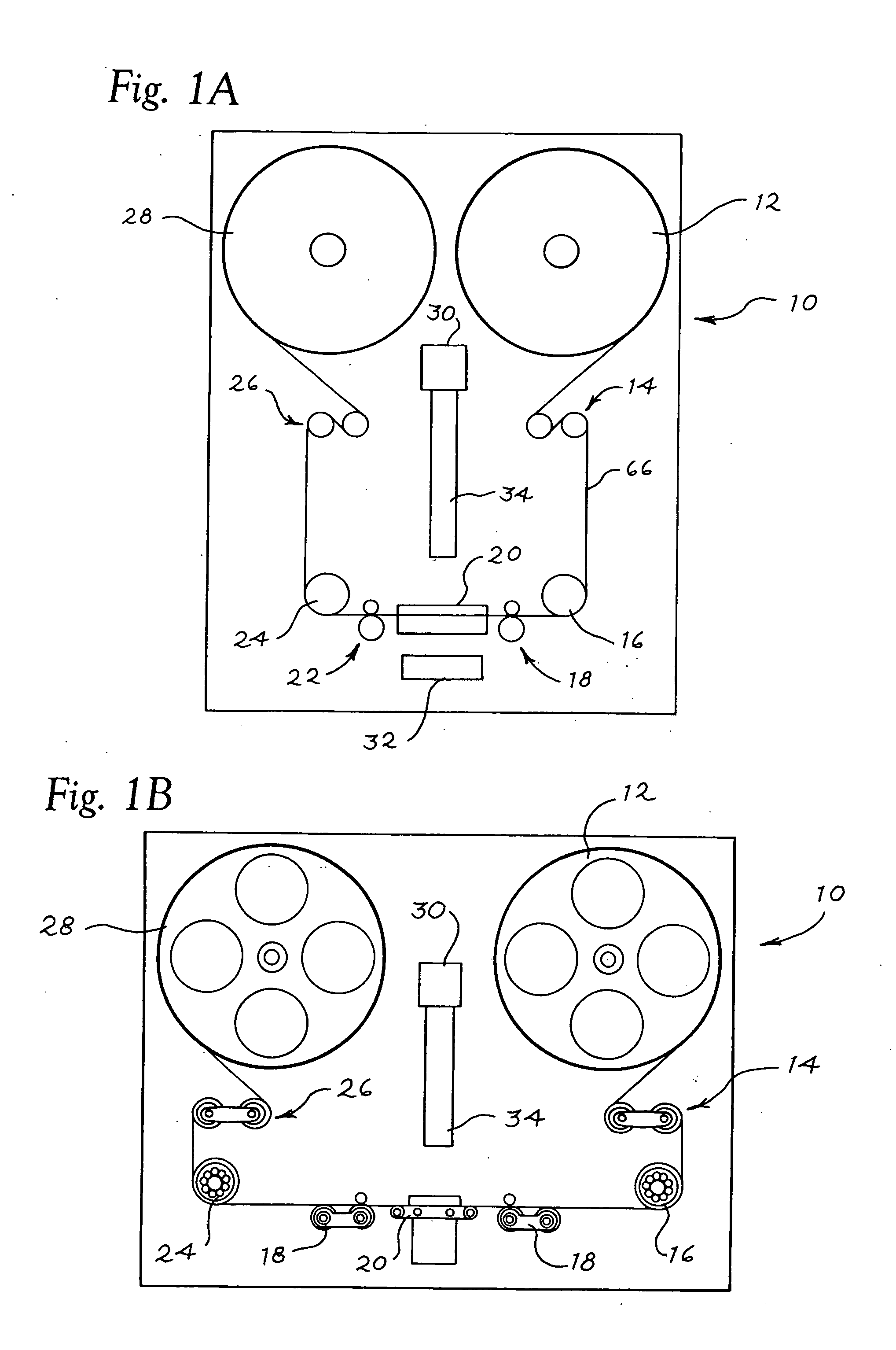
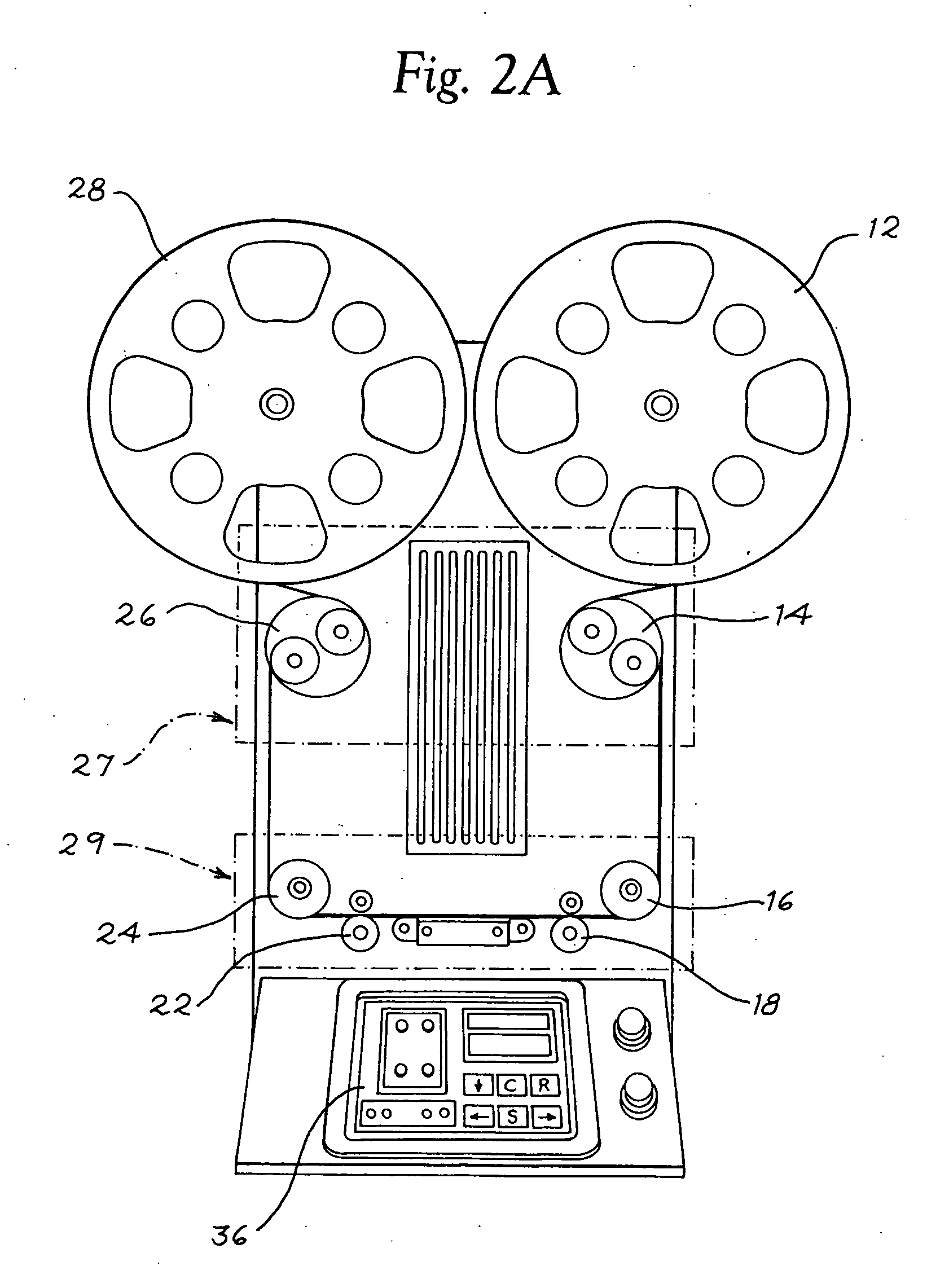
ActiveUS20130076890A1Facilitates high resolution digital duplicationSignificant informationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsFilm-outDigital image
A continuous film scanning system for high resolution digital archival and duplication of motion picture film on a frame by frame basis. Film is driven through the film scanning system through the use of rollers and maintained at a consistent tension throughout the scanning process. Optical interrogation of the perforations associated with each film frame is used to trigger digital image capture. The continuous film scanning system is particularly well adapted to safely handle imperfect or damaged film stock.
Owner:REFLEX TECH
Synchronous, clocked communication system with relative clock and method for configuring such a system
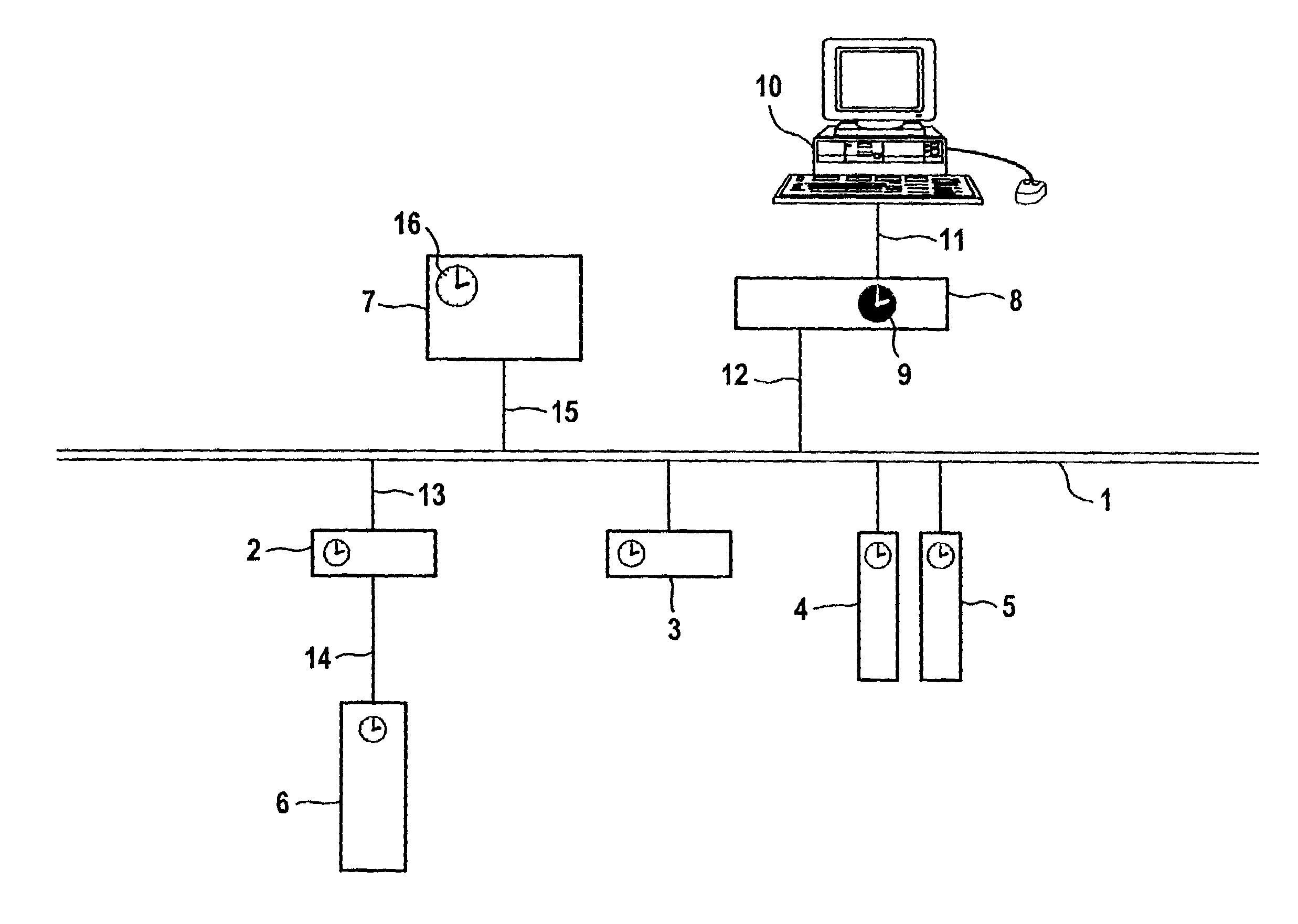
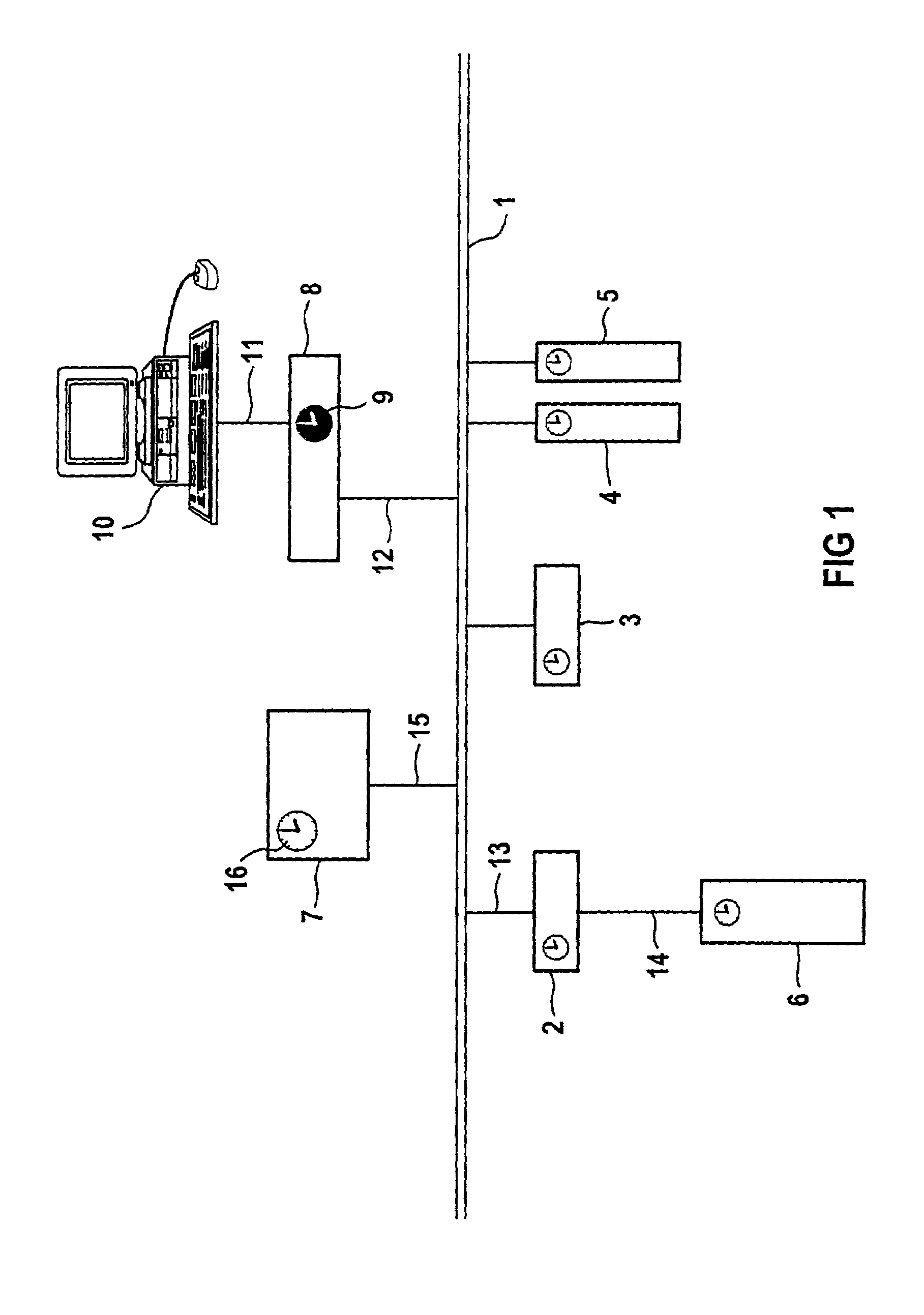
ActiveUS7012980B2Reduce dependenceHigh precisionTime-division multiplexGenerating/distributing signalsTiming generatorReal-time computing
The invention relates to a synchronous, clocked communication system, for example a distributed automation system, the stations of which can be arbitrary automation components which are coupled to one another via a data network (1) for the purpose of mutual data exchange. In this arrangement, all possible bus systems such as, e.g. field bus, professional field bus, Ethernet, industrial Ethernet etc. are available for use as the data network (1) of the communication system. One station of this communication system is designated as timing generator and ensures the distribution and maintenance of the communication clock used to and by all stations. The timing generator can also introduce a relative clock (9) in the entire communication system at all stations via the same mechanism. This station is thus also the master of the relative clock (9) or the applicable relative time (16). All stations of the communication system are, therefore, continuously synchronized to the relative clock (9), which is applicable throughout this system, with the valid relative time (16) and, therefore have the same understanding of time at any time. This distinctly improves or even makes possible, respectively, the implementation of applicative sequences, synchronization of events occurring simultaneously, accuracy in time during the detection of events or, respectively, switching of outputs.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Novel image registering method
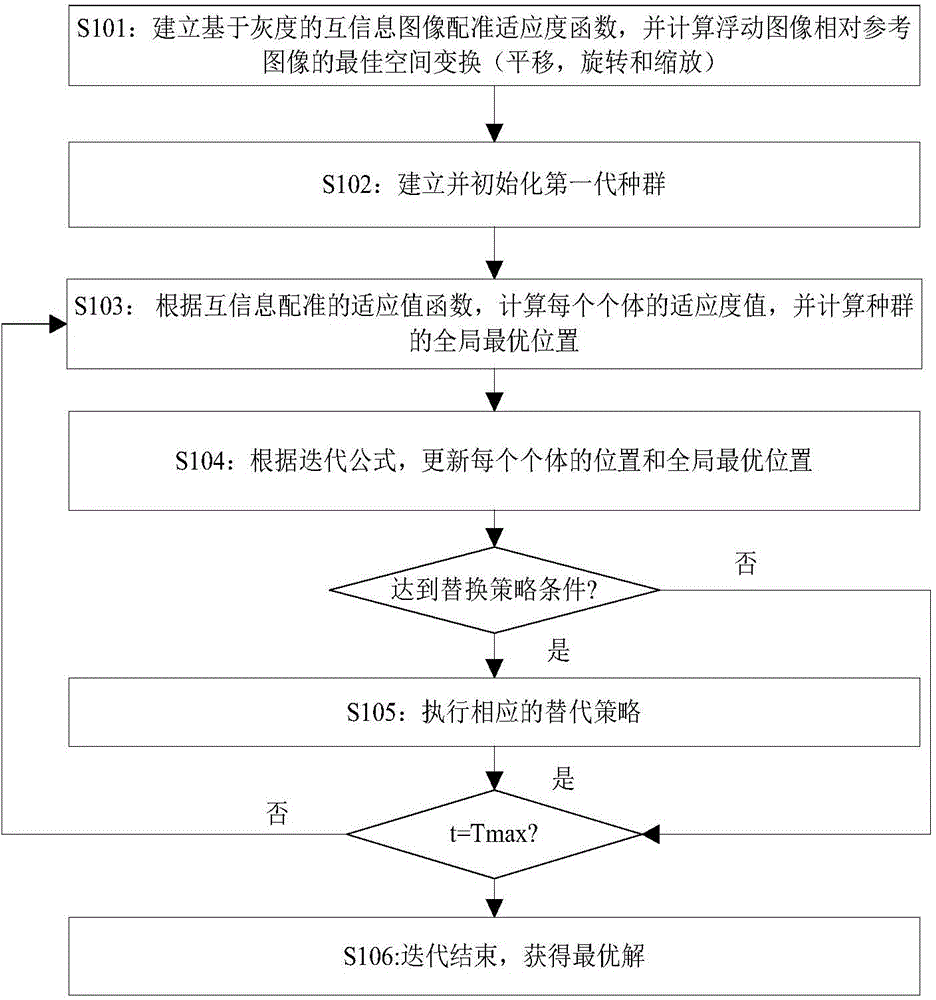
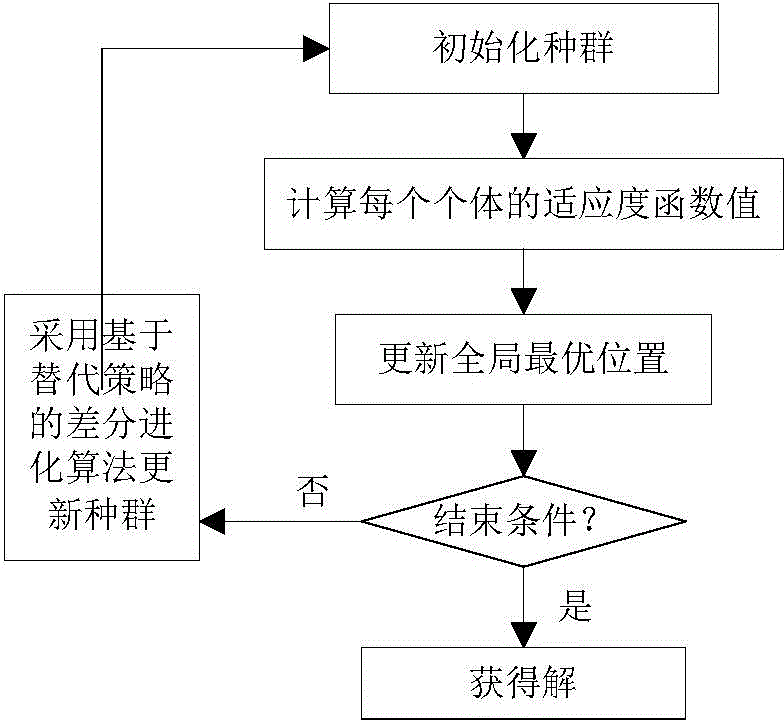
ActiveCN106204415AStrong global search capabilityImprove registration speedGeometric image transformationImaging processingAlternative strategy
The invention brings forward a novel image registering method. The method comprises the following steps: establishing gray-scale-based mutual information registering adaptation value function; establishing and initializing a group, wherein four dimensions of each individual in the group respectively represents horizontal translation, vertical translation, a rotation angle and a zoom coefficient of a floating image; according to the mutual information registering adaptation value function, calculating a fitness value of each individual, and calculating an optimal position of the whole group; by use of an iteration mechanism of a differential evolution algorithm, updating a position vector of each individual, and updating the optimal position of the whole group; determining whether conditions for executing an alternative strategy is satisfied, and if so, executing the corresponding alternative strategy; and repeatedly executing the aforementioned steps until maximum iteration frequency Tmax of the differential evolution algorithm is satisfied. The novel image registering method has the advantages of good registering stability and high precision, greatly improves the performance of an image registering algorithm and lays a reliable foundation for subsequent image processing work.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
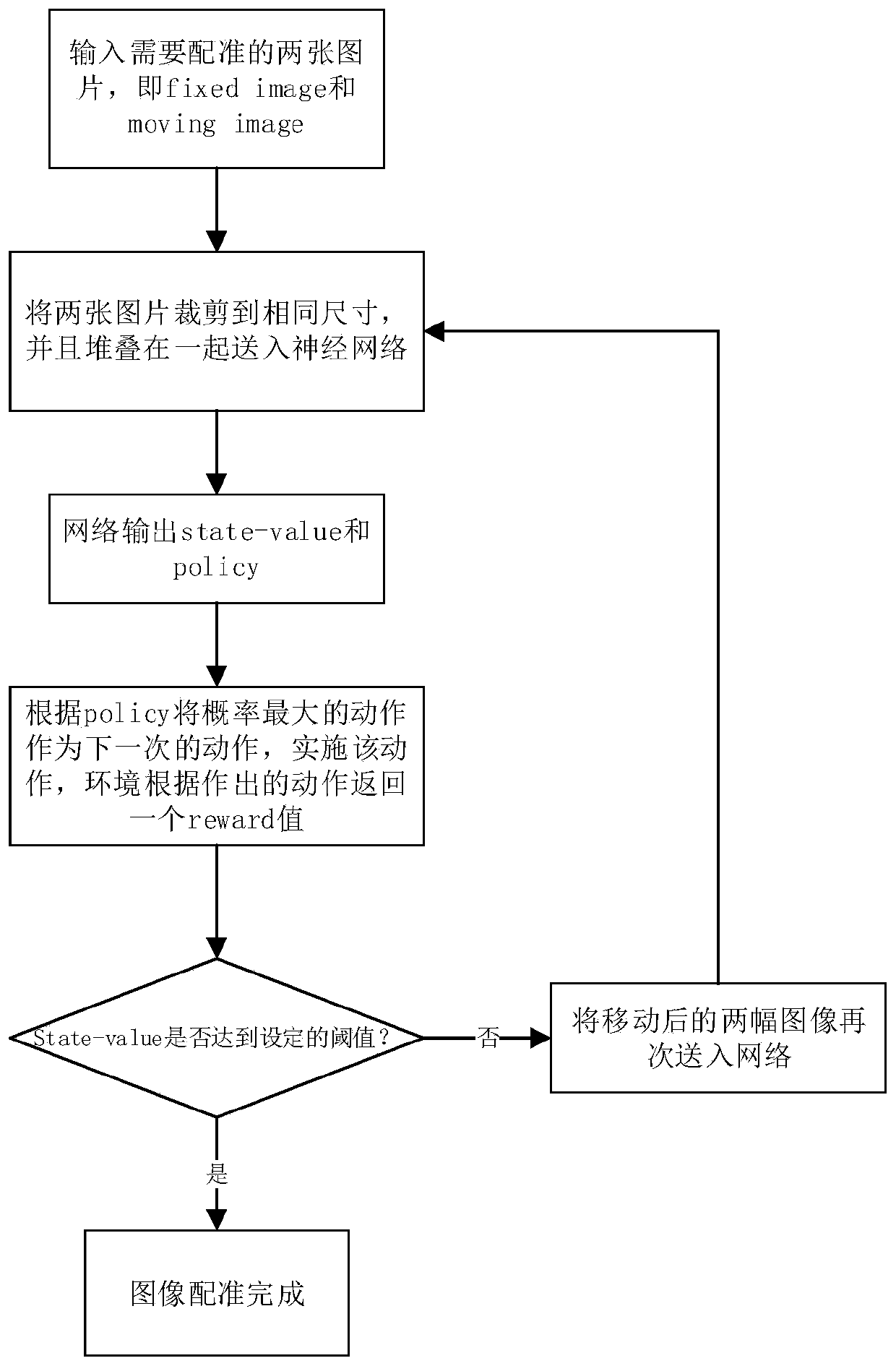
Image multi-mode registration method based on asynchronous deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN110211165ARegistration stabilizationImprove registrationImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmReward value
The invention discloses an image multi-mode registration method based on asynchronous deep reinforcement learning. The registration method comprises the following steps: inputting two pictures of different modes (such as CT and MRII) into a neural network in a stacking manner for processing, and outputting current state value information and probability distribution information of strategy actions; moving the dynamic image in the environment according to the probability distribution information and returning a reward value; judging whether the current network state value information reaches athreshold; and sampling the current image registration and outputting a final result. The method is based on reinforcement learning (A3C algorithm). According to the technical scheme, a user-defined reward function is provided, a cyclic convolution structure is added to make full use of space-time information, Monte Carlo is adopted for image registration, the registration performance is improved,and compared with an existing registration method, the registration result is closer to a standard registration image, and the registration of images with large differences is more stable.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
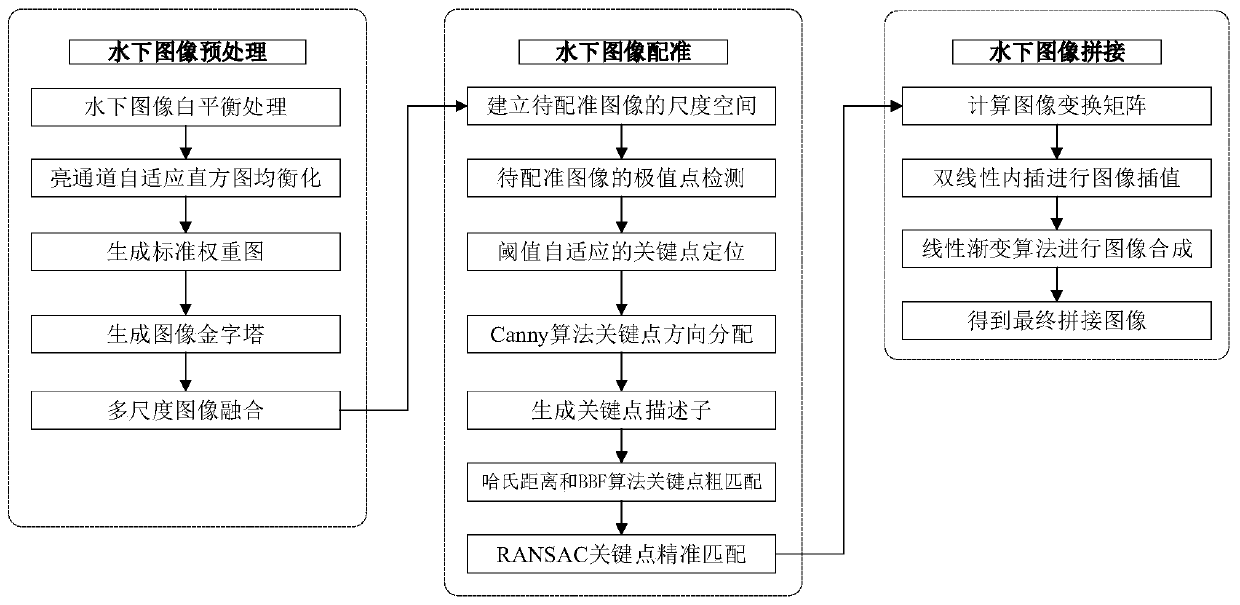
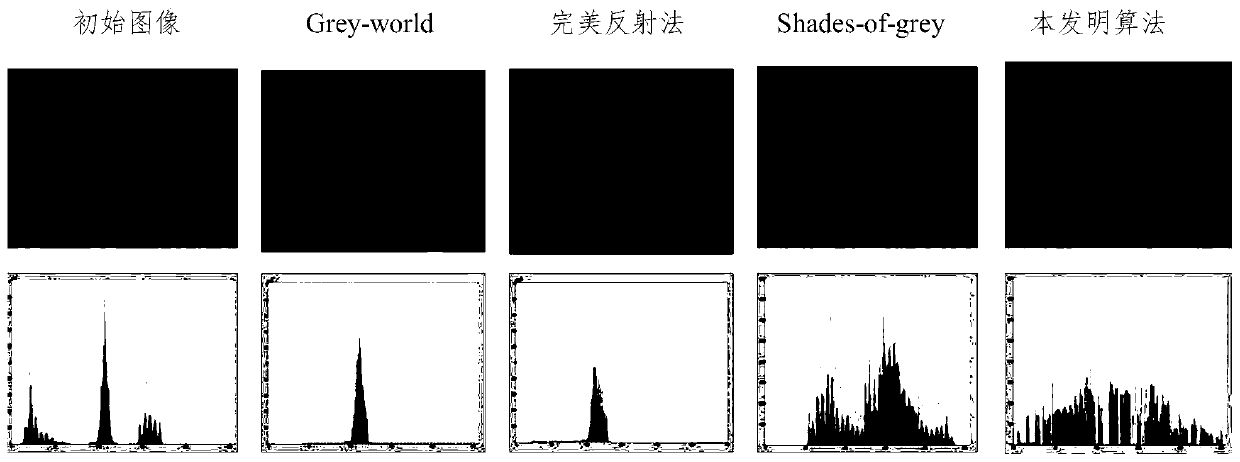
Underwater image splicing method based on multi-scale image fusion and SIFT features
ActiveCN111260543AImprove registration accuracyReduce edge effectsImage enhancementGeometric image transformationPattern recognitionEngineering
The invention discloses an underwater image splicing method based on multi-scale image fusion and SIFT features. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing image enhancement on an underwater image by adopting an improved white balance algorithm and a linear interpolation-based CLAHE algorithm; 2) fusing an image after image enhancement by adopting a double pyramid image fusion methodto obtain an underwater preprocessed image; 3) performing underwater image registration on the underwater preprocessed image through an improved SIFT algorithm; and 4) calculating to obtain an image affine transformation matrix, and completing final underwater image splicing by adopting a linear gradual change synthesis algorithm. Experiments prove that the method fully considers the underwater environment and underwater imaging characteristics, and can obviously improve the effects and accuracy of underwater image enhancement, registration and splicing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Spatially variant image deformation
ActiveUS7646936B2Improve registrationFast and accurate resultImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageSpatial change
Disclosed are systems for and methods of registering (i.e., aligning) a deformable image with a reference image subject to a spatially variant flexibility model and / or a non-Gaussian smoothing model. These systems and methods allow for the consideration of differences between the ways in which structures of interest may move within a patient. The registration includes modifying the deformable image to match similar features in the reference image. The systems include a deformation engine configured for performing a deformation algorithm subject to the spatially variant flexibility and / or smoothing models.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Inkjet printing system
InactiveUS8398226B2Reducing cost and complexity and energy consumption and footprintGood flexibilityDuplicating/marking methodsInksPolymer sciencePolymer chemistry
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Double-registration method for different-exposure images in wide dynamic camera
InactiveCN104202538AImprove registration accuracyImprove registrationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging qualityImaging Feature
The invention relates to a double-registration method for different-exposure images in a wide dynamic camera. An existing wide dynamic camera is overlarge in calculation amount due to the fact that an image feature based registration algorithm is utilized to realize registration of the different-exposure images. The double-registration method for the different-exposure images in the wide dynamic camera includes that multichannel data of video images different in exposure are acquired through shooting hardware, videos with same exposure are registered respectively, the different-exposure images are reregistered by utilizing registered video images, registration accuracy of the different-exposure video images is improved, and needed wide dynamic images are synthesized finally. By the method, registration effect of the different-exposure video images of the handle wide dynamic camera can be improved, the wide dynamic video better in imaging effect is synthesized, and registration operation amount is reduced. By the method, by the aid of double registration, registration accuracy of the different-exposure images is improved, and imaging quality of the wide dynamic image is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG RADIO AND TELEVISION GROUP
System and Method for Adjusting Selected Operating Parameters of Image Forming Device Based on Selected Environmental Conditions to Improve Color Registration
ActiveUS20100080587A1High voltageSelective operationRecording apparatusElectrographic process apparatusPotential differenceImage formation
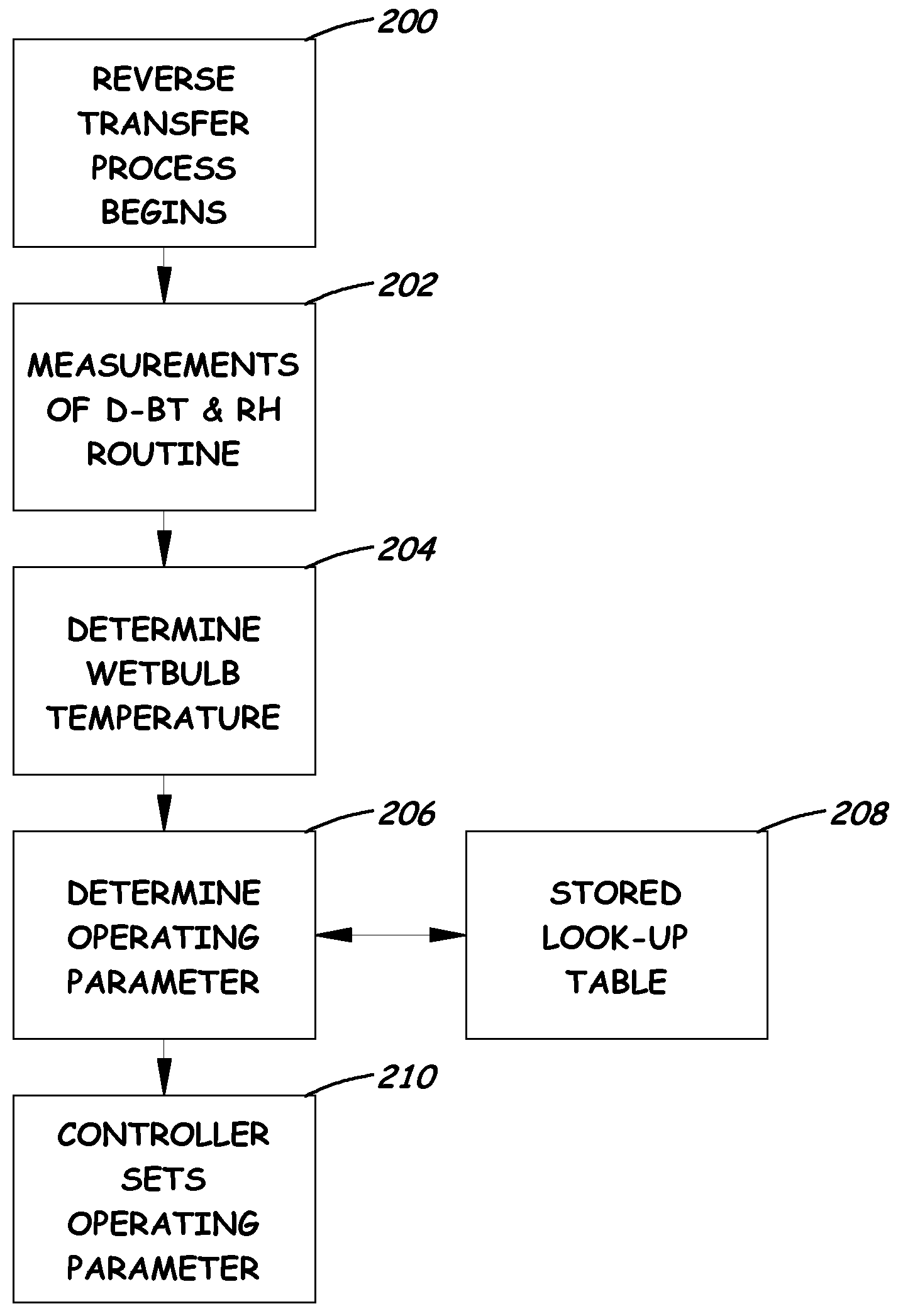
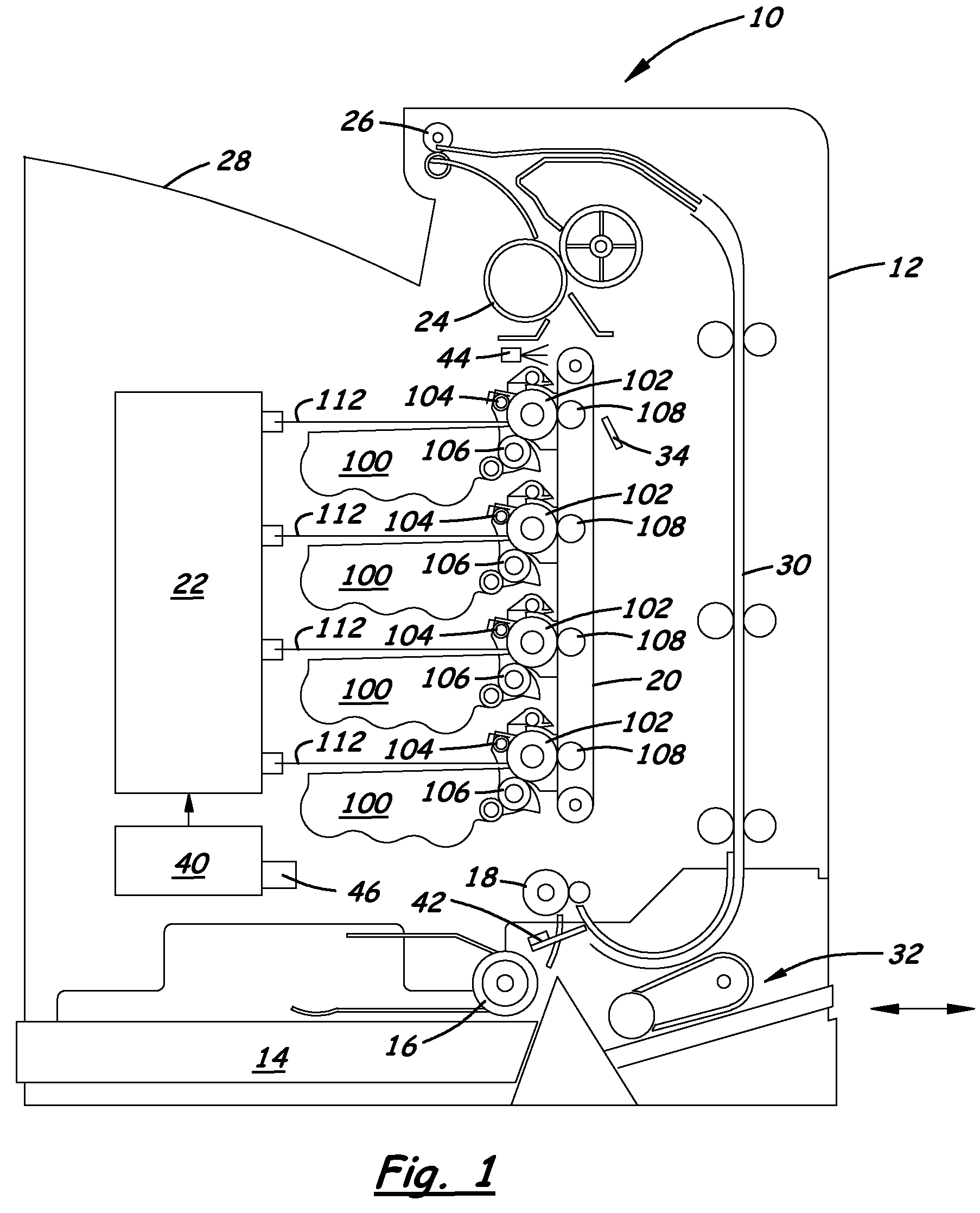
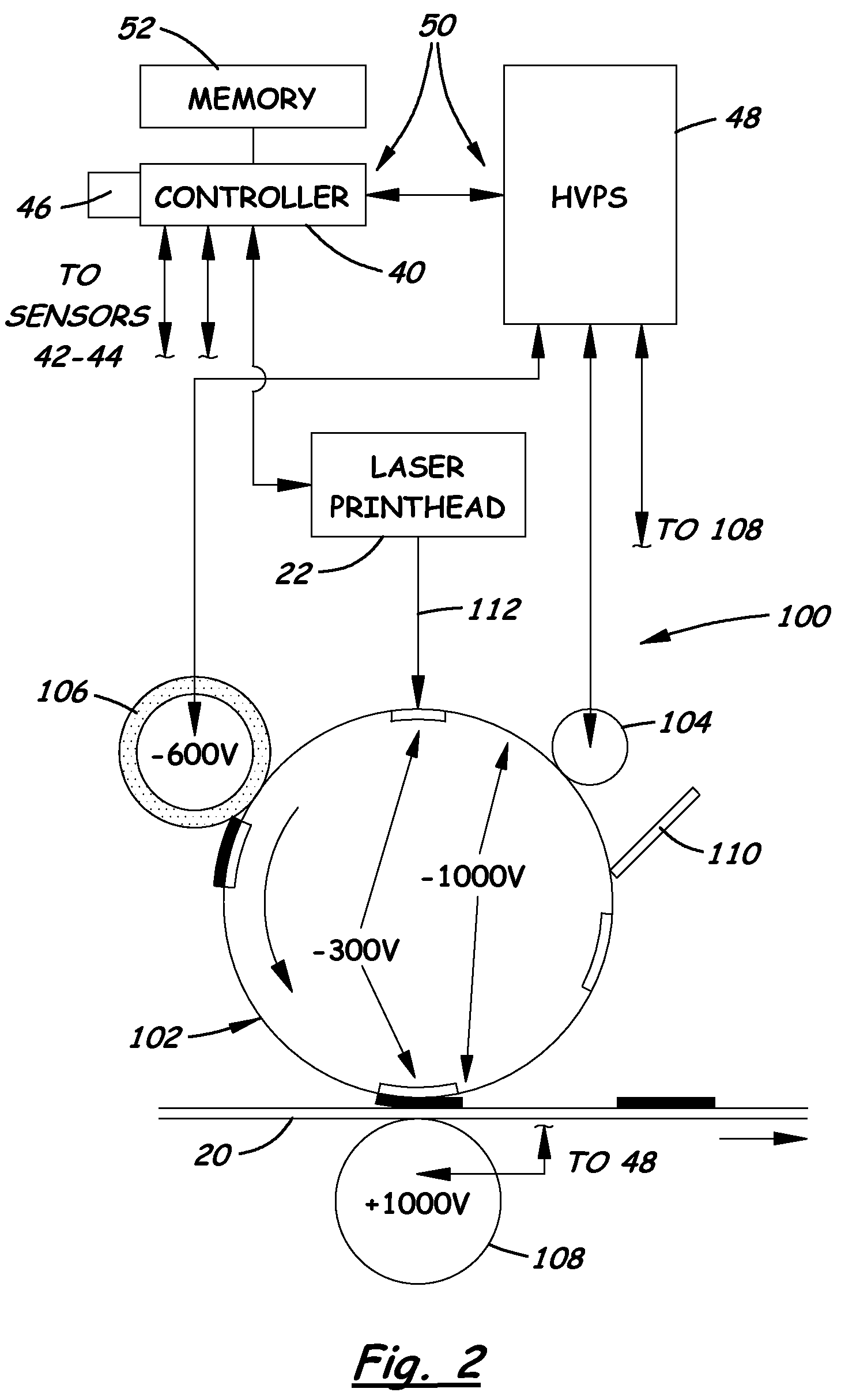
A system for adjusting selected operating parameters of an image forming device to improve color registration based on selected environmental conditions includes a first image forming station to print a first registration mark on a substrate, a second image forming station to at least partially erase the first registration mark to form a registration pattern in a reverse transfer process of the color registration, and a control mechanism to adjust voltage biases of charge and developer rolls of the second image forming station based on wet-bulb temperature values determined from measured dry-bulb temperature and relative humidity values and stored in a lookup table so as to maintain a predetermined potential difference between charged and uncharged areas of a PC drum of the second image forming station that avoids Paschen breakdown and the development of toner at charged areas of the PC drum during the reverse transfer process of the color registration.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
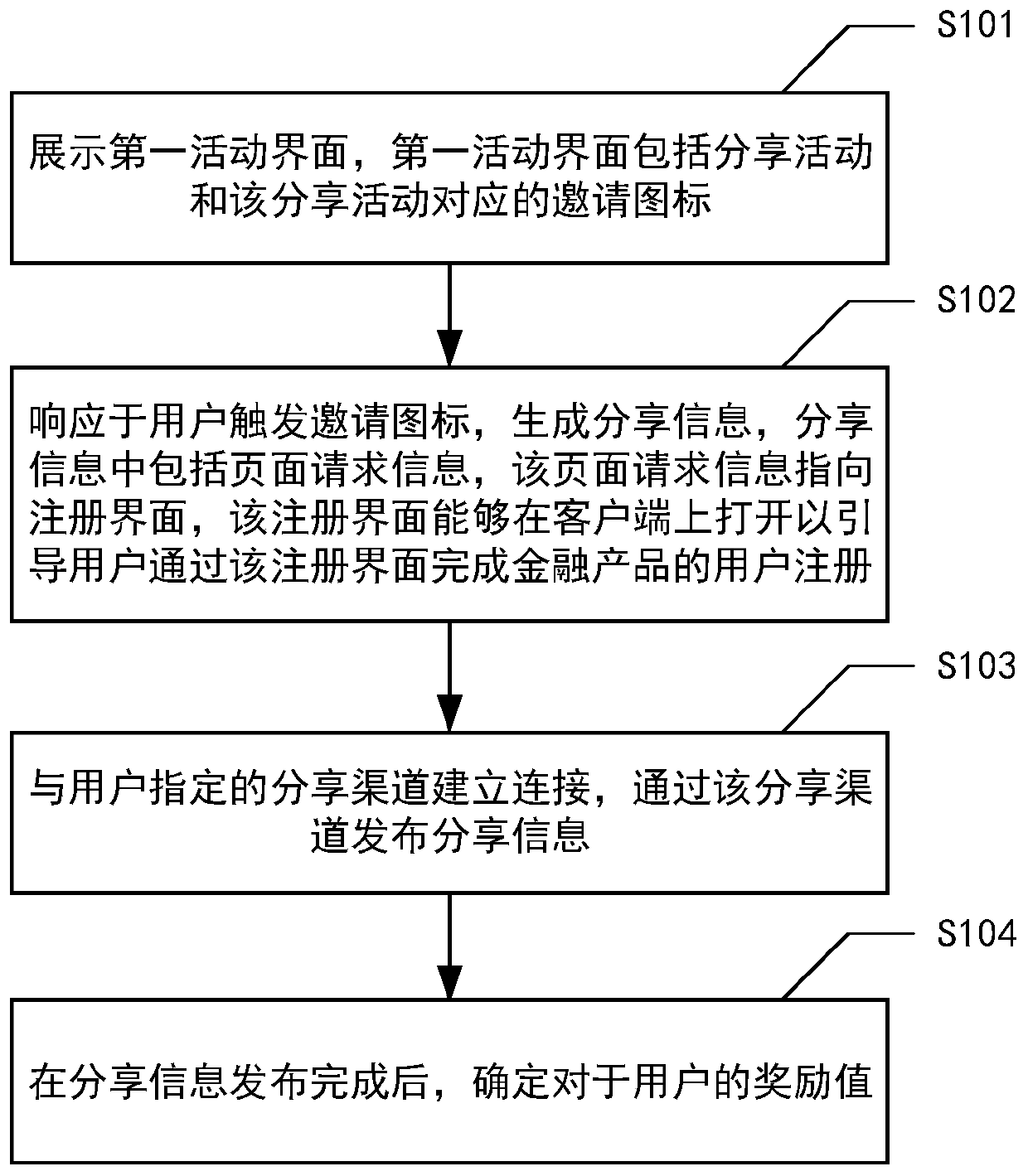
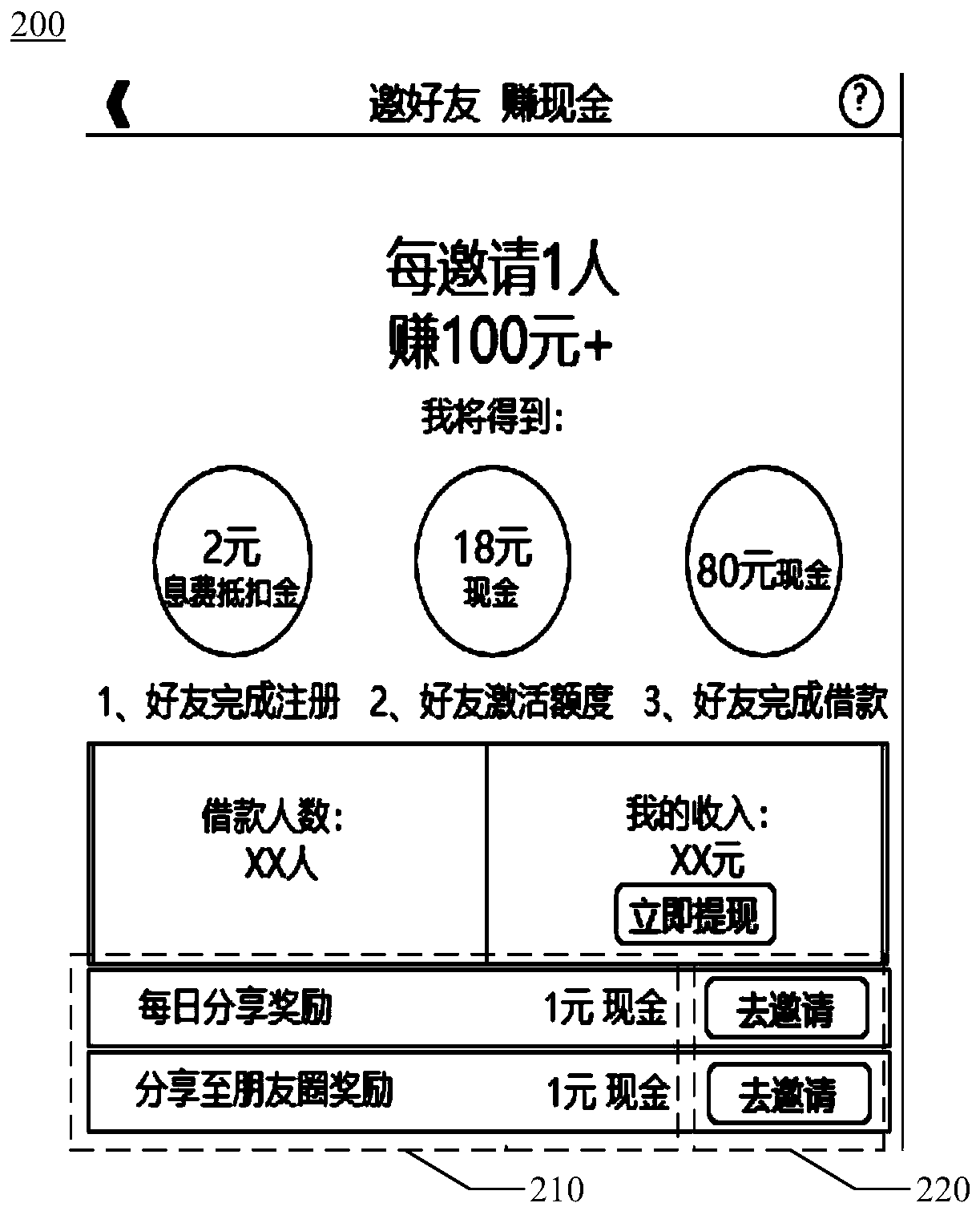
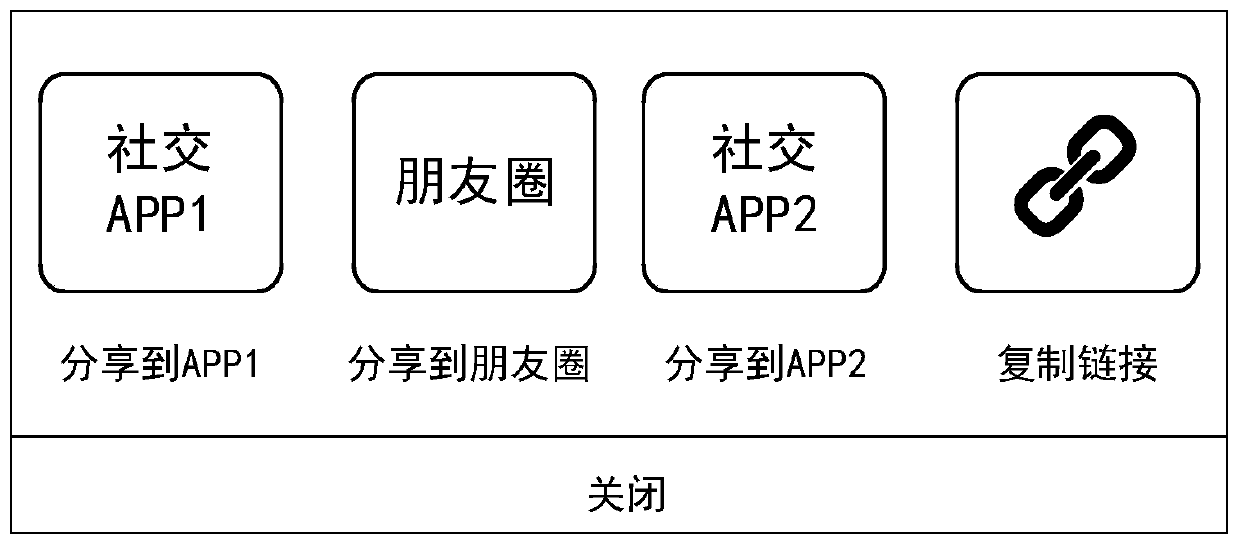
Sharing method and device for financial product invitation activities
InactiveCN110766446AImprove registrationReduce customer acquisition costsFinanceAdvertisementsInternet privacyEngineering
The invention discloses a sharing method for financial product invitation activities. The method comprises: displaying a first activity interface, wherein the first activity interface comprises a sharing activity and an invitation icon corresponding to the sharing activity; responding to an invitation icon triggered by a user; generating shared information, wherein the sharing information comprises page request information; wherein the page request information points to a registration interface; the registration interface can be opened on the client to guide a user to complete user registration of the financial product through the registration interface, establishes connection with a sharing channel specified by the user, publishes the sharing information through the sharing channel, and determines a reward value for the user after the sharing information is published. According to the method, after the user triggers the invitation icon of the sharing activity and publishes the sharinginformation, the reward value for the user to complete the sharing activity is determined, so that the user can be encouraged to complete the sharing activity through reward measures to invite more users to register, the customer obtaining cost is reduced, and the user registration amount is increased.
Owner:北京淇瑀信息科技有限公司
Registration apparatus for registering images
ActiveUS20180174314A1Improve registration qualityImproved image reconstructionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionConfidence mapImaging Feature
The invention relates to a registration apparatus (14) for registering images comprising a unit (11) for providing a first and a second image of an object, such that an image element of the first image at a respective position has been reconstructed by multiplying projection data values of rays traversing the image element with weights and by backprojecting the weighted projection data values, a unit (12) for providing a confidence map comprising for different positions in the first image confidence values being indicative of a likelihood that an image feature is caused by a structure of the object, the confidence value being calculated as a sum of a function, which depends on the respective weight, over the rays traversing the respective image element, and a unit (13) for determining a transformation for registering the first and second image to each other under consideration of the confidence map.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
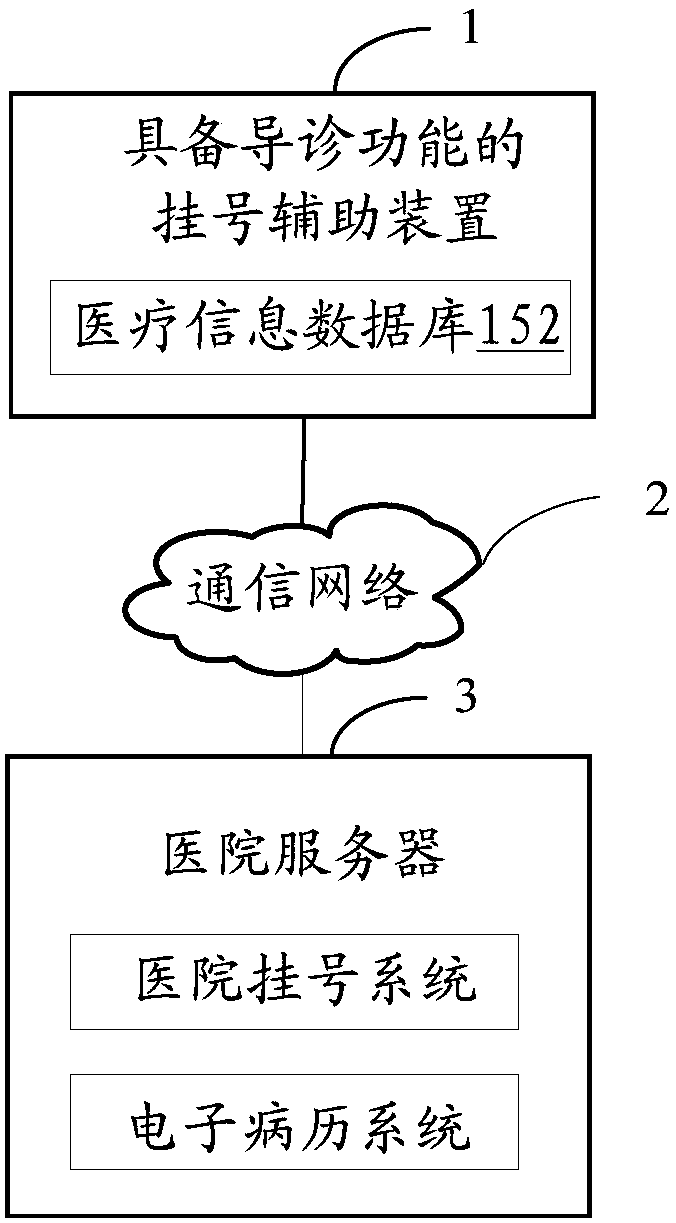
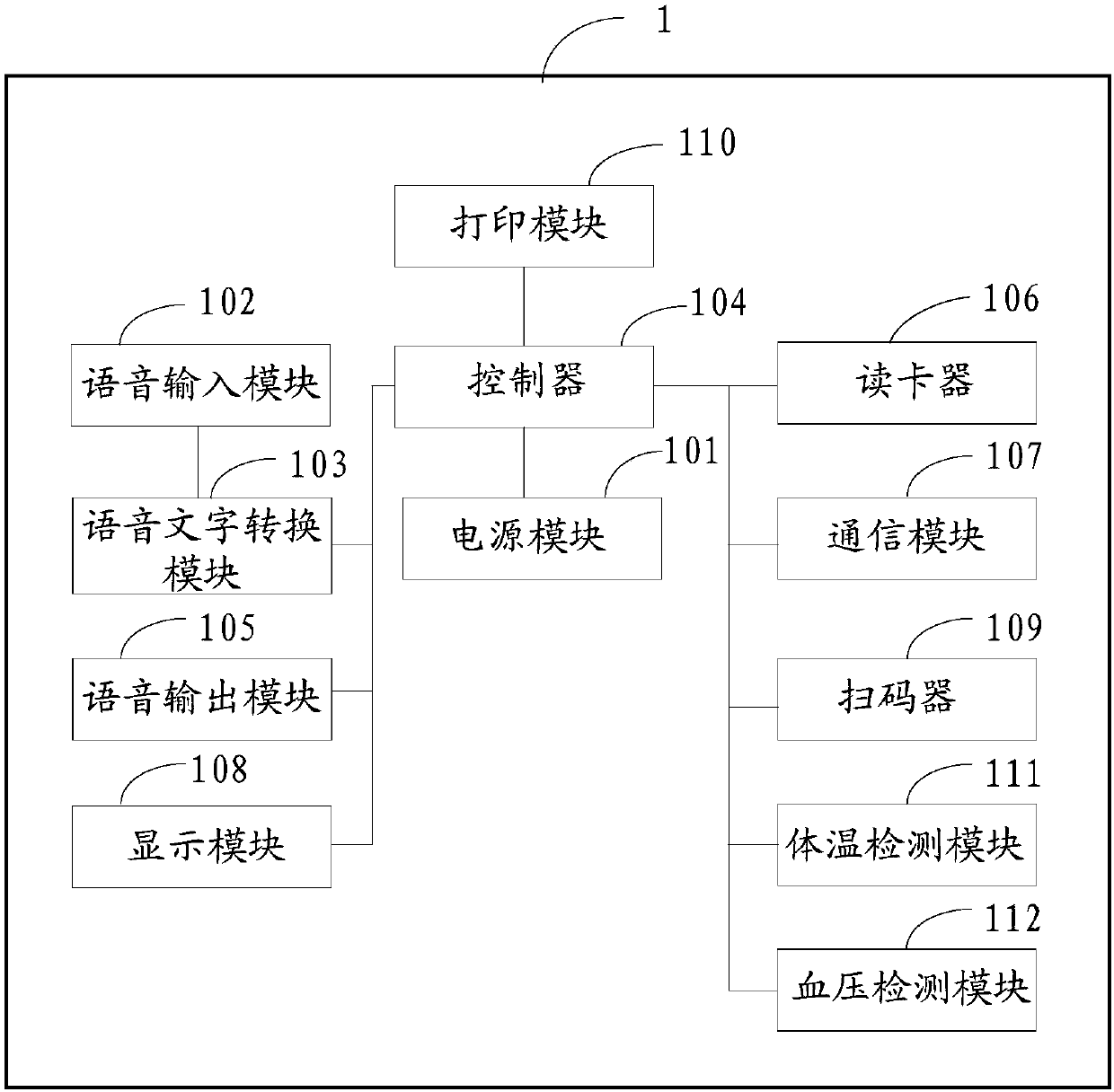
Auxiliary registration device with hospital guiding function
InactiveCN107818625AImprove registrationImprove the efficiency of medical treatmentData processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisPatient VisitSpeech sound
The invention discloses an auxiliary registration device with a hospital guiding function. The auxiliary registration device with the hospital guiding function is characterized in that voice messagesof patients are collected, and the collected voice messages of the patients are converted into text messages of the patients; key words are extracted from the text messages of the patients, and the extracted key words are compared with a medical information database; when the key words are matched with the medical information database, patient symptom key words contained in the key words are determined; according to the patient symptom key words, patient visiting department information is inquired from the medical information database, identity information of the patients is collected, and theidentity information of the patients, the patient visiting department information and patient registration requests are sent to a hospital server; furthermore, the collected patient body temperaturevalues, patient blood pressure and patient text information are sent to the hospital server. The auxiliary registration device with the hospital guiding function disclosed by the invention can improveregistration and doctor visiting efficiencies and improve user experience.
Owner:E TECHNO INFORMATION TECH +1
Financial product new user inviting method and system
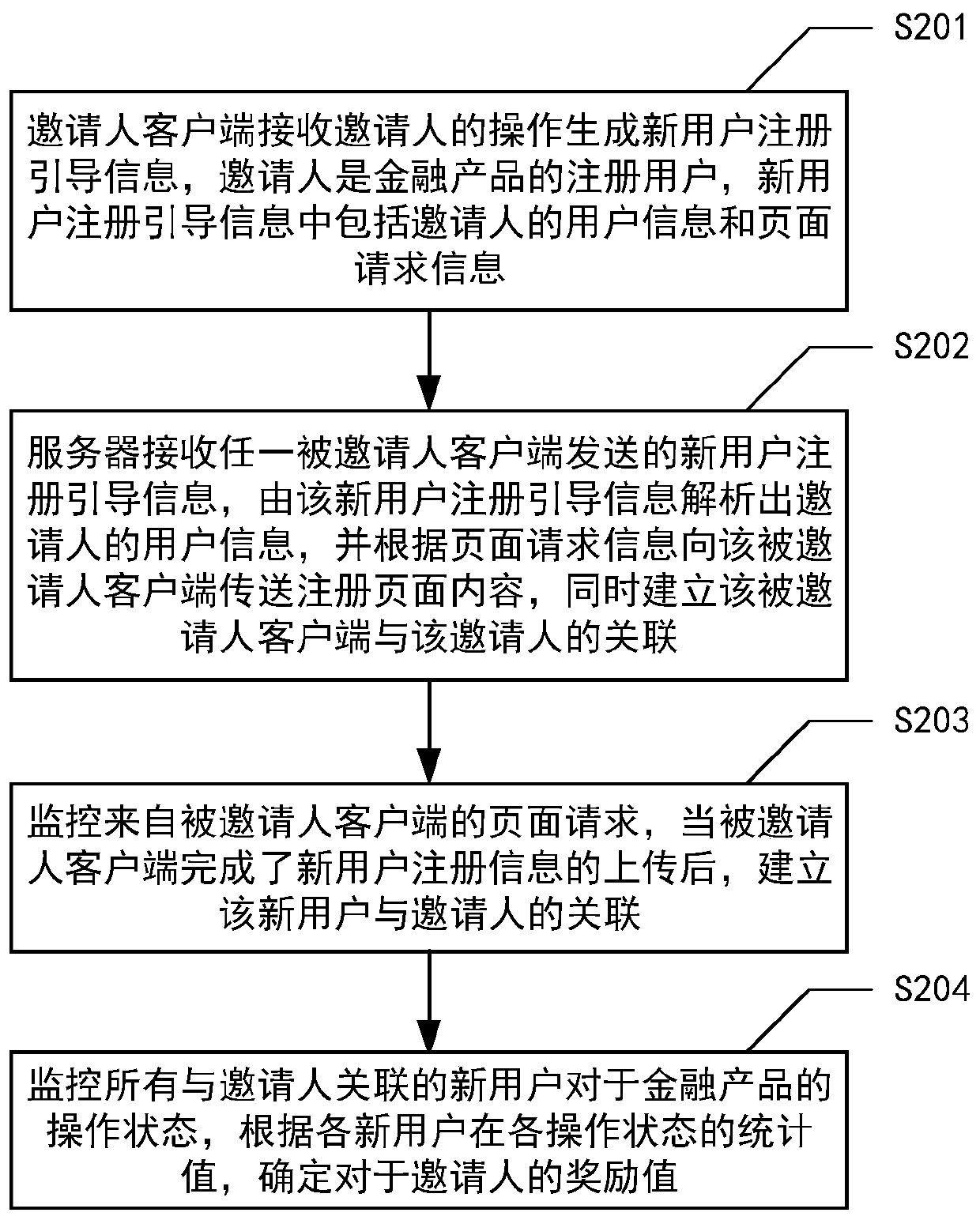
InactiveCN110807650AImprove registrationReduce customer acquisition costsFinanceMarketingInternet privacyDatabase
The invention discloses a financial product new user invitation method which comprises the steps that an inviter client receives operation of an inviter to generate new user registration guide information, the inviter is a registered user of a financial product, and the new user registration guide information comprises user information and page request information of the inviter; the server receives new user registration guide information sent by any invitee client, analyzes the user information of the inviter according to the new user registration guide information, transmits registration page content to the invitee client according to the page request information; meanwhile, the association between the invitee client and the inviter is established to monitor a page request from an invitee client; and after the invitee client completes uploading of the registration information of the new user, association between the new user and the inviter is established to monitor operation statesof all the new users associated with the inviter for the financial product, and an award value for the inviter is determined according to a statistical value of each new user in each operation state.
Owner:北京淇瑀信息科技有限公司
Image registration method and device
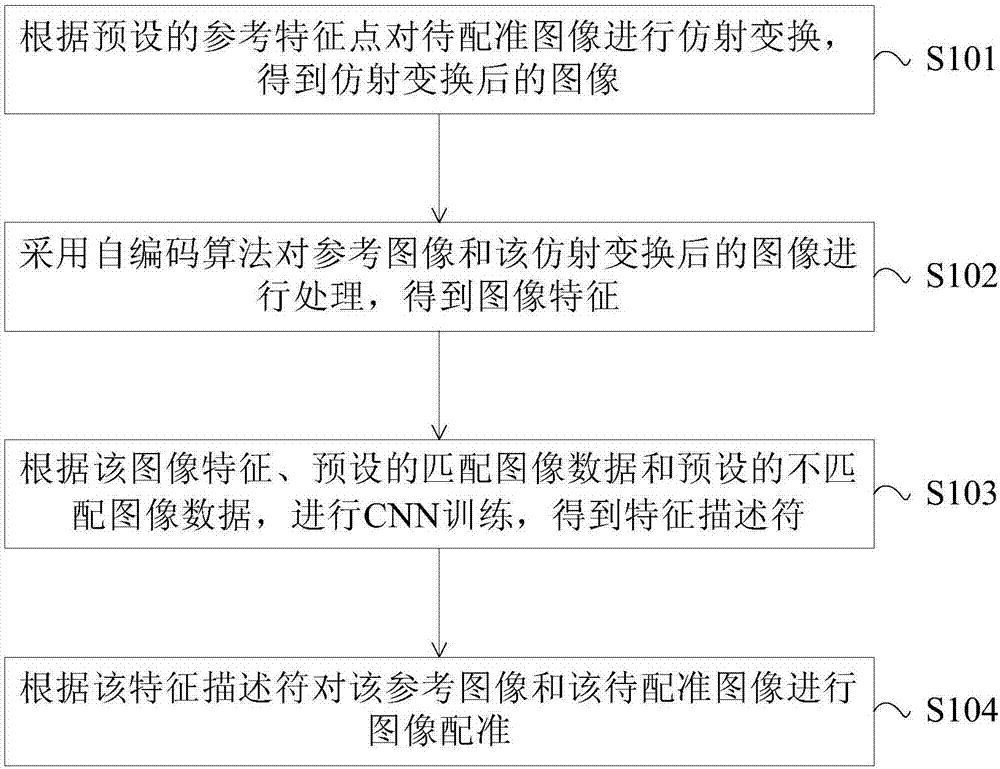
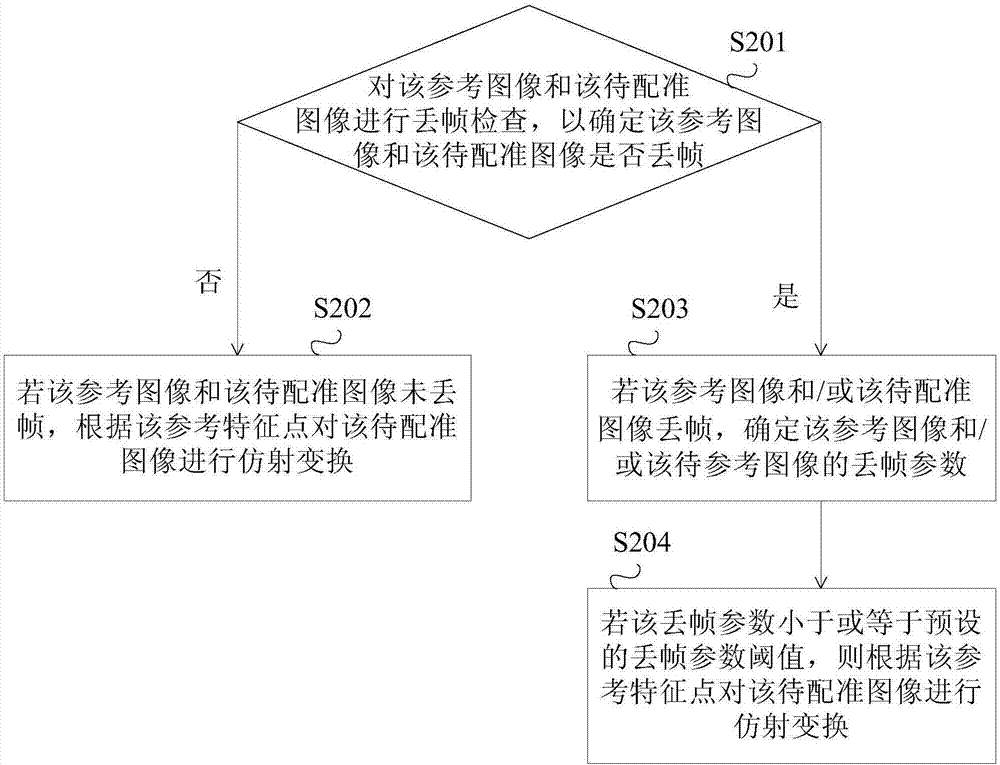
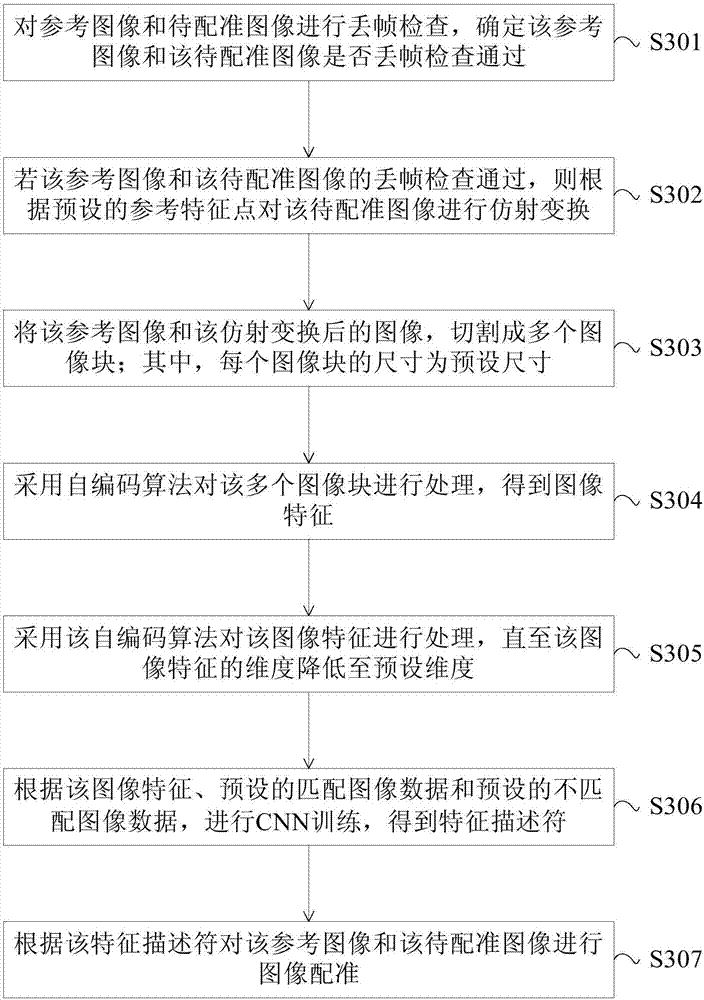
ActiveCN106952223AImprove registrationImprove registration accuracyGeometric image transformationNeural learning methodsReference imageMultispectral image
The invention provides an image registration method and device. The image registration method may comprises steps of: subjecting a to-be-registered image to affine transformation according to a preset reference feature point to obtain an image subjected to the affine transformation; processing a reference image and the image subjected to the affine transformation by using a antoencoding algorithm to obtain an image feature; performing CNN training based on the image feature, preset matched image data and preset unmatched image data to obtain a feature descriptor; and subjecting the reference image and the to-be-registered image to image registration according to the feature descriptor. The image registration method and device achieve high registration accuracy of multispectral images and improve an image registration effect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Implement method and device for infrared image registration
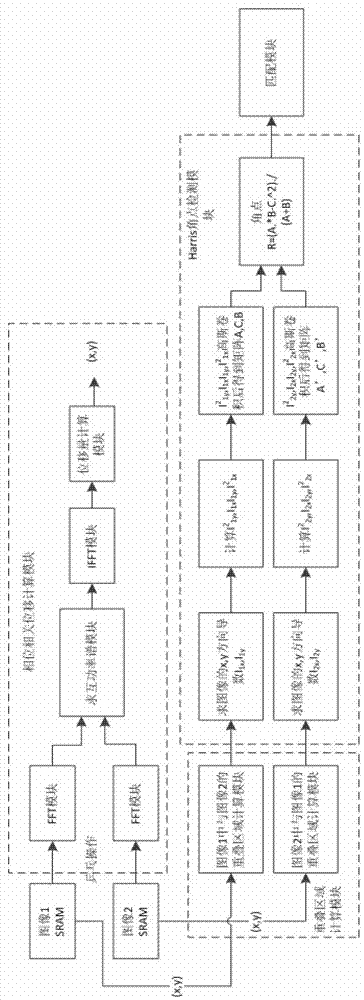
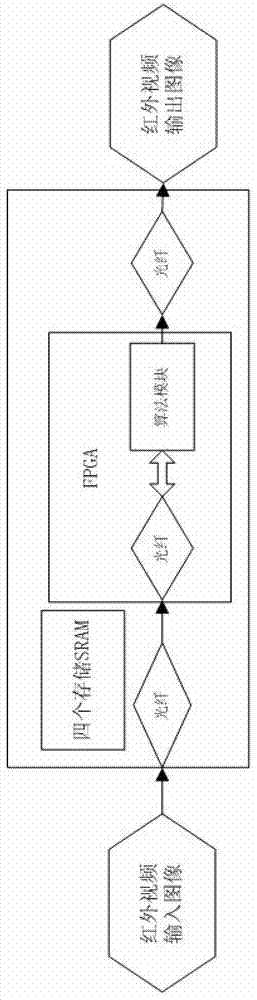
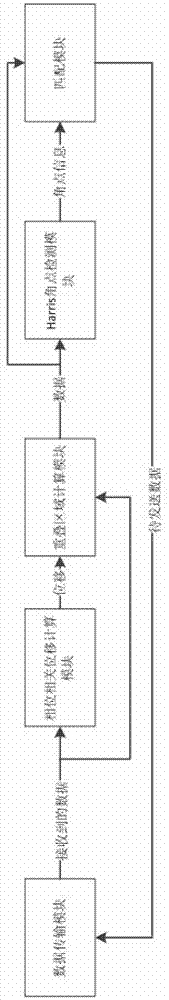
InactiveCN103295222AReduce complexityImprove registrationImage analysisPhase correlationSufficient time
The invention discloses an implement method and device for infrared image registration. The device for the infrared image registration comprises a data transmission module, a phase correlation displacement calculation module, an overlapping region calculation module, a Harris corner detection module and a matching module. The data transmission module is connected with the phase correlation displacement calculation module, the data transmission module and the phase correlation displacement calculation module are both connected with the overlapping region calculation module, the overlapping region calculation module is connected with the Harris corner detection module, the overlapping region calculation module and the Harris corner detection module are both connected with the matching module, and the matching module is connected with the data transmission module. According to the implement method and device for the infrared image registration, a phase correlation method and a Harris corner detection method are combined, an FPGA with a Rocket IO module is sued for transmitting data in high speed, therefore, in an infrared pixel searching tracking system, image registration preprocessing can be carried out fast and accurately, the requirements of precision and instantaneity of registration can be met, and sufficient time margins can be left for follow-up algorithms.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Systems and methods for implementing unique offsetting stacker registration using omni-directional wheels for set compiling in image forming devices
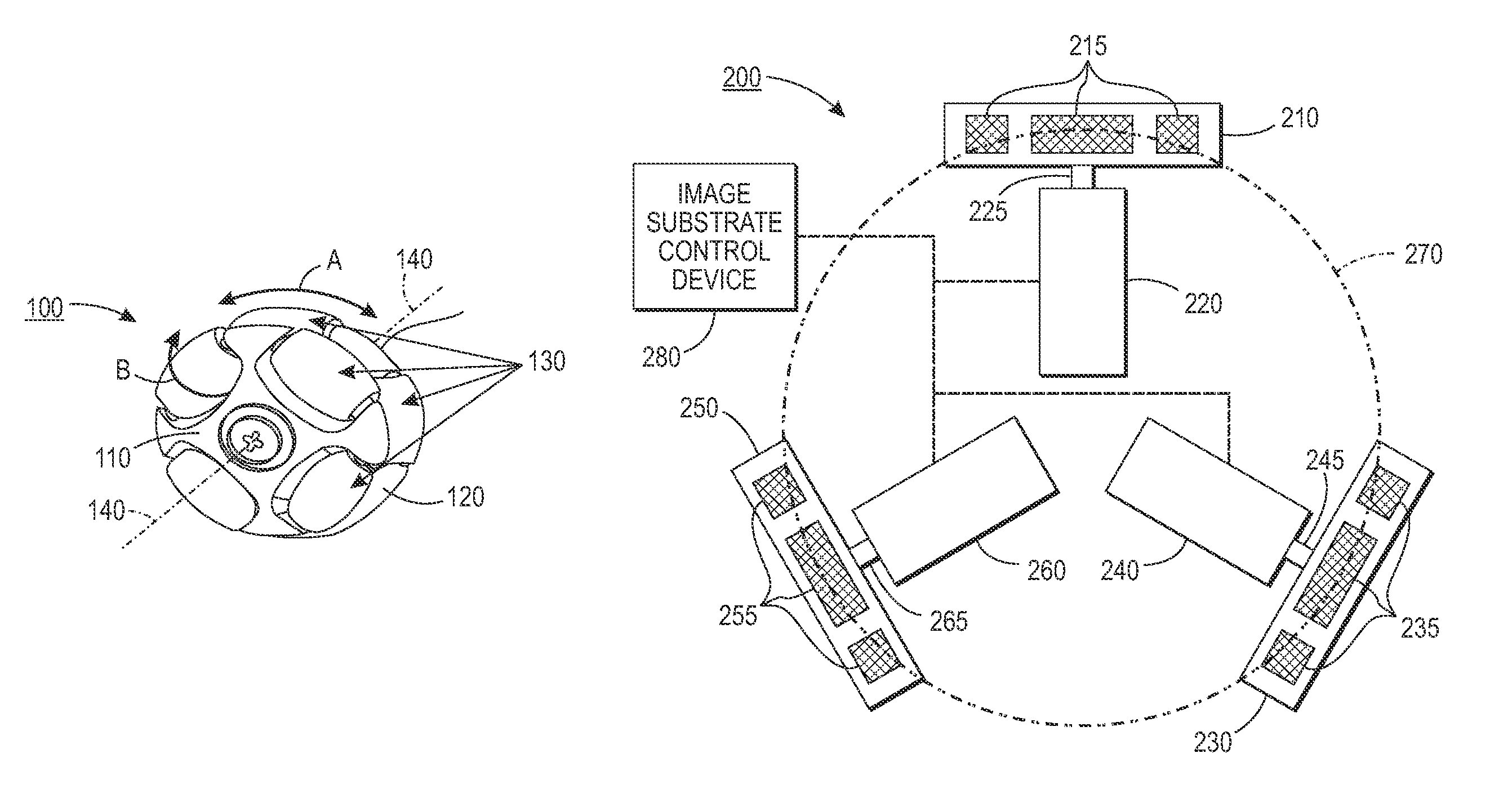
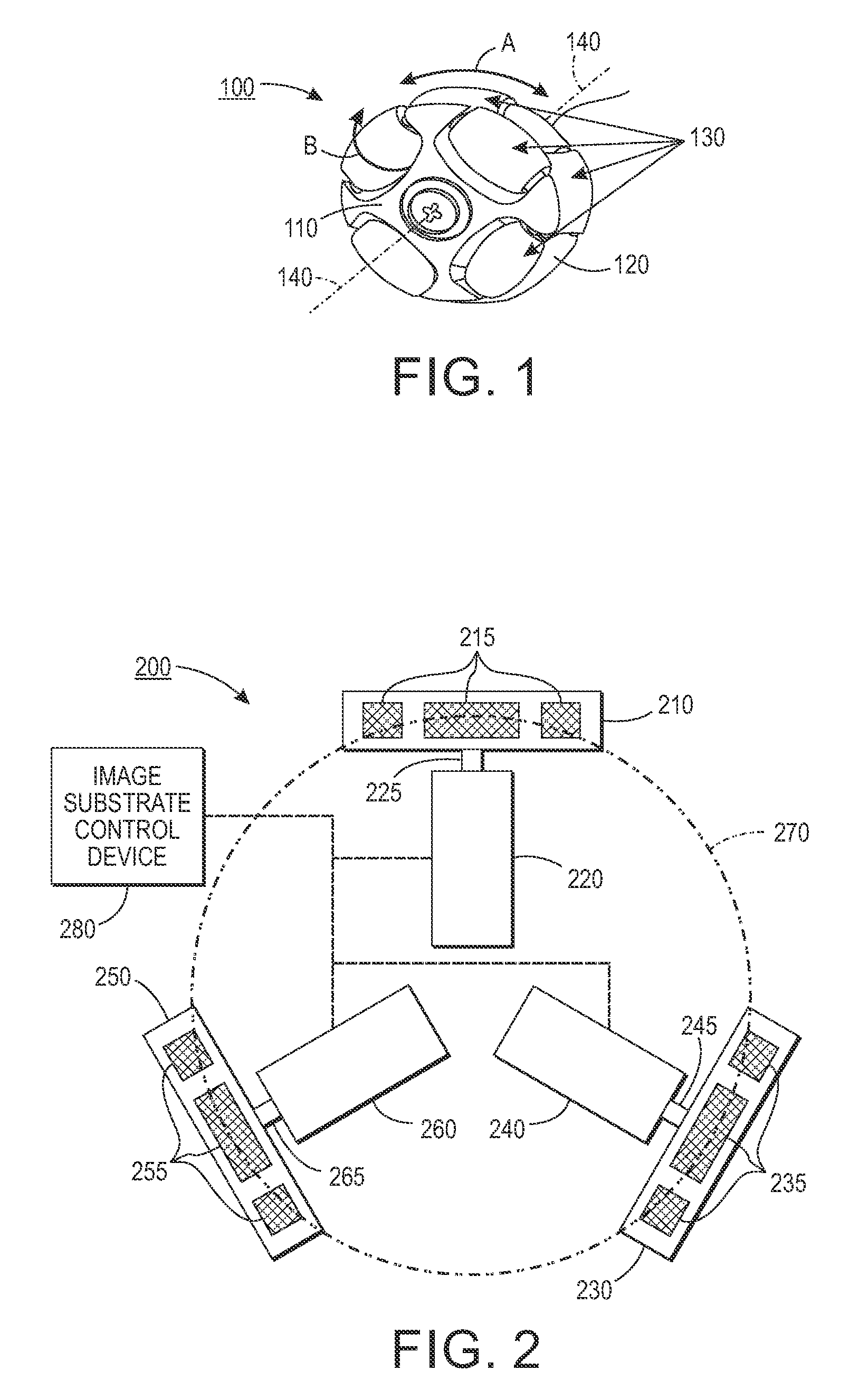
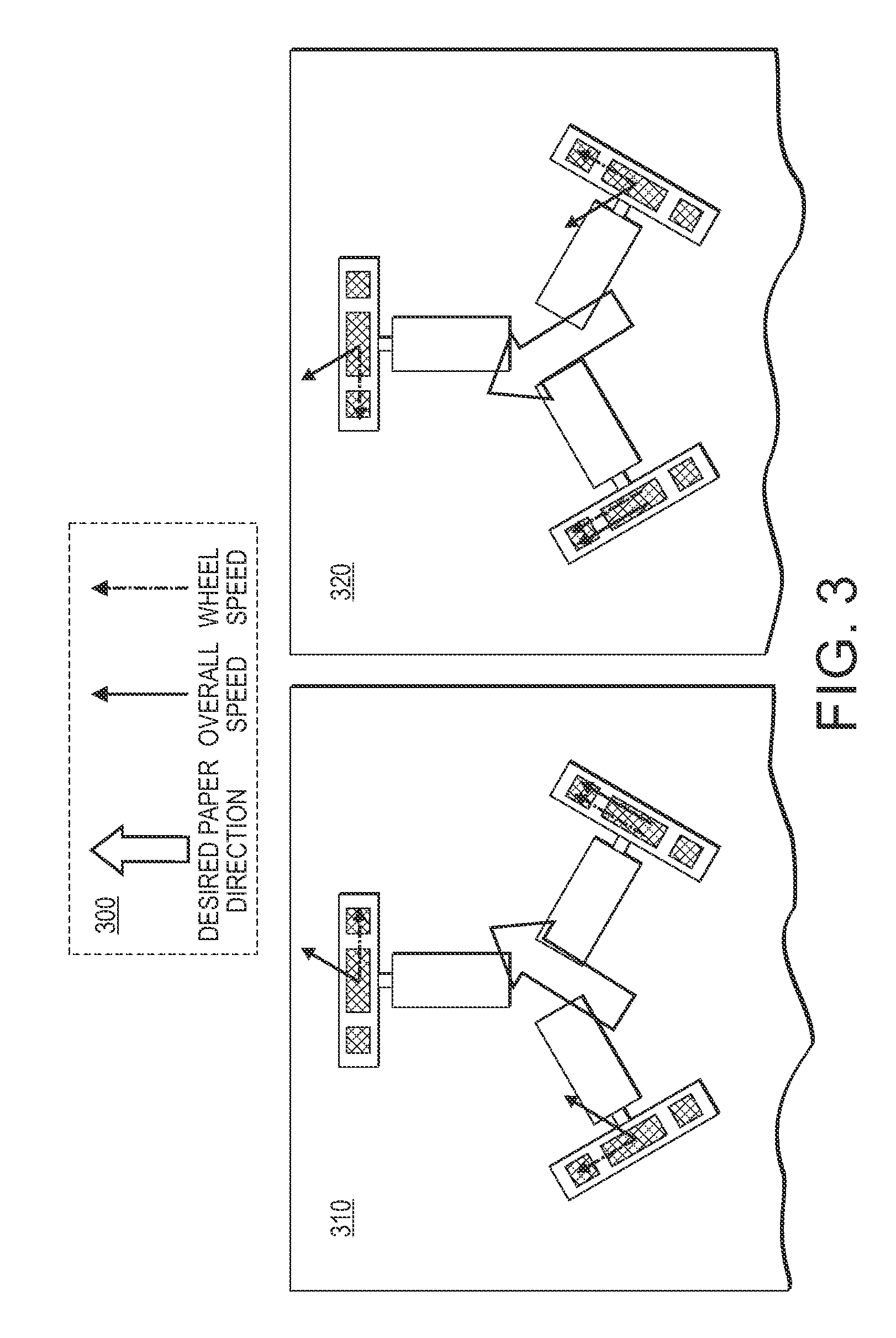
InactiveUS9156642B2Convenient registrationImprove abilitiesRegistering devicesElectrographic process apparatusControl engineeringImage formation
A system and method are provided for improving stack integrity for a set of image receiving media substrates at an output of a compiler in an image forming device by positioning a particularly configured substrate handling device downstream of the output of the compiler in a process direction. The substrate handling device is configured of a plurality of omni-directional wheeled devices that provide drive (traction) normal to a motor axis under control of one of a respective plurality of independent motors while allowing sliding in the motor axis direction. The omni-directional wheeled devices, in one embodiment, are configured with small roller wheels along the periphery of the wheel. When using three or more omni-directional wheeled devices, translational movement can be combined with rotation to deliver sheets of image receiving media exiting the compiler at a correct angle and lateral position for further processing.
Owner:XEROX CORP
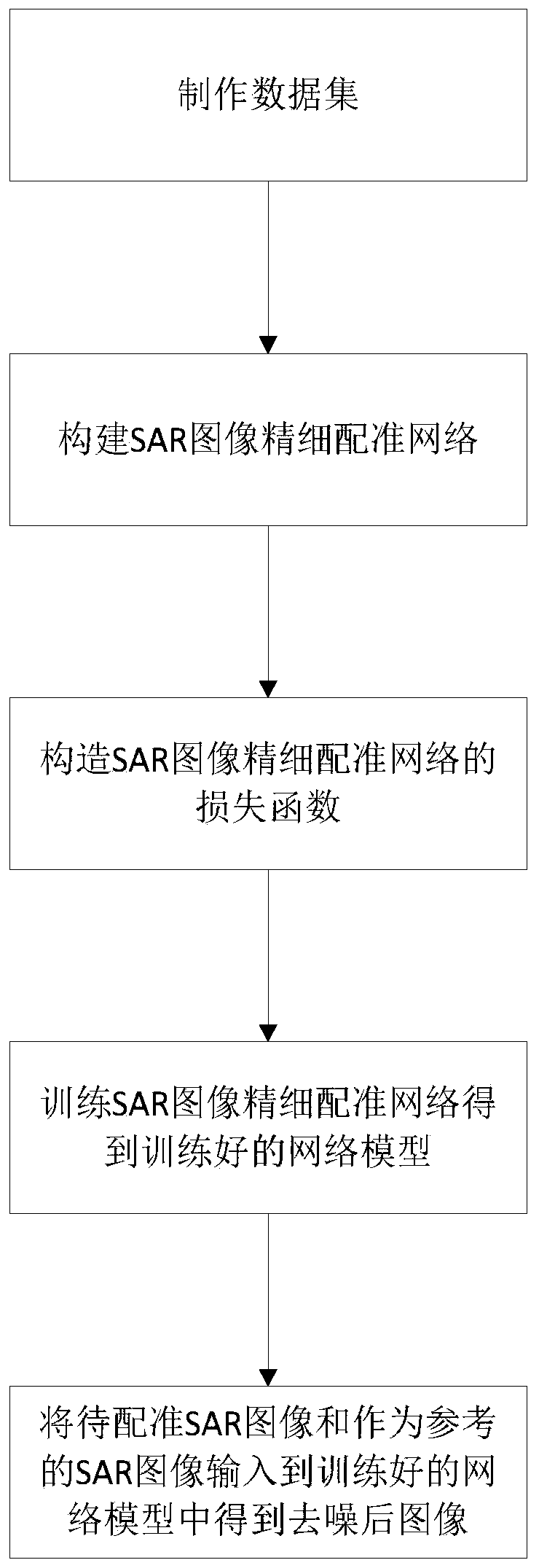
SAR image fine registration method based on deep learning
ActiveCN110728706AImprove registration performanceAvoid the extraction processImage enhancementImage analysisTraining data setsSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses an SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image precise registration method based on deep learning, and mainly solves the problems that local distortion cannot be corrected and time isconsumed in a traditional method. According to the implementation scheme, the method comprises the steps of 1) obtaining a training data set; 2) constructing a neural network for SAR image fine registration; 3) constructing a loss function of a neural network model for SAR image fine registration; 4) training a neural network for SAR image fine registration by using the training data set to obtain a trained network model; and 5) inputting the SAR image to be registered and the SAR image as a reference into the trained network model to obtain a registered SAR image. The SAR image registrationmethod can correct the overall deformation and local distortion between the SAR images, improves the registration performance, accelerates the registration speed, and can be used for SAR image fusionand change detection.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com