Large-scale MIMO low-complexity hybrid precoding method and system
A low-complexity, pre-coding technology, applied in transmission systems, radio transmission systems, diversity/multi-antenna systems, etc., can solve problems such as high cost and complexity, and achieve reduced computational complexity, low complexity, and low complexity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
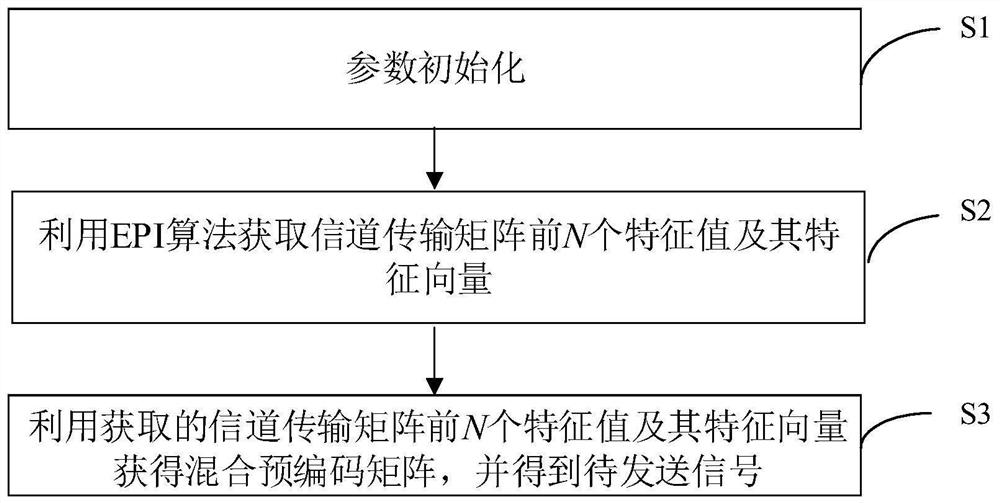
[0038] Such as figure 1 Shown is a flowchart of a massive MIMO low-complexity hybrid precoding method provided by an embodiment of the present invention. figure 1 The method shown includes the following steps:
[0039] S1: parameter initialization;
[0040] In this embodiment, parameter initialization includes: setting the number of transmitting antennas MN, where N represents the number of sub-arrays, M represents the number of antennas corresponding to each sub-array, the number of user antennas K, and the channel transmission matrix H.
[0041] S2: Use the EPI algorithm to obtain the first N eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the channel transmission matrix;
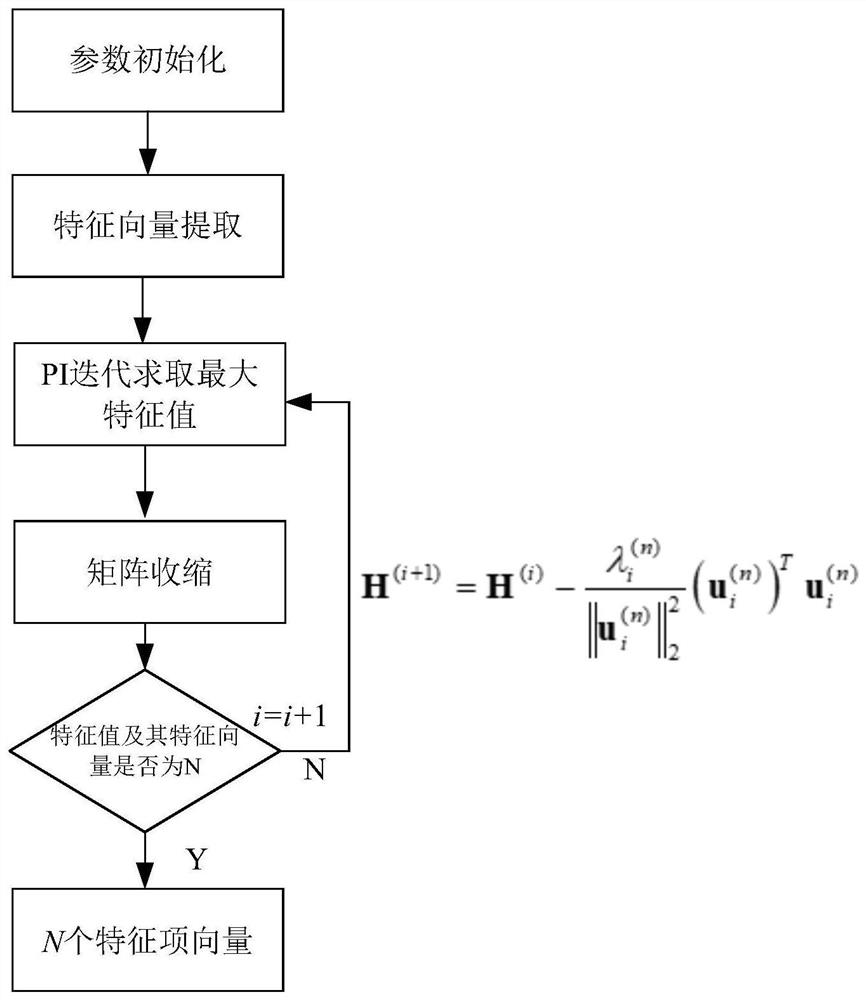
[0042] In this embodiment, after the parameter initialization setting is completed, the Extend power iteration method (Extend poweriteration, EPI) is used to obtain the first N eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the channel transmission matrix, such as figure 2 As shown, it can be achieved in the following ways:
...
Embodiment 2
[0063] This embodiment provides a massive MIMO low-complexity hybrid precoding system, including:
[0064] The initialization module is used to set the number of transmitting antennas, the number of user antennas and the channel transmission matrix;
[0065] The extended power iteration module is used to obtain the first several eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the channel transmission matrix by using the extended power iteration method;
[0066] In this embodiment, the above-mentioned extended power iteration module includes:
[0067] The power multiplication module is used to obtain the channel transmission matrix H in the ith iteration by using the power multiplication algorithm PI (i) The largest eigenvalue of and its eigenvector;
[0068] The matrix contraction module is used to use the matrix contraction algorithm to transmit the matrix H from the channel transmission matrix of the i-th iteration (i) Remove the channel transmission matrix H in the ith iteration (i) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com