Methods for differentiating pluripotent stem cells in dynamic suspension culture
A technology of human pluripotent stem cells and dynamic suspension, which is applied in the field of cell biology, neuroectoderm and glial lineage cells, and can solve problems such as not easy to expand
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
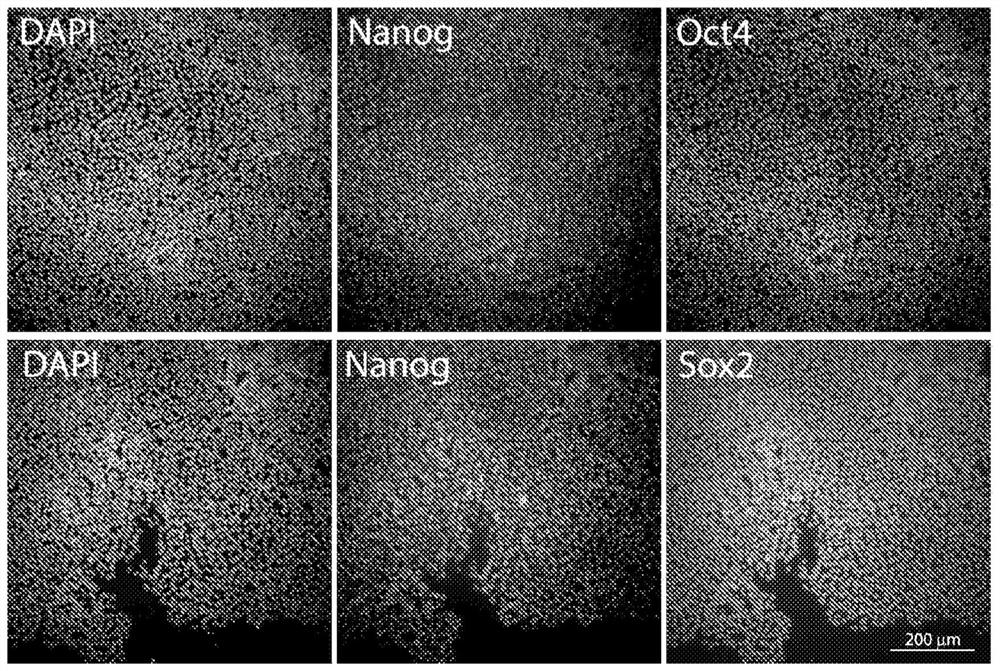
[0111] Example 1 - Culture and Expansion of Undifferentiated Human Embryonic Stem Cells
[0112] From the H1 line (WA01; Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998 Nov 6; 282(5391): 1145- 7) Working Cell Bank (WCB) generated from undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells (uhESC) in recombinant human laminin-521 (Corning #354224) coated, tissue culture treated polystyrene 225cm 2 Complete mTeSR on culture flasks (Corning #431082) TM -1 medium (StemCell Technologies #85850). Complete media changes daily until cells reach approximately 80-90% confluency, then use ReLeSR TM Reagents (Stem Cell Technologies #05872) were used to passage uhESCs. Will ReLeSR TM Lifted uhESC cells were seeded onto fresh laminin-521-coated 225 cm 2 flasks, and resume daily medium changes two days after inoculation. Cultured uhESCs from WCBs were expanded in this way for 2 to 5...
Embodiment 2
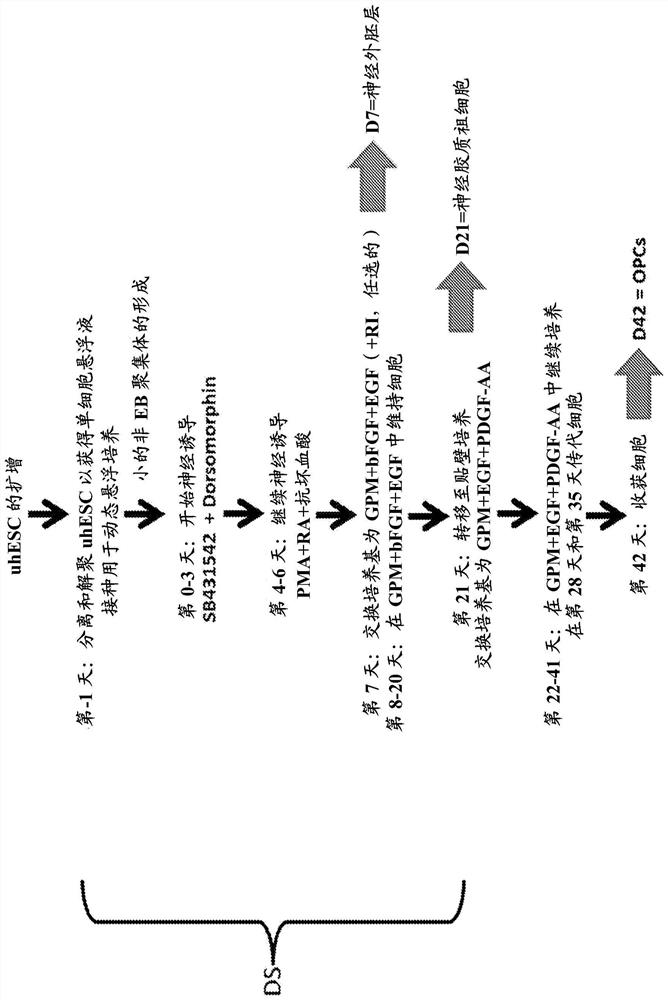
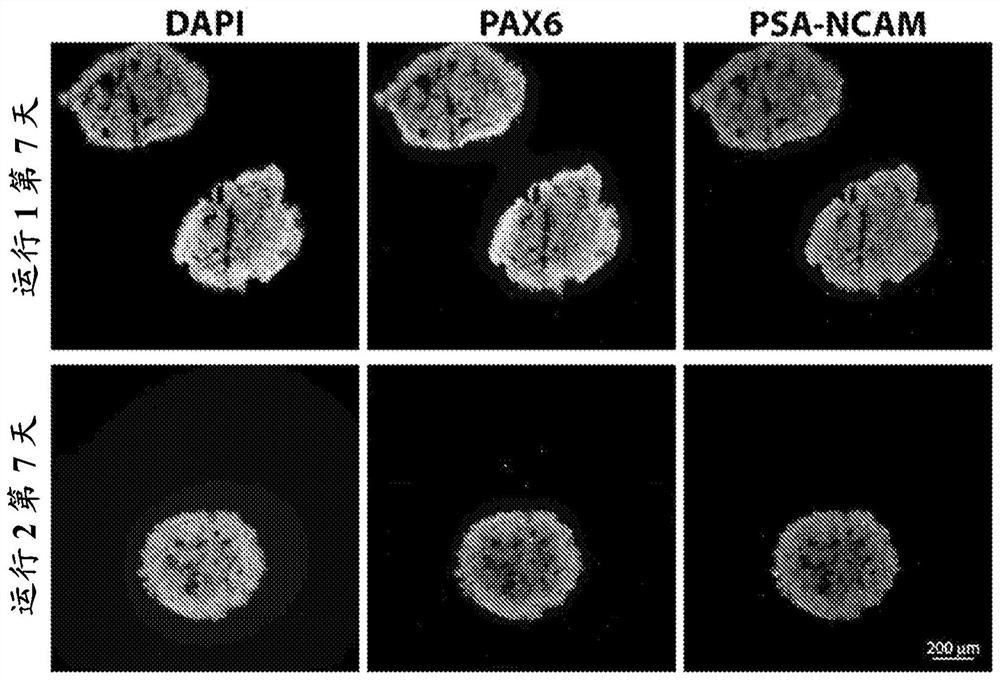
[0113] Example 2 - Method for Differentiating Human Embryonic Stem Cells into Neuroectodermal Progenitor Cells in Dynamic Suspension Culture
[0114] Day 1 : Expanded uhESCs (approximately 90% confluent) were isolated and cultured with (Stem Cell Technologies #07920) disaggregates to form a single cell suspension, allowing accurate cell counts and uniform seeding density. The depolymerized uhESCs were then plated at 1x10 6 A concentration of viable cells / mL was inoculated into a PBS-0.1 or PBS-0.5 microbioreactor system (PBS Biotech) (set to rotate at 35RPM or 25RPM, respectively (Day -1)) for dynamic suspension culture. Cells were seeded in Glial Progenitor Cell Medium (GPM; prepared with 2% B27 supplement (Gibco cat. no. 17504-044) and 0.04 μg / ml triiodo-thyronine (Sigma cat. no. T5516-1MG) DMEM / F12 (Gibco Cat. No. 10565-018)) and undifferentiated hESC medium (as in Example 1) supplemented with 10 μM Rho Kinase Inhibitor (RI, Tocris Cat. No. 1254) to support cell surviv...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Example 3 - Method for Differentiating Human Embryonic Stem Cells into Glial Lineage Cells in Dynamic Suspension Culture
[0119] Differentiation of uhESCs to neuroectoderm / neural progenitor cells (days 0-6) was performed as described in Example 2. On day 7, the differentiation medium was supplemented with 20 ng / mL human basic fibroblast growth factor (hbFGF, ThermoFisher, catalog number PHG0263), 10 ng / mL epidermal growth factor (EGF, Thermo Fisher, cat. ) and 10 μM RI of GPM to initiate differentiation into glial progenitor cells. For the next two weeks (days 8-20), the cell aggregates were placed in dynamic suspension at 45 rpm (PBS-0.1 mini-bioreactor) or 32 RPM (PBS-0.5 mini-bioreactor) supplemented with 20 ng / GPM of mL bFGF and 10 ng / mL EGF was maintained, and the medium was replenished daily using gravity settling and 70-80% medium exchange. On day 14, 10 μM RI was also added to fresh medium.
[0120] A subset of differentiated cells was harvested at day 21 o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com