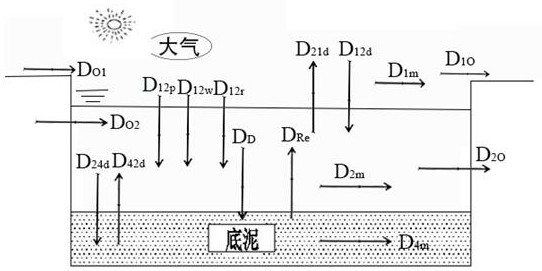
Method for simulating dynamic fate distribution of pollutants in reclaimed water replenishment lake
A technology for reclaiming water and pollutants, applied in the directions of instrumentation, design optimization/simulation, calculation, etc., which can solve problems such as disregarding spatial specificity, low resolution of large-scale models, and inapplicable pollutant fate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Sample collection and determination method used in the present invention
[0076] 1.1 Sample collection
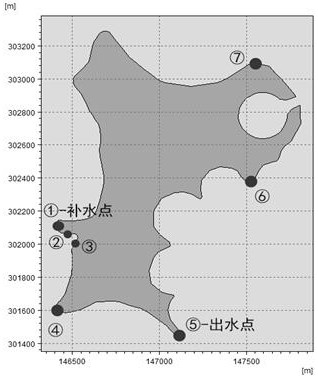
[0077] Taking Tianjin J Lake as the research object, such as figure 2 As shown, 7 sampling locations were determined according to the actual situation on site, as shown in image 3 As shown, the water sample sampling points are named W-1 (water supply port), W-2, W-3, W-4, W-5 (water outlet), W-6, W-7, and the sediment sampling points are named For S-2, S-3, S-4, S-5 (water outlet), S-6 and S-7, take 1.5L water samples from each sampling point and put them in clean brown glass bottles. Samples were collected with a stainless steel grab bucket, transferred to a clean tin foil bag, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. The concentration of pollutants detected by W-1 is used as the input data of the model, and the concentration data of other points are used to verify the accuracy of the model.
[0078] 1.2 Sample concentration detection
[0079] Water and sediment...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Coupling calculation of hydrodynamic and fugacity models
[0087] 2.1 Simulation results of lake hydrodynamics
[0088] MIKE 21 is used to establish the hydrodynamic model, the simulation step is 1 day, and the simulation time is 90 days; the flow direction of the study area is as follows: Image 6 shown. The flow velocity in the study area is as Figure 7 As shown, it is 2.09×10 -7 ~0.02 m / s, the flow velocity near the water supply point and the water outlet point is slightly higher, about 0.01~0.02 m / s, other areas, especially the boundary, the flow velocity is very slow, there are dead water areas, which is consistent with the actual situation of the lake.
[0089] 2.2 Detection of the effectiveness and accuracy of the method of the present invention
[0090] The measured value of DBP concentration in the lake water and sediment was compared with the simulated value of the model, respectively as follows: Figure 8 and Figure 9 shown. In the water phase, from ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com