Cooperative unloading and resource allocation method based on multi-agent DRL under MEC architecture
A multi-agent, resource allocation technology, applied in electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of not considering edge server cooperation, not extending to the continuous arrival of multiple services, not considering the problem of resource allocation, etc., to reduce the system Average latency and energy consumption, improve resource utilization, and achieve the effect of dynamic management
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The technical solution of the present invention will be specifically described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
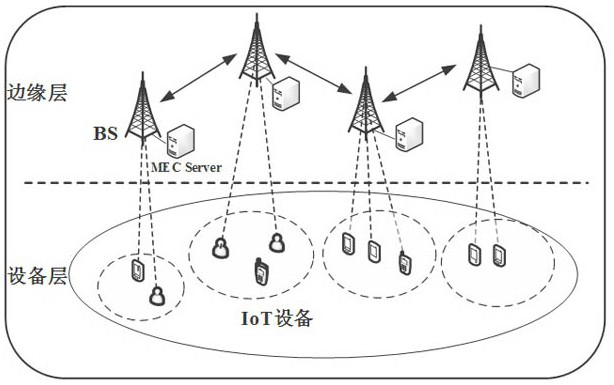
[0033] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a network architecture scenario to which an embodiment of the present invention can be applied, including a device layer and an edge layer. The device layer is composed of various IoT devices, and the edge layer is composed of multiple base stations. The base stations are connected through a wired network, and each base station is equipped with an MEC server with computing and storage capabilities. Therefore, when offloading tasks to edge servers, the selection of target edge servers should consider the current resource remaining status of each edge server. The user will first choose to offload the task to the edge server associated with the access base station. However, due to the difference in the number of users served by different edge servers and the arrival rate of user tasks, the spati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com