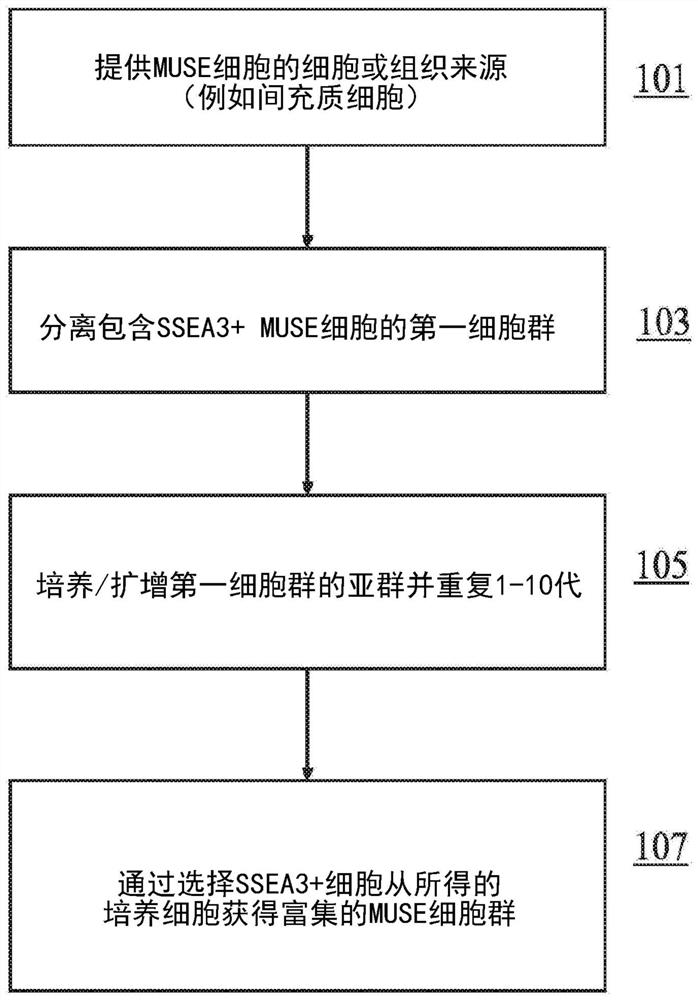
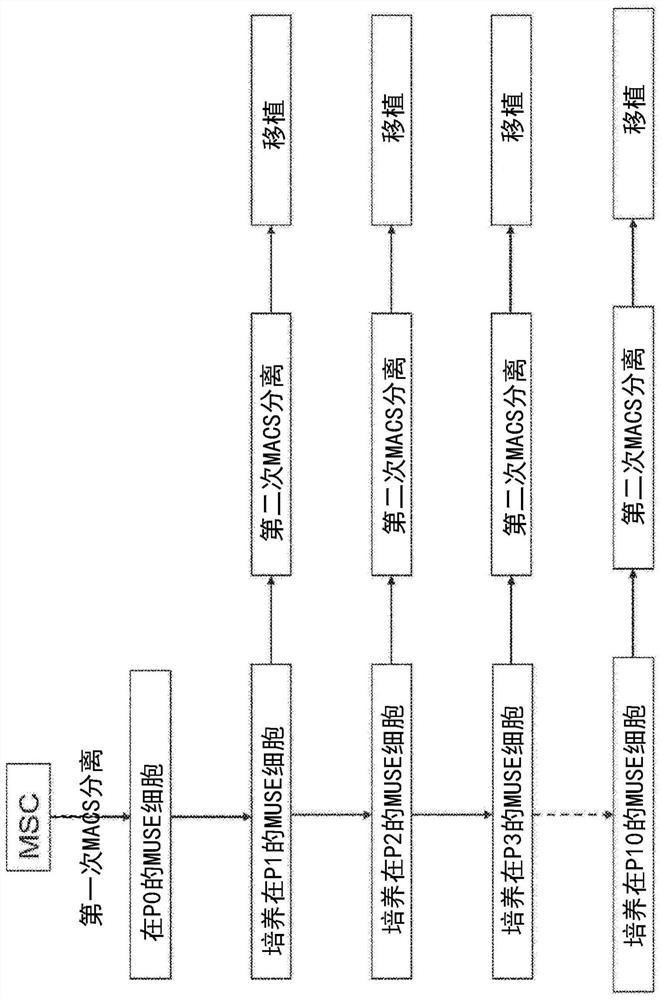
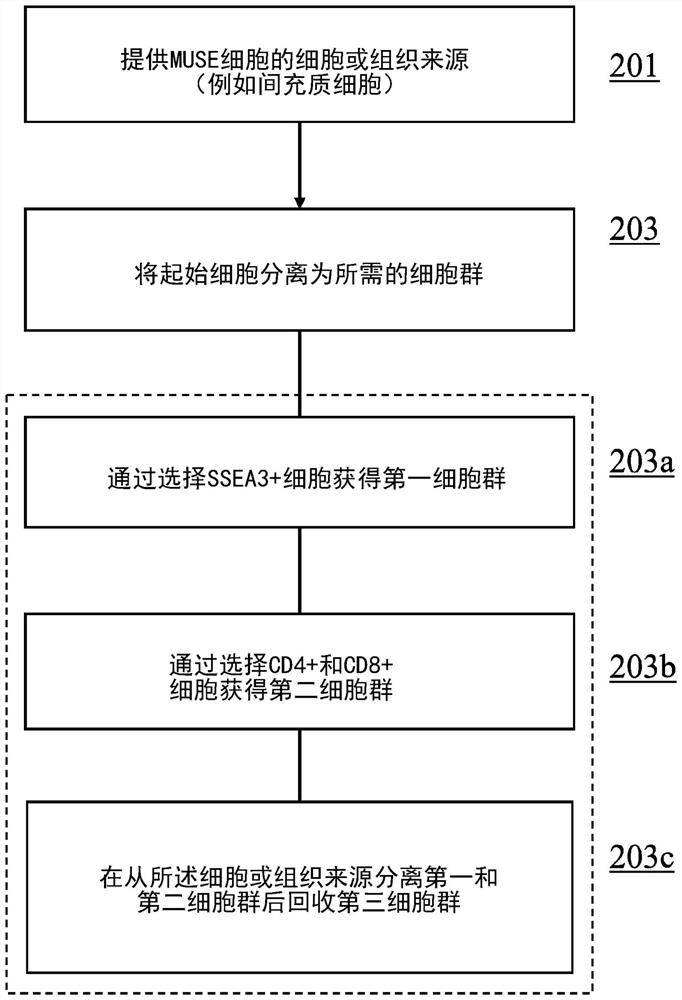
Methods for enriching populations of cells
A cell group and cell technology, applied to embryonic cells, animal cells, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve problems such as high cost and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] This example describes the materials and methods used in the subsequent examples.
[0098] Isolation of HUC-MSCs
[0099] HUC is packaged in a bottle filled with shipping medium, which includes KH 2 PO 4 (0.20g / L), Na 2 HPO 4 (anhydrous, 1.15g / L), KCl (0.20g / L) and NaCl (8.00g / L). The bottle was kept at 4°C by surrounding it with ice. All cords were collected with patient consent and in compliance with the requirements of the Rutgers University Ethics Committee. The transport from the patient to the lab took a day. Table I lists the antibodies used in this study.
[0100] Isolation of human umbilical cord (HUC) MSCs followed the protocol described below. First, place HUC in a 10-cm Petri dish. HUC was then cut into 1-cm pieces and dissected longitudinally. Next, the HUC artery and vein were removed, and the HUC tissue was washed, followed by isolation of Wharton's jelly and umbilical cord intima tissue. Treat tissue with collagenase and seed cells into cell...
Embodiment 2
[0116] Both HUC WJ and CL produced a large number of MSCs. Table II shows the number of passage 0 MSCs and SSEA3+. The average concentration of MSCs and SSEA3+ cells per gram of tissue was 3.7 ± 0.55 × 10 4 WJ-MSC, 1.89±1.67×10 3 WJ-SSEA3+, 3.00±0.80×10 4 CL-MSC and 2.24±2.00×10 3 CL-SSEA3+ cells. Heavier umbilical cords have more WJ MSCs (R 2 =0.64, p=0.01 Figure 4 ). The 99WJ group had an abnormally high 42.37% SSEA+ cells at passage 0. However, cord weight was not associated with CL-MSC / WJ-SSEA3+ / CL-SSEA3+. The number of WJ-MSCs did not correlate with CL-MSCs or WJ-SSEA3+. There was also no correlation between CL-MSCs and CL-SSEA3+.
[0117] WJ and CL cells were cultured alone, and the percentage of SSEA3+ in multiple passages was compared (see Figure 5). In the P0 group, more than 98% of the total cells from both WJ and CL were positive for CD105, and it was even higher in P1 and P2. At P0, the percentages of SSEA3+ cells in WJ and CL were 4.97%±4.30% and 5.26%±...
Embodiment 3
[0123] Two adult Sprague-Dawley rats with 12.5-mm T11 spinal cord weight drop contusion were transplanted with HUC SSEA3+ and CD105+ cells into the spinal cord 2 weeks after spinal cord injury (SCI). The cells are injected into the dorsal root entry zone of the spinal cord above and below the injury site. Cells survived 4 weeks after transplantation. Rats were not immunosuppressed. Transplanted cells were stained with antibodies against human nuclei (Stem 101+), but were negative for Nestin, GFAP, NeuN, NF155, and Iba1. When transplanted into the brain and spinal cord, human MUSE cells can survive for a long time and will not be immune rejected (Uchida H et al. Stem Cells. 2016; 34(1): 160-173; Uchida H et al. Stroke. 2017; 48(2):428-435).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com